![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
hydrolysis
|
cleavage of a bond, such as an anhydride or peptide bond, by the addition of the elements of water, yielding two or more products
|
|
|
condensation
|
formation of a bond accompanied by the release of the elements of water from the joining atoms
|
|
|
Henderson-Hasselbalch equation
|
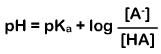
an equation relating the pH, the pK{a}, and the ratio of the concentrations of the proton acceptor (A-) and proton donor (HA) species in a solution
|
|
|
buffer
|
a system capable of resisting changes in pH, consisting of a conjugate acid-base pair in which the ratio of proton acceptor to proton donor is near unity
|
|
|
titration cure
|
a plot of the pH versus the quivalents of base added during tiration of an acid
|
|
|
pK(a)
|
the negative logarithm of an equilibrium constant
|
|
|
dissociation constant K{a}
|
Equilibrium constants for ionization reactions are usually called ionization or dissociation constants, often
designated K{a} |
|
|
conjugate acid-base pair
|
a proton donor and its corresponding deprotonated species; for example, acetic acid (donor) and acetate (acceptor)
|
|
|
pH
|
the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration of an aqueous solution
|
|
|
ion product of water K(w)
|
the product [H+][OH-] in aqueous solutions at
25 C always equals [1x10^14] M |
|
|
equilibrium constant K(eq)
|
a constant, characteristic for each chemical reaction; relates the specific concentrations of all reactants and products at equilibrium at a given temp and pressure
|
|
|
hypotonic
|
describes a solution of lower osmolarity than that from which it is separated by a semipermeable membrane
|
|
|
hypertonic
|
describes a solution of higher osmolarity than that from which it is separated by a semipermeable membrane
|
|
|
isotonic
|
describes a solution of the same osmolarity as that from which it is spearated by a semipermeable membrane
|
|
|
osmosis
|
bulk flow of water through a semipermeable membrane into another aqueous compartment containing solute at a higher concentration
|
|
|
hydrophobic interactions
|
the association of nonpolar groups, or compounds, with each other in aqueous systems, driven by the tendency of the surrounding water molecules to seek their most stable (disordered) state
|
|
|
micelle
|
an aggregate of amphipathic molecules in water, with the nonpolar portions in the interior and the polar portions at the exterior suface, exposed to water
|
|
|
amphipathic
|
containing both polar and nonpolar domains
|
|
|
hydrophobic
|
nonpolar; describing molecules or groups that are insoluble in water
|
|
|
hydrophillic
|
polar or charged; describing molecules or groups that associate with (dissolve easily in) water
|
|
|
bond energy
|
the energy required to break a bond
|
|
|
hydrogen bond
|
a weak electrostatic attraction between on electronegative atom (i.e. nitrogen or oxygen) and a hydrogen atom covalently linked to a second electronegative atom
|

