![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
259 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Functions of Cholesterol |
Structural component of cell membrane, modulating their fluidity Precursor of steroid hormones, vit D, bile acids |
|
|
|
Liver cholestrol Influx and Efflux |
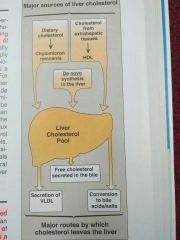
|
|
|
|
Cholestrol Structure |
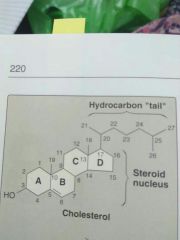
>very hydrophobic compound >consists of 4 fused hydrocarbons rings (A-D) called the Steroid Nucleus >Ring A has a Hydroxyl group at C3 >Ring B has a double bond between C5 and C6 >D ring has an 8 carbon branched hydrocarbons chain attached to C17 |
|
|
|
Sterol |
Steroids with 8 to 10 carbon atoms in the side chain at C17 and a hydroxyl group at C3 are classified as sterols >cholestrol is major sterol in animal tissues >it arises from the de novo synthesis and absorption of dietary cholestrol |
|
|
|
Methods to Reduce Absorption of Dietary Choelestrol |
√Intestinal uptake of cholestrol is mediated, in part, by the protein Niemann-pick C-1 like 1 protein NPC1-L1, which is target of the drug ezetimibe that reduces the absorption of dietary cholestrol √Plant sterols or phytosterols such as beta-sitosterol are poorly absorbed by humans. 5% as compared to 40% for cholestrol >After entering enterocytes theyre actively transported back into intestinal lumen >Defects in transporter results in rare condition of sitosterolemia >because some cholestrol is transported back as well, phtosterols reduce absorption of cholestrol >Daily ingestion of plant sterol esters suppliesd in juices or spreads is a dietary strategy to reduce plasma cholestrol conc. |
|
|
|
How does liver regulate blood glucose after meal? |
It containes high Km glucokinase that promotes increased hepatic utilization of glucose |
|
|
|
Location of Glycolysis |
Cytosolic pathway |
|
|
|
Function of Glycolysis |
Metabolism of glucose or glycogen to pyruvate and lactate |
|
|
|
Loading of liver with frustose may result in? |
Hyperuricemia Hypertriacylglycerolemia Hypercholestrolemia |
|
|
|
Renal threshold for glucose |
10mmol/L |
|
|
|
Glucosuria |
>Venous blood glucose concentration exceeds the renal threshold for glucose that is 10mmol/L >Glomerular filtrate contains more glucose than can be reabsorbed in hyperglycemia |
|
|
|
Capacity of renal tubular system to reabsorb glucose |
2mmol/min |
|
|
|
Function of Glucokinase |
Considerbaly highwr Km(low affinity) for glucoseso its activity onc witj inc in glucose conc in hepatic portal vein Promotes hepatic uptake of large amounts of glucose after meal |
|
|
|
Role of pro Elastase |
Cleaves amino acids from the carboxyl end of peptide |
|
|
|
Function of Amylases |
Break down starch molecules into smaller sugers Also break down carbs into maltose |
|
|
|
The 2 phases of Pentose Phosphate Pathway |
Oxidative Phase irreversible and generates NADPH Non Oxidative phase reversible and provides ribose precursors for nucleotide synthesis |
|
|
|
The 2 phases of Pentose Phosphate Pathway |
Oxidative Phase irreversible and generates NADPH Non Oxidative phase reversible and provides ribose precursors for nucleotide synthesis |
|
|
|
Causes of Digestive Disorders |
1.Enzyme deficiency e.g. lactase and sucrase 2.Malabsorption eg. Of glucose and galactose as a result of defects in Na+ glucose cotransporter (SGLT1) 3.Absorption of unhydrolyzed polypeptides leading to an immune response eg in celiac disease 4.Precipitation of cholestrol from bile as gallstones |
|
|
|
Function of Liver |
√Metabolizes proteins, carbs and cholestrol √Detoxification of toxins, drugs, hormones |
