![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
A girl who has repeatedly had hypoglycemic episodes presents with:
-hypoglycemia -ketonuria -ketonemia along with an appropriately low insulin level Blood Alanine is abnormally low; however, infusion of alanine produces a rapid rise in blood glucose. What is the most likely defect? |
Protein Catabolism in muscle
|
|
|
Under fasting conditions, what is the primary substrate for Gluconeogenesis?
|
Alanine derived from muscle protein
|
|
|
What 2 AA's are predominantly present in Histones?
|
Lysine & Arginine = positively charged & bind tightly to negatively charged DNA
|
|
|
What does Pyruvate Kinase deficiency cause?
|
Hemolytic Anemia
*normally converts PEP -> Pyruvate in Glycolysis |
|
|
What is the most important buffer WITHIN cells? Extracellularly?
|
Within = Phosphate
EC = Bicarbonate |
|
|
Women on a fat-free diet notices that her "hair is falling out"...what is this due to?
|
Vitamin A
|
|
|
Vitamin that is a lipid antioxidant that is important in the stabilization of cell membranes
|
Vitamin E
|
|
|
From which intermediate in the glycolytic pathway does the Pentose Phosphate Pathway shunt?
|
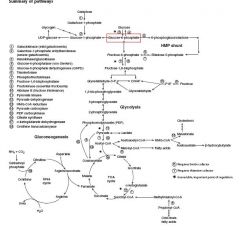
Glucose-6-Phosphate
|
|
|
What is the purpose of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway?
|
Alternative route for the oxidation of glucose
-supplies NADPH = for fatty acid & cholesterol synthesis -supplies Pentoses = synthesis of Nucleotides & some coenzymes |
|
|
Proteins destined for the Cytosol & organelles are synthesized where?
|
"free" ribosomes
|
|
|
Proteins destined to be secreted from a cell are synthesized where?
|
RER
**vs. cytosol-bound proteins = "free" ribosomes |
|
|
A 25-year old woman with Type I Diabetes Mellitus has maintained good glycemic control for several years. Recently she has gained 10 lbs. & joined a group exercise program. By the end of her first 1-hr aerobics session, she is dizzy, nauseated, & feels faint. Which underlying mechanism is the most likely explanation for this episode?
|
Translocation of GLUT4 to the cell membranes of Myocytes due to increased AMP associated with exercising muscle
*this is INDEPENDENT of Insulin |
|
|
What is the mechanism by which cells secrete plasma proteins?
|
Constitutive Exocytosis
-also involved with supplying the PM with newly synthesized lipids & proteins |
|
|
An infant PKU would be expected to be deficient in which of the following nonessential AA's?
|
Tyrosine
|
|
|
WHat structure is common to all Sphingolipids?
|
Ceramide
|
|
|
What is involed in the oxidation of Fatty Acids...it is important in transferring FA's from the Cytoplasm into the Mitochondria
|
Carnitine
|
|
|
9 year old girl with mental retardation has elevated levels of Isoleucine, Leucine, & Valine. What enzyme is deficient & what is the disease?
|
Branched Chain Ketoacid Dehydrogenase
Maple Syrup Disease *I Love Vermont Maple Syrup |
|
|
What enzyme is deficient in Homocystinuria? What cofactor is needed?
|
Cystathionine Synthase
B6 |
|
|
Urea cycle enzyme deficiency associated with Hyperammonemia
|
Ornithine Transcarbomoylase deficiency
|
|
|
Glycogen storage disease caused by Glucose-6-Phosphatase deficiency
|
von Gierke
|
|
|
2 month old has severe fasting hypoglycemia, hepatomegaly, & lactic acidosis
|
von Gierke disease = Glucose-6-phosphatase deficiency
|
|
|
A 2-year-old child is brought to the pediatrician b/c of hematuria. Examination reveals HTN & an abdominal mass. A tumor is localized to the right kidney & biopsy reveals a stroma containing smooth & striated muscle, bone, cartilage, & fat, with areas of necrosis. What disease & what chromosome?
