![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
x |
y |
|
|
xc |
y |
|
|
x |
y |
|
|
Controllers of cell cycle phases |
Cyclins, Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), tumour suppressors |
|
|
M phase |
Mitosis = Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase Cytokinesis = cytoplasm splits in two |
|
|
CDKs |
Cyclin-dependent kinases Constitutive and inactive |
|
|
Cyclins |
Regulatory proteins - control cell cycle events Phase specific Activate CDKs |
|
|
Cyclin-CDK complexes |
Phosphorylate other proteins to coordinate cell cycle progression Must be activated and inactivated at appropriate times for cell cycle to progress |
|
|
Tumour suppressors |
P53 + hypophophosphorylated Rb - normally inhibit G1-to-S progression Mutations in these genes = unrestrained cell division Li Fraumeni syndrome |
|
|
Cell cycle phases |
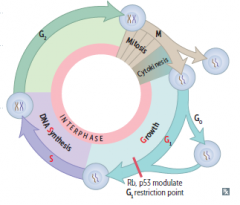
M, G0, G1 (growth), S (DNA synthesis), G2 |
|
|
Permanent cells |
Remain in G0 Regenerate from stem cells Neurons, skeletal/cardiac muscle, RBCs |
|
|
Stable cells |
= qulescent Enter G1 from G0 when stimulated Hepatocytes, lymphocytes |
|
|
Labile cells |
Never go to G0 Divide rapidly with a short G1 Most affected by chemo Bone marrow, gut epithelium, skin, hair follicles, germ cells |
|
|
RER |
Synthesises secretory proteins + N-linked oligosaccharide addition to many proteins Nissl bodies = RER in neurons - make peptide NT for secretion Free ribosomes = unattached to any membrane - make cytosolic and organellar proteins Mucus-secreting goblet cells of SI + Ab-secreting plasma cells are rich in RER |
|
|
SER |
Site of steroid synthesis + detoxification of drugs and poisons Lacks surface ribosomes Liver hepatocytes and steroid hormone-producing cells of adrenal cortex are rich in SER |
|
|
Golgi bodies |
Distribution centre for proteins and lipids from ER -> vesicles and plasma membrane Modifies N-oligosaccharides on asparagine Adds O-oligosaccharides on serine and threonine Adds mannose-6-phosphate to proteins for trafficking to lysosomes |
|
|
Endosomes |
Sorting centres for material from outside the cell/from Golgi Sends material to lysosomes for destruction or back to membrane/Golgi for further use |
|
|
I-cell disease = Inclusion cell dx |
Inherited lysosomal storage disorder Defect in N-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase -> Failure of Golgi to phosphorylate mannose residues on glycoproteins -> proteins secreted extracellularly VS delivered to ribosomes = Coarse facial features, clouded corneas, restricted joint movement, high plasma levels of lysosomal enzymes. Can be fatal in childhood |
|
|
Signal recognition particle (SRP) |
Abundant cytosolic ribonucleoprotein Traffics proteins from ribosome to RER Absent/dysfxn -> proteins accumulate in cytosol |
|
|
Vesicular trafficking proteins |
COPI = Golgi -> Golgi (retrograde) -> cis-Golgi -> ER COPII = ER -> cis-Golgi (anterograde) Clathrin = trans-Golgi -> lysosomes -> plasma membrane -> endosomes = receptor-mediated endocytosis |
|
|
Peroxisome |
Membrane-enclosed Involved in catabolism of very-long-chain fatty acids/branched FA/amino acids |
|
|
Proteasome |
Barrel-shaped protein complex Degrades damaged/ubiquitin-tagged proteins Defects in ubiquitin-proteasome system have been A/W Parkinson dx |
|
|
Microfilaments |
Muscle contraction, cytokinesis Actin |
|
|
Intermediate filaments |
Maintain cell structure Vimentin, desmin, cytokeratin, lamins, glial fibrillary acid proteins (GFAP), neurofilaments |
|
|
Microtubules |
