![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The peptide backbone of the primary protein structure allows some flexibility that creates secondary structures due to ____________
|
the bonds of the alpha carbon
|
|
|
Because of resonance, the double bond nature of the ____________ in the primary structure of proteins does not allow rotation
|
peptide bonds
|
|
|
Secondary structures are held together by __________________ within the protein backbone
|
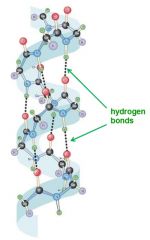
hydrogen bonds
|
|
|
What is the most common secondary structure?
|
alpha helix
|
|
|
What is the main secondary structure in transmembrane domains? Why?
|
alpha helices. You can incorporate hydrophobic amino acids and their hydrophobic R groups will be pointing away from the helix, allowing them to span the hydrophobic transmembrane region
|
|
|
Side groups point away from the helix to minimize _________
|
steric hindrance
|
|
|
Strands of antiparallel beta sheets are connected by _____________
|

BETA TURNS
|
|
|
Beta turns are turns formed from ___ amino acids and are stabilized by ____________
|
4 amino acids
a single hydrogen bond |
|
|
What are the 3 main domains of transmembrane proteins? Give an example of a transmembrane protein
|
ligand binding domain extracellularly
transmembrane domain consisting of alpha helices formed by hydrophobic amino acids cytoplasmic domain transmembrane protein: G-protein coupled receptor |
|
|
What are two types of proteins that have a quarternary structure?
|
globular proteins and fibrous proteins
|
|
|
Globular protein--a quarternary structure--is tertiary protein subunits held together by __________ bonds
|
non-covalent (sometimes disulfide) bonds
|
|
|
Fibrous protein--a quarternary protein--are protein chains held together by __________ bonds
|
covalent
|
|
|
Describe the structure of type II collagen. What is the overall structure called?
|
-3 identical protein chains held together by covalent bonds and non-covalent interactions
-homotrimer |
|
|
Describe the structure of a G-protein. What is the overall structure classified as?
|
-3 DIFFERENT protein chains held together by noncovalent interactions
-heterotrimer |
|
|
what is a heterotrimer?
|
a protein composed of 3 different subunits
|
|
|
describe the structure of hemoglobin. What is this structure classified as?
|
-2 alpha and 2 beta chains held together by noncovalent interactions
-a2b2 tetramers |
|
|
Globular proteins tend to be _________ in water.
|
soluble
|
|
|
Fibrous proteins tend to be _____________ in water.
|
insoluble
|
|
|
Collagens, elastin and fibrillin are all ____________.
|
fibrous proteins
|
|
|
Blood transport proteins, enzymes and antibodies are all___________________
|
globular proteins
|
|
|
What are the benefits of quarternary structure (3)?
|
-stable (collagen due to covalent bonds between 3 units)
-cooperativity (hemoglobin) -regulate overall activity of protein (in g proteins, the alpha subunit cannot perform its function until it dissociates from the beta and gamma subunits) |
|
|
Myoglobin is the main ____________ molecule in skeletal and heart muscle. Its 8 alpha helices form a pocket in which a prosthetic __________ group binds oxygen
|
-oxygen storage molecule
-heme iron (Fe2+) |
|
|
In alpha helices, you will not find the amino acid _________
|
proline
|
|
|
Which amino acids will you find in a transmembrane alpha helix?
|
leucine, isoleucine, valine, phenylalanine, tryptophan, cysteine and methionine. all hydrophobic
NOT PROLINE--although it is hydrophobic it breaks the alpha helix |
|
|
Hemoglobin is the major __________ molecule in red blood cells. It can bind _____ oxygen molecules
|
oxygen transport
-4 |
|
|
Hemoglobin subunits don't bind O2 in the _______ state. They bind in the ________ state.
|
-T (taut)
-R (relaxed) |
|
|
Under low O2 conditions, hemoglobin ___________ O2 and myoglobin __________.
|
-hemoglobin releases
-myoglobin picks it up |
|
|
Fetal hemoglobin has a _________ oxygen binding capability than adult hemoglobin
|
higher
|
|
|
Igs (immunoglobulins) are composed of __________________________ held together by _________
|
two heavy and two light chains held together by noncovalent interactions and disulfide bonds
|
|
|
The __________ region of the Igs forms the antigen binding site that recognizes the foreign invader
|
variable
|
|
|
The ___________ region of the ___________ chain binds macrophages and facilitates clearance
|
-constant region
-heavy chain |
|
|
Protein folding occurs in what organelle?
|
the ER
|
|
|
What determines a protein's primary structure?
|
primary structure (the amino acid sequence)
|
|
|
Some proteins require __________ to help them fold
|
accessory proteins (chaperonins)
|
|
|
What does hsp70 do?
|
-binds to elongating protein chain to prevent premature folding
|
|
|
What does hsp60 do?
|
it's a chamber that folds proteins using ATP
|
|
|
What are the 4 ways proteins can be denatured?
|
-oxidative damage
-pH -temp -solvents |
|
|
The myoglobin binding curve is described as ____________. Hemoglobin?
|
myoglobin - hyperbolic
hemoglobin - sigmoidal |
|
|
A ____________ deficiency causes intracellular proteins to become denatured by oxygen radicals, causing dark spots in red blood cells called ___________ due to the accumulation of damaged proteins.
|
G6PD, Heinz bodies
|
|
|
What is the abbreviation describing the normal conformation of prion protein? Misfolded?
|
Normal: PrPC
Misfolded: PrPSC |