|
Wilm's tumor
Chr. 11 |
|
|
Chromosome that is the site of a tumor suppressor gene involved in the pathogenesis of colon CA & Familial Adenomatous Polyposis
|
Chr. 5 = APC tumor suppressor
|
|
|
Chr. that contains the Retinoblastoma gene. What other cancer is the person susceptible to?
|
Chr. 13
Osteosarcoma **Chr. 13 is also site of BRCA-2 |
|
|
What 3 important genes are contained on Chr. 17?
|
p53
Neurofibromatosis-1 BRCA-1 |
|
|
What chr. is NF-2 gene on?
|
22
|
|
|
Syndrome characterized by bronchiectasis, sinusitis, & situs inversus
|
Kartagener syndrome = absence of inner or outer dynein arm
|
|
|
Sphingomyelinase deficiency that results in progressive neurodegeneration, hepatosplenomegaly, & cherry-red spot on retina
|
Niemann-Pick disease
|
|
|
HExosaminidase A deficiency that occur commonly in Ashkenazi jews
|
Tay-Sachs
|
|
|
Fibrillin deficiency resulting in a person who is tall & thin, fingers are spider-like (arachnodactyly). Displaced lens of the eye & aortic dilation leading to aortic aneurysm
|
Marfin Syndrome
|
|
|
Liver & Steroidogenic tissues have this receptor that recognizes HDL & mediates transfer of Cholesterol into these tissues
|
Scavenger Receptor SR-B1
|
|
|
This acts as a carrier of "activated carboxyl" groups for 3 key enzymes that catalyze carboxylation reactions. Symptoms of deficiency include dermatitis & enteritis
|
Biotin
|
|
|
Dermatitis, diarrhea, & dementia
|
Pellagra = niacin deficiency
|
|
|
Vitamin deficiency that leads to convulsions, hyperirritability. It's deficiency is can be induced by Isoniazid or Oral Contraceptives
|
B6 = Pyridoxine
|
|
|
Vitamin deficiency in which person presents with lesions of the lips, mouth, skin, & genatalia
|
Riboflavin = B2
|
|
|
What does the Nucleolus manufacture?
|
rRNA = ribosomal RNA = protein production capability
|
|
|
Where does Uric Acid come from?
|
Purines
|
|
|
What are Glucose molecules complexed with during Glycogen synthesis?
|
UDP
Glucose-1-Phosphate + UDP -> UDP-Glucose + PPi |
|
|
When is GTP made in the TCA cycle?
|
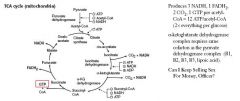
Succinyl-CoA -> Succinate
|
|
|
What is Hereditary Fructose Intolerance due to a deficiency of? What 2 sugars should the patient avoid?
|
Aldolase B
Fructose & Sucrose & Sorbital |
|
|
In the Citric Acid Cycle, Succinate Thiokinase catalyzes the cleavage of the Succinyl-CoA thioester bond with formation of a high-energy compound. What is this compound & what biochemical pathway is it used in?
|
GTP
Elongation of the Polypeptide chain |
|
|
What AA has the best buffering capacity?
|
Histidine = pKa is within range of the pH range
|
|
|
What AA can be a precursor of Niacin?
|
Tryptophan
|
|
|
Disease that presents as muscle weakness & can also cause cataracts, testicular atrophy, heart disease, dementia, & baldness. What disease & what chromosome?
|
Myotonic Dystrophy
Chr. 19 |
|
|
In what Carbon form does Glucose enter the TCA cycle?
|
Acetyl-CoA
|
|
|
Explain the timeline & processes involved in energy usage & production in a marathon runner
|
ATP stores are used up in 1 second
Creatine phosphate will be the primary source of energy for the next 3-4 seconds Glycolysis occurs after this After extended periods of time = Gluconeogenesis & Lypolysis |
|
|
Which enzyme in the TCA cycle would need Riboflavin to be active?
|
Succinate Dehydrogenase = needs FAD
|
|
|
What type of Amino Acids are present on the surface of protein molecules?
|
Hydrophilic = Aspartate, Glutamate, Lysine, & Arginine (Histidine possibly)
|