|
|
|
Synthesis of Galactose |
Synthesized from glucose in lactating mammary gland and other tissues where its required for the synthesis if glycolipids, proteoglycans and glycoproteins |
|
|
|
Role of Insulin |
√Secreted in direct response to hyperglycemia √Stimulates liver to store glucose as glycogen √Inc extrahepatic uptake of glucose |
|
|
|
Newbornbaby develops diarrohoea, abdominal distension, foul breath after breast feeding. Stool contains reducing substances. Hydrogen breath test is positive. Diagnosis? |
Lactose Intolerance |
|
|
|
Alkaline Tide |
Inc of bicarbonate ions in blood after taking proteins due to production of Hcl by the parietal cells |
|
|
|
Composition of Gastric Juice |
1-99% water 2-1% Organic or Inorganic √Organic: mucin, pepsinogen, gastric lipase, traces of other enzymes and intrinsic factors, traces of lactic acid √Inorganic: HCL, Na, K, to lesser extent phosphate, alkaline tide |
|
|
|
Functions of Gastric Juice |
HCL: antibacterial effect, causes denaturation of proteins, activates pepsinogens Pepsin: hydrolyzes proteins, curdles milk Gastric Lipase: hydrolyzes fats Mucins: protects stomach walls from digestion Intrinsic Factors : cause absorption of vit B12 |
|
|
|
Normal blood glucose concentration |
90mg/dl |
|
|
|
Deficiency of UV specific exonucleus causes which disease? |
Xeroderma pigmentosum |
|
|
|
Sources of ammonia in body? |
Amino acids From. Amines From bacterial action From glutamine From purines and pyrimidines |
|
|
|
Factors affecting basal energy expenditure? |
1.age of individual 2.body temp 3.climate 4.diet 5.drugs 6.gender 7.hormones 8.habits 9.pregs and lactation 10.race |
|
|
|
Hormonal regulation of glycolysis? |
-insulin favours glycolysis by activating regulatory enzymes of glycolysis -Glucocorticoids inhibit glycolysis and favour gluconeogenesis -Glucagon inhibits keys enzymes of glycolysis and reduces it |
|
|
|
Which enzyme catalyzes the formation of final phosphodiester bond between 5'-phosphate group on DNA chain,synthseized by prokaryotic DNA polymerase lll, and the 3'-hydroxyl group on DNA chain, synthesized by DNA polymerase l? |
DNA Ligase |
|
|
|
Azide? |
Function: inhibitors of oxidative phosphorylation Mechanism if inhibition: e'transport inhibitor Site of Action: complex lV |
|
|
|
Genetic code? |
The genetic code is a dictionary that identifies the correspondence between a sequence of nucleotide bases and a sequence of amino acids -Each individual word in the code is composed of 3 nucleotide bases. These genetic words are called codons |
|
|
|
Degradation of glycogen by lysosomal Acid Maltase? |
-Acid Maltase or Alpha-1,4 glucosidase continuously degrades a small quantity of glycogen - Deficiency results in accumulation of glycogen causing Pompe's disease |
|
|
|
What are the effects on hepatic glycolysis and gluconeogenesis in patient of type l Diabetes Mellitus? |
Due to deficiency of insulin, glycolysis is inhibited and gluconeogenesis is stimulated |
|
|
|
Role of Citric Acid Cycle in Metabolism? |
1. Provides substrates for amino acid syn by transamination 2. Provides substrates for gluconeogenesis and fatty acid synthesis >its amphibolic as it functions on both oxidative and synthetic processes |
|
|
|
Fate of Glucose? |
>oxidize to give energy >stored as glycogen(muscles) >converted to triglycerides, amino acids and proteins |
|
|
|
Clinical Role of LDL? |
1. Transports cholestrol from liver to peripheral tissues 2.LDL conc in blood haa positive correlation with CV diseases and considered atherogenic 3. Specially oxidized LDL creates a procoagulant surface on endothelium causing blood clot formation. 4. Found in higher levels in Cigeratte smokers, diabetes and insulin resistance |