Movement, cell division Cilia, flagella, mitotic spindle, axonal trafficking, centrioles |
|
|
Connective tissue stain |
Vimentin |
|
|
Muscle stain |
Desmin |
|
|
Epithelial cells stain |
Cytokeratin |
|
|
Neuroglia stain |
GFAP |
|
|
Neurons stain |
Neurofilaments |
|
|
Molecular motor proteins |
Transport cellular cargo toward opposite ends of microtubules tracks Dynein = retrograde to microT (+=-) Kinesin = anterograde to microT (-=+) |
|
|
Drugs that act on microtubules |
Mebendazole = antihelminthic Griseofulvin = antifungal Colchicine = antigout Vincristine/Vinblastine = anticancer Paclitaxel = anticancer Microtubules Get Constructed Very Poorly |
|
|
Kartagener syndrome |
Primary ciliary dyskinesia Immotile cilia due to dynenin arm defect = Male and female infertility due to immotile sperm and dysfunctional fallopian tube cilia Increased risk of ectopic pregnancy Can cause bronchiectasis, recurrent sinusitis, situs inversus |
|
|
Plasma membrane |
Asymmetric lipid bilayer Cholesterol, phospholipids, sphingolipids, glycolipids, proteins Fungal membranes = ergosterol |
|
|
NaK pump |
Located on plasma membrane - ATP on cytosolic side Each ATP consumed = 3Na out, 2K in Ouabain inhibits pump by binding to K site Cardiac glycosides (digoxin and digitoxin) directly inhibit NaK ATPase -> indirect inhibition of Na/Ca exchange -> increased Ca -> increased cardiac contractility |
|
|
Collagen |
Most abundant protein in body Modified by posttranslational modification Organises and strengthens extracellular matrix |
|
|
Collagen 1 |
Most common = 90% Bone - made by osteoblasts - decreased production in osteogenesis imperfecta type 1 Skin Tendon Dentin Fascia Cornea Late wound repair |
|
|
Collagen 2 |
Cartilage - including hyaline Vitreous body Nucleus pulposus |
|
|
Collagen 3 |
Reticulin - skin, BV, uterus, fetal tissue, granulation tissue Deficient in vascular type of Ehler-Danlos syndrome - rare |
|
|
Collagen 4 |
Basement membrane Basal lamina Lens Defective in Alport syndrome Targeted by Ab in Goodpasture syndrome |
|
|
Osteogenesis imperfecta |
Genetic bone disorder AD form most common - decreased production of otherwise normal type 1 collagen Multiple fractures + minimal trauma, blue sclerae (due to translucency of connective tissue over choroidal veins), hearing loss (AB ossicles), dental imperfections (lack of dentin) |
|
|
Ehler-Danlos syndrome |
Faulty collagen synthesis = hyperextensible skin, tendency to bleed, hypermotile joints Multiple types - can be AD/AR May be A/W joint dislocation, berry/aortic aneurysms, organ rupture Hypermotility type = joint instability - common Classical type = joint + skin sym - mutation in collagen 4 Vascular type = vascular and organ rupture - deficient collagen 3 |
|
|
Menkes disease |
X-linked R connective tissue dx Cause d by impaired copper absorption and transport due to defective Menkes protein = ATP7A -> lack of lysyl oxidase (Cu is necessary cofactor) Brittle/kinky hair, growth retardation, hypotonia |
|
|
Elastin |
Stretchy protein Skin, lungs, large arteries, elastic ligament, vocal cords , ligamenta flava Rich in nonhydroxylated proline, glycine and lysine residues Tropoelastin + fibrillin scaffolding Elastic properties due to extraC cross-linking Broken down by elastase - inhibited by A1AT |
|
|
Marfan syndrome |
Defect in fibrillin = glycoprotein that forms sheath around elastin |
|
|
Emphysema |
Can be caused by A1AT def => XS elastase activity |
|
|
Wrinkles |
Aging Due to decreased collagen and elastin production |
|
|
x |
y |

