![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
induced fit
|
a change in the conformation of an enzyme in response to substrate binding that renders the enzyme catalytically active; also used to denote changes in the conformation of any macromolecule in response to ligand binding such that the binding site of the macromolecule better conforms to the shape of the ligand
|
|
|
specificity
|
the ability of an enzyme or receptor to discriminate among competing substrates or ligands
|
|
|
binding energy ∆G'(b)
|
the energy derived from noncovalent interactions between enzyme and substrate or receptor and ligand
|
|
|
rate constant
|
the proportionality constant that relates the velocity of a chemical reaction to the concentration of the reactants
|
|
|
equilibrium constant K{eq}
|
a constant, characteristic for each chemical reaction; relates the specific concentrations of all reactants and products at equilibrium at a given temp and pressure
|
|
|
rate limiting step
|
1) generally, the step in an enzymatic reaction with the greatest activation energy or the transistion state of highest free energy
2) The slowest step in a metabolic pathway |
|
|
reaction intermediate
|
any chemical species in a reaction pathway that has a finite chemical lifetime
|
|
|
activation energy
|
the amount of energy in Joules required to convert all the molecules in 1 mole of a reacting substance from the ground state to the transistion state
|
|
|
transistion state
|
an activated form of a molecule in which the molecule has undergone a partial chemical reaction; the highest point on the reaction coordinate
|
|
|
standard free energy change
|
the free energy change for a reaction occurring under a set of standard conditions; temp=298K; pressure=1 atm or 101.3 kPa; and all solutes at 1 M concentration
|
|
|
ground state
|
the normal, stable form of an atom or molecule; as distinct from the excited state
|
|
|
substrate
|
the specific compound acted upon by an enzyme
|
|
|
active site
|
the region of an enzyme surface that binds the substrate molecule and catalytically transforms it; also known as the catalytic site
|
|
|
apoprotein
|
the protein portion of a protein, exclusive of any organic or inorganic cofactors or prosthetic groups that might be required for activity
|
|
|
apoenzyme
|
the protein portion of an enzyme, exclusive of any organic or inorganic cofactors or prosthetic groups that might be required for catalytic activity
|
|
|
holoenzyme
|
a catalytically active enzyme including all necessary subunits, prosthetic groups, and cofactors
|
|
|
prosthetic group
|
a metal ion or an organic compound (other than an amino acid) that is covalently bound to a protein and is essential to its activity
|
|
|
coenzyme
|
an organic cofactor required for the action of certain enzymes; often contains a vitamin as a component
|
|
|
cofactor
|
an inorganic ion or a coenzyme required for enzyme activity
|
|
|
enzyme
|
a biomolecule, either protein or RNA, that catalyzes a specific chemical reaction. It does not affect the equilibrium of the catalyzed reaction; it enhances the rate of a reaction by providing a reaction path with a lower activation energy
|
|
|
protein kinases
|
enzymes that transfer the terminal phosphoryl group of ATP or another nucleoside tiphosphate to a Ser, Thr, Asp, or His side chain in a target protein, thereby regulating the activity or other properties of that protein
|
|
|
allosteric enzyme
|
a regulatory enzyme, with catalytic activity modulated by the noncovalent binding of a specific metabolite at a site other than the active site
|
|
|
turnover number
|
the number of times an enzyme molecule transforms a substrate molecule per unit time, under conditions giving maximal activity at substrate concentrations that are saturating
|
|
|
Lineweaver-Burk equation
|

an algebraic transform of the Michaelis-Menten equation, allowing determination of V{max} and K{m} by extrapolation of [S] to infinity
|
|
|
Michaelis-Menten equation
|
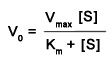
the equation describing the hyperbolic dependence of the initial reaction velocity, V{0}, on substrate concentration, [S], in many enzyme catalyzed reactions
At V = 1/2 V{max}, the substrate concentration [S] is equal to the K{m} |
|
|
Michaelis constant K{m}
|
the substrate concentration at which an enzyme catalyzed reaction proceeds at one-half its maximum velocity
|
|
|
V{max}
|
the maximum velocity of an enzymatic reaction when the binding site is saturated with substrate
|