|
|
|
Diseases in which prolonged elevation of blood levels of cholestrol rich proteins occur? |
1. Diabetes Meliitus 2. Lipid nephrosis 3. Hypothyroidism 4. Several conditions of hyperlipidemia |
|
|
|
Elevated levels of cholestrol present in VLDL, LDL or IDL are associated with? |
Atherosclerosis |
|
|
|
The disease processes involving sphingolipids and phospholipids? |
>infant respiratory distress syndrome(lack of surfactant) >Multiple sclerosis (demyelination) >Sphingolipidoses(inability to break down sphingolipids in lysosomes due to inherited defects in hydrolase enzymes) |
|
|
|
Normal blood glucose level? |
5mM or 90mg/dl |
|
|
|
Carbon loss in glycolysis? |
None |
|
|
|
FUnction of 2,3 BPG? |
Binds to beta subunits of hemoglobin and kicks off oxygen from them in peripheral tissues |
|
|
|
Component of ETC? |
Cytochrome |
|
|
|
Reducing equivalents are first transferred from cytochrome b to which electron acceptor? |
Cytochrome c |
|
|
|
Enzyme of glycolysis? |
Phosphoglycerate kinase |
|
|
|
Which enzyme of TCA cycle catalyzes oxidative decarboxylation? |
Alphaketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex |
|
|
|
Enzyme deficient in Von Gierke's disease? |
Glucose 6 phosphatase |
|
|
|
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase catalyzes formation of? |
6-phosphogluconate |
|
|
|
Which is a precursor for glucose synthesis via gluconeogenesis? |
Glycerol |
|
|
|
Primary oxyluria? |
Glycine |
|
|
|
Lactation promoter hormones? |
Estrogen and prolactin |
|
|
|
Preproinsulin? |
110 AAs |
|
|
|
Methotraxate? |
Folate |
|
|
|
Fasting hormone? |
Cortisol |
|
|
|
HMP |
Ribose |
|
|
|
Metabolic acidosis |
Diarrhoea |
|
|
|
Atherosclerosis |
Dec HDL inc LDL |
|
|
|
Antibody assay |
ELISA |
|
|
|
Cori's sites? |
Brain Blood Liver |
|
|
|
Steatorrhoea? |
Excess fat on feces |
|
|
|
Hyperuricemia |
Purine degradation |
|
|
|
NADPH |
Malic pathway |
|
|
|
Essential FA cant be synthesized due to deficiency of? |
Delta15desaturase |
|
|
|
Stop codon |
UAA |
|
|
|
H2S inhibits? |
Conplex 1V |
|
|
|
Cholestrol synthesis is regulated by? |
HMG CoA Reductase |
|
|
|
Insulin rises after how many hours of CHO meal? |
2 hours |
|
|
|
Lipoic acid is coenzyme in oxidation of? |
Pyruvate |
|
|
|
d TMP is formed from? |
From dUMP by using THF |
|
|
|
Removal of stomach causes deficieny of? |
Vit B12 |
|
|
|
Glutamine synthetase absent in? |
Hyperammonimea |
|
|
|
Beta oxidation occurs in? |
Mitochondrial matrix |
|
|
|
Arsenic poisoning causes death by affecting the brain. It does by inhibiting which enzyme? |
Pyruvate dehydrogenase |
|
|
|
Blurring of vision is a symptom of? |
Ammonia intoxication |
|
|
|
Which compound is expected to be in highest concentration in brain as a result of ammonia intoxication? |
Glutamine |
|
|
|
Rate limiting enzyme for catecholamine biosynthesis? |
Tyrosine hydroxylase |
|
|
|
Glycogenin? |
Protein primer for glycogen synthesis |
|
|
|
Reactions of pentose phosphate pathway occur in? |
Cytosol |
|
|
|
What protects erythrocytes against hemolysis? |
1. Pentose phosphate pathway 2. Glutathione peroxidase |
|
|
|
Fructose and sorbitol in lens are associated with? |
Diabetic cataract |
|
|
|
G6PD: oxidant drugs inducing hemolytic anemia? |
Antibiotics e.g sufamethoxazole Antimalarial e.g primaquine Antipyretics e.g acetanilid but not aspirin or acetaminophen |
AAA |
|
|
Aerobic Glycolysis pathway |
Oxidation of glucose into pyruvate with generation of ATP 32ATP in lover and heart and 30 in muscle |
|
|
|
Number of ATP molecules generated per glucose in anaerobic glycolysis? |
2NETATP/Glucose molecule |
|
|
|
3 regulatory enzymes of glycolysis |
1. Hexokinase(Glucokinase in liver) 2. Phosphofructokinase 3. Pyruvate kinase |
|
|
|
Hexokinase distinguishing features |
1. Ubiquitous 2. High affinity (low Km) 3. Low capacity (lowVmax) 4. Uninduced by insulin 5. Feedback inhibited by G6P |
|
|
|
Glucokinase distinguishing features |
1. Liver and beta cells of pancreas 2. Low affinity (highKm) 3. High capacity (high Vmax) 4. Induced by insulin |
|
|
|
Pyruvate kinase deficiency |
Inadequate production of ATP reduces activity of Na+/K+ stimulated ATPase pump in RBCS. The cells swell and lyse resulting in hemolytic anemia |
|
|
|
TCA cycle components |
Citrate Isocitrate α-ketoglutarate Succinyl coA Succinate Fumarate Malate Oxaloacetate |
Citrate Is Krebs Starting Substrate For Making Oxaloacetate |
|
|
Von Gierke's Disease Type 1 |
Findings: severe fasting hypoglycemia Inc liver glycogen Inc blood lactate Hepatomegaly >Ahtosomal recessive |
|
|
|
Deficient enzyme in Von Gierke's Disease? |
G6P |
|
|
|
Pompe's Disease Type 2 |
Findings: Cardiomegaly and systemic findings leading to early death >autosomal recessive >Pompe's trashes the Pump (♥ liver 💪) |
|
|
|
Deficient enzyme in Pompe's Diaease |
α-1,4-glucosidase (acid maltase) |
|
|
|
Cori's disease type 3 |
Findings: Milder form of type 1 with Normal blood lactate levels >autosomal recessive >gluconeogenesis is intact |
|
|
|
Deficient enzyme in Cori's disease |
Debranching enzyme (α-1,6-glucosidase) |
|
|
|
McArdles disease type V |
Findings : Inc glycogen in muscles, but cant break it down leading to muscle cramps Myoglobinuria with strenous exercise >autosomal recessive |
Mcardles=Muscle |
|
|
Deficient enzyme in McArdles |
Skeletal muscle glycogen phophorylase |
|
|
|
Binding of growth hormone to its receptor results in phosphorylation of? |
JAK-2 growth hormone receptor STATs MAPKinase |
|
|
|
Which intermediate of TCA cycle in involved in glutamate formation? |
α keto glutarate |
|
|
|
RNA primer is formed by the enzyme? |
Primase |
|
|
|
Rifampicin inhibits? |
Initiation of transcription |
|
|
|
Oxidation of which fatty acids is impaired in this defect? |
Very long chain fatty acids |
|
|
|
In small intestine trypsin hydrolyzes peptide linkages containing? |
Arginine |
|
|
|
In small intestine trypsin hydrolysis peptide linkages containing |
Arginine |
|
|
|
Coenzyme q in electron transport chain normally receives electrons from? |
Directly from FMN |
|
|
|
The most likely Lethal mutation is |
Deletion of 3 nucleotides |
|
|
|
Glycerol released from adipose tissue by hydrolysis of triglycerides is mainly? |
Taken up by liver |
|
|
|
Most important risk factor for patients of Tangier disease due to decrease level of HDL? |
Atherosclerosis |
|
|
|
Fate of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator protein which is modified by the cells by attaching ubiquitin molecules to it? |
It is degraded by proteasome |
|
|
|
A plasmid is a? |
Double stranded circular DNA |
|
|
|
Pancreatic lipase converts triacylglycerol into |
2 monoacylglycerol |
|
|
|
Fragments of DNA can be identified by the technique of |
Southern blotting |
|
|
|
An uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation such as dinitrophenol will cause |
Allow electron transport to proceed without ATP synthesis |
|
|
|
By hyrdoxilation, tyrosine is formed from? |
Phenylalanine |
|
|
|
The reaction of urea cycle in which urea is synthesized is catalyzed by? |
Arginase |
|
|
|
Phenyketonuria results from deficiency of? |
Phenylalanine hydroxylase |
|
|
|
Cyclooxygenase catalyzes the synthesis of? |
Prostaglandins |
|
|
|
Nurotransmitter 5-Hydroxytryptamine is derived from which amino acid? |
Tryptophan |
|
|
|
Which amino acid is the structural component of glutathione? |
Glycine |
|
|
|
Ketone bodies cannot be utilised by liver because it lacks? |
Thiophorase |
|
|
|
Which is involved for the entry of long chain fatty acids into the mitochondria true inner mitochondrial membrane? |
Carnitine |
|
|
|
Triglycerols contained in chylomicrons are hydrolysed by which enzyme? |
Lipoprotein lipase |
|
|
|
Reducing equivalents required for the de novo synthesis of fatty acids are supplied by? |
Hexose monophosphate pathway |
|
|
|
Structures involve in the initiation of protein synthesis? |
>ribosomal subunit >MRNA >amioacyl tRNA >initiation factor |
|
|
|
In eukaryotes RNA sequences which not code for protein are called? |
Introns |
|
|
|
Which hormone receptors are not associated with G protein? |
Aldosterone |
|
|
|
A molecule of DNA to which The fragment of DNA to be cloned is joined is called? |
Cloning vector |
|
|
|
In dehydration body water should be replaced by intravenous infusion of which solution? |
5%glucose solutions |
|
|
|
Metabolic alkalosis main result you to? |
Severe vomiting |
|
|
|
Respiratory acidosis results due to the excessive accumulation of which acid? |
Carbonic acid |
|
|
|
Peptide hormones? |
Erythropoietin vasopressin parathyroid hormone calcitonin |
|
|
|
There are intracellular receptors for which hormone? |
Thyroxine |
|
|
|
Not true about the action of growth hormone? |
Decreases liver glycogen store |
|
|
|
CAMP activates which enzyme? |
Protein kinase A |
|
|
|
Most significant source of stored energy in human body? |
Adipose tissue |
|
|
|
Complete oxidation of 1 gram of Fat in human body heals how much energy in kilo calories? |
2kcal |
|
|
|
Where does all the energy released from oxidation of carbohydrate fat and protein go? |
Energy is made available in mitochondria as reducing equivalent( H or e). These are funneled into respiratory chain where they are passed down a Redox gradient of Carriers to their final reaction with oxygen to form water |
|
|
|
How are tissues protected from oxygen toxicity caused by superoxide free radical? |
By specific enzyme superoxide dismutase |
|
|
|
Function of oxidoreductases? |
Function in metabolism |
|
|
|
Function of oxidases and dehydrogenases? |
Major role in respiration |
|
|
|
Function of hydro peroxidases? |
Protect the body against damage by free radicals |
|
|
|
Function of oxygenases? |
Mediate hydroxylation of drugs and steroids |
|
|
|
Cytochromes found in the endoplasmic reticulum of liver? |
Cytochromes p450 are found together with cytochrome b5 and have an important role and detoxification |
|
|
|
Respiration is coupled to generation of high energy intermediate ATP by? |
Oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
|
Function of ATP synthase? |
It closely couples oxidation to phosphorylation to meet the energy needs of cell. It's spans the membrane and acts like a rotatory motor using the potential energy of proton gradient to synthesise ATP from ADP and Pi |
|
|
|
Function of barbiturates? |
Barbiturates such as amobarbital inhibit electron transport via Complex 1 by blocking transfer from Fe-S to Q. At sufficient dose they are fatal in Vivo |
|
|
|
H2S inhibits? |
Complex lV |
|
|
|
Cataract? |
Galactokinase |
|
|
|
Carcinoma of bladder? |
Hyperkalemia acidosis |
|
|
|
Potassium increased by which hormone? |
Aldosterone |
|
|
|
Inhibitors of respiratory Chain and complex 3 |
Antimycin a and dimercaprol |
|
|
|
Inhibitors of electron transport chain at Complex IV |
The Classic poisons H2S carbon monoxide and cyanide inhibit Complex 4 and totally arrest respiration |
|
|
|
Competitive inhibitor of complex 2 |
Malonate |
|
|
|
Inhibitor of oxidative phosphorylation by inhibiting Transporter of ADP ATP transport |
Atractyloside |
|
|
|
Role of antibiotic oligomycin |
Completely blocks oxidation and phosphorylation by blocking flow of protons through ATP synthase |
|
|
|
Role of uncouplers |
> dissociate oxidation in respiratory chain from phosphorylation > toxic in vivo causing respiration to become uncontrolled since rate is no longer limited by the concentration of ADP or Pi > most frequently used is 2 4 DNP |
|
|
|
Role of thermogenin |
Physiological uncoupler found in brown adipose tissue that functions to generate body heat specially in newborn and during hibernation in animals |
|
|
|
Ionophores |
- lipophilic molecules - Complex with specific cations and facilitate the air transport through biological membranes - for example valinomycin(K+) |
|
|
|
The Classic uncouplers such as DNP are infact |
Proton ionophores |
|
|
|
Fetal infantile mitochondrial myopathy and renal dysfunction |
Involves severe diminution or absence of most oxidoreductases of respiratory chain |
|
|
|
MELAS? |
- mitochondrial encephalopathy, lactic acidosis, stroke - inherited condition due NADH-Q oxidoreductase (complex l) or cytochrome oxidase (conplex lV) deficiency - caused by a mutation in mitochondrial DNA - may be involved in Alzheimer's and diabetes mellitus - a number of drugs and poisons act by inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation |
|
|
|
Phosphorylation cascade |
Becomes active when blood glucose is low |
|
|
|
Gluconeogenesis |
Process of synthesizing glucose to glycogen from non carbohydrate precursors |
|
|
|
Importance of gluconeogenesis |
Important when carbohydrate is not available from the diet |
|
|
|
Significance substrates for gluconeogenesis |
Amino acids lactate cholesterol and propionate |
|
|
|
Comparison of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis |
The share the same path way that operate in opposite directions in so their activities must be regulated reciprocal |
|
|
|
Stimulus and action of release of glucagon |
Secreted as a response to hypoglycemia and n activates both glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in liver causing release of glucose into blood |
|
|
|
Supply of glucose is specially necessary for |
Nervous system and erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Hypoglycemia is dangerous |
Causes brain dysfunction which can lead to comma and death |
|
|
|
Importance of glucose in citric acid cycle |
Important in maintaining the level of intermediates of citric acid cycle even and fatty acids are the main source of acetyl coa in tissues |
|
|
|
Function of gluconeogenesis |
Clears lactate produced by muscle and erythrocytes and glycerol produced by adipose tissue |
|
|
|
Hexokinase |
Has a low Km for glucose |
|
|
|
Premature and low birth weight babies are susceptible to |
Because they have little adipose tissue to provide free fatty acids the enzymes of gluconeogenesis may not be completely functional at the time and it's dependent on a supply of free fatty acids for energy |
|
|
|
Body's ability to utilise glucose may be tested by |
Measuring glucose tolerance |
|
|
|
Insulin resistance associated with obesity |
Leads to development of hyperlipidemia then atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease as well as overt diabetes it is known as metabolic syndrome |
|
|
|
Citric acid cycle |
Final pathway for oxidation of cards lipids and proteins > the common and metabolite acetyl coa reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate > secret is decorated releasing 2CO2 and regenerating oxaloacetate |
|
|
|
Reduced coenzymes are oxidised by |
Respiratory chain |
|
|
|
Function of citric acid cycle |
Citric acid cycle is amphibolic in addition to oxygen its important for provision of carbon skeletons for gluconeogenesis fatty acid synthesis and n interconversion of amino acids |
|
|
|
ATP formed per turn of citric acid cycle |
10 from 3 molecules of N A D H and 1 of FADH2 |
|
|
|
Vitamins in the citric acid cycle |
1. Riboflavin 2. Niacin 3.thiamin Vitamin B1 4. Pantothenic acid |
|
|
|
Role of riboflavin in citric acid cycle |
In FAD, a cofactor for succinate dehydrogenase |
|
|
|
Role of niacin in citric acid cycle |
In NAD, the electron acceptor for isocitrate dehydrogenase, ketoglutarate dehydrogenase and malate dehydrogenase |
|
|
|
Function of thiamine in citric acid cycle |
As thiamin diphosphate, the coenzyme for decarboxylation in the ketoglutarate dehydrogenase reaction |
|
|
|
Role of pantothenic acid in citric acid cycle |
As part of coenzyme a the cofactor attached to active carboxylic acid Residue such as acetyl coa and succinyl coa |
|
|
|
How can glycolysis function anaerobically |
Buy regenerating oxidized NAD+, by reducing pyruvate to lactate |
|
|
|
How is lactate the end product of glycolysis |
Under anaerobic conditions for example in exercising muscle and when metabolic machinery is absent for further the oxidation of pyruvate for example in erythrocytes |
|
|
|
Glycolysis is regulated by three enzymes catalyzing non equilibrium reactions |
Hexokinase phosphofructokinase and pyruvate kinase |
|
|
|
When the first site of generation of ATP in glycolysis in the erythrocytes is passed |
Leads to formation of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate which is important in decreasing the affinity of hemoglobin for O2 |
|
|
|
Pyruvate is oxidised to acetyl coa by |
A multi enzyme Complex pyruvate dehydrogenase which is dependent on vitamin derived cofactor thiamine diphosphate |
|
|
|
Molecules of ATP yielded bythe oxidation of glucose |
Anaerobic conditions up to 32 molecules of ATP Under anaerobic conditions only 2 molecules of ATP |
|
|
|
What does glycogen represent |
The principal storage carbohydrate in the body mainly in liver and muscle |
|
|
|
Function of glycogen in liver |
Major function is to provide glucose for extrahepatic tissues |
|
|
|
Function of glycogen in muscle |
Serves mainly as a ready source of metabolic fuel for use in muscle |
|
|
|
Why cant muscle released free glucose from glycogen |
Muscles lack glucose 6 phosphate |
|
|
|
Glycogen synthesis and breakdown Pathways |
Glycogenesis and glycogenolysis |
|
|
|
Role of cyclic AMP in regulation of glycogenolysis and glycogenesis |
It integrates the regulation by promoting the simultaneous activation of phosphorylase and inhibition of glycogen synthase. insulin acts reciprocal to it by inhibiting glycogenolysis and stimulating glycogenesis |
|
|
|
Location of pentose phosphate pathway |
Cytosol |
|
|
|
What happens when Fructose bypasses the main regulatory step in glycolysis that is catalyzed by phosphofructokinase |
It stimulates fatty acid synthesis and hepatic triacylglycerol secretion |
|
|
|
Role of pentose phosphate pathway in erythrocytes |
It prevents haemolysis by providing NADPH to maintain glutathione in reduced state as a substrate for glutathione peroxidase |
|
|
|
Function of uronic acid pathway |
Source of glucuronic acid for conjugation of many endogenous and exogenous substances before excretion as glucuronides in urine and bile |
|
|
|
NADPH |
Malic pathway |
|
|
|
Insulin |
Tyrosine kinase pathway |
|
|
|
Growth hormone |
JAK stat |
|
|
|
NADPH source for fatty acid synthesis |
Malic pathway |
|
|
|
Essential fatty acids cannot synthesized due to deficiency of |
Delta 15 desaturase |
|
|
|
Stop codon |
UAA |
|
|
|
H2S inhibits |
Complex 4 |
|
|
|
Xeroderma |
Pyrimidine dimers |
|
|
|
Cobalophillin |
In saliva |
|
|
|
Cholesterol synthesis is regulated by |
HMG CoA reductase |
|
|
|
Ammonia detoxify in liver to |
Urea |
|
|
|
Cataract |
Galactokinase |
|
|
|
Km of glucokinase |
High |
|
|
|
What time does Insulin rise after CHO meal |
2 hrs |
|
|
|
Lipoic acid is a coenzyme in |
Oxidation of pyruvate |
|
|
|
The carcinoma of bladder causes |
Hyperkalemia acidosis |
|
|
|
Acetyl coa Plus propionyl coa |
Isolucin |
|
|
|
Secondary active transport in git |
Glucose |
|
|
|
Second messenger system for a c t h |
Camp |
|
|
|
Fluoride inhibits which enzyme to decrease dental caries |
Enolase |
|
|
|
Calmodulin which second messenger system |
Calcium ions |
|
|
|
Lactase is released from |
Jejunum |
|
|
|
Enzyme absent in hyperammonemia |
Glutamine synthetase |
|
|
|
Enzyme in brain |
Glutamine synthase |
|
|
|
Site of Beta oxidation |
Mitochondrial matrix |
|
|
|
In the morning before the growth hormone suppression test which activity of the patient will most likely to cause a decrease in growth hormone levels |
She ate 4 large doughnuts for breakfast |
|
|
|
Compounds produced during GABA shunt |
- C O2 - succinate - n a d h - glutamate |
|
|
|
How many ATP produced when steroyl-CoA an18 carbon saturated acyl coa is oxidised completely to C O2 and H2O |
148 |
|
|
|
Lack of glucocorticoids and mineral corticoids might be consequence of which defect in adrenal cortex |
C 21-hydrolase deficiency |
|
|
|
Calcitonin causes |
Activation of osteoblastic activity |
|
|
|
Fructose 1 6 bisphosphate is inhibited by |
Frustose 2 6 bisphosphate |
|
|
|
During each cycle of Beta oxidation |
Two carbon atoms are removed from carboxyl end of fatty acid |
|
|
|
For catecholamine biosynthesis the rate limiting enzyme is |
Tyrosine hydroxylase |
|
|
|
What is homocystinuria |
Accumulation of homocysteine and decrease cystathione |
|
|
|
Which enzyme causes milk curdling |
HCL |
|
|
|
Sickle Cell anaemia is caused by deficiency of |
Intrinsic factor |
|
|
|
Activator of cps1 |
N-acetyl glutamate |
|
|
|
Which substance doesn't retain water |
Angiotensin II |
|
|
|
Primary oxyluria |
Glycine |
|
|
|
Hyperlipidemia type 2 |
LDL receptors |
|
|
|
Substance involved in formation of cataract |
Sorbitol |
|
|
|
Amino acids in preproinsulin |
110 amino acids |
|
|
|
Lactation is caused by |
Oestrogen and prolactin |
|
|
|
Strongest bond is between |
2 phosphates |
|
|
|
Chymotrypsin in small intestine hydrolysis peptide linkages containing |
Phenylalanine |
|
|
|
TPP deficiency is caused by |
Pyruvic acid |
|
|
|
Celiac disease is caused by |
Gluten |
|
|
|
Conditions leading to atherosclerosis |
Dec HDL inc LDL |
|
|
|
Insulin secretion is decreased during |
Stress |
|
|
|
Termination is brought about by |
Nonsense codon |
|
|
|
Ketone bodies are produced in |
Liver |
|
|
|
HMG CoA reductase |
Mevalonate |
|
|
|
Cori's disease |
Brain blood liver |
|
|
|
cDNA |
mRNA |
|
|
|
Serotonin is derived from |
Tryptophan |
|
|
|
Deficiency of which enzyme causes albinism? |
Tyrosinase |
|
|
|
Insulin is not involved in? |
Lipolysis |
|
|
|
Hyperlipidemia type 2 |
LDL receptors |
|

