![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
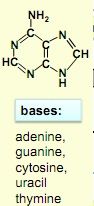
examples of base structures
|
|
|
|
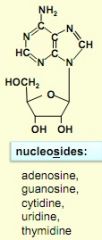
examples of nucleoside structures
|
|
|
|
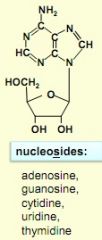
examples of nucleoside structures
|
|
|
|
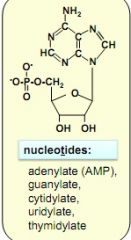
nucleotide structure examples
|
|
|
|
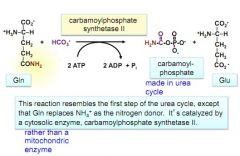
The first step in pyrimidine biosynthesis
|
|
|
|
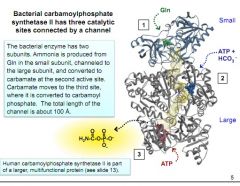
note the structure and functions of carbamoylphosphate synthetase II
|
|
|
|
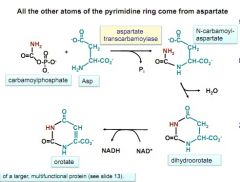
second step of pyrimidine synthesis. happens right after making carbanoylphosphate. ends in an acid
|
|
|
|
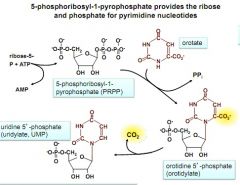
pyrimidine synthesis part 3, starting w/ an acid, ending with a NMP
|
|
|
|
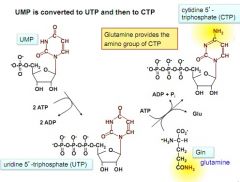
turning UMP into CTP. 4th step of pyrimidine biosynthesis
|
|
|
|
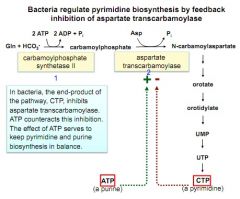
pyrimidine synthesis regulation in bacteria
|
|
|
|
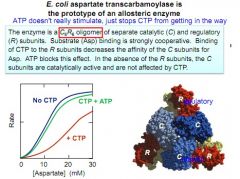
Structure of E. coli aspartate transcarbamoylase and graph of it's activity vs [Aspartate]
|
|
|
|
what are the conformational states of E. coli transcarbamoylase?
|
unbound "taught" state and bound "relaxed" state in the catalytic region. C = catalytic region, R = regulatory region
|
|
|
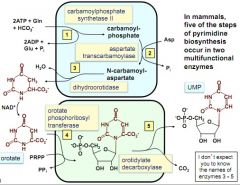
mammal pyrimidine synthesis enzyme
|
|
|
|
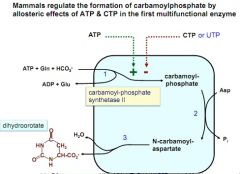
regulation of formation of carbamoylphosphate in mammals
|
|
|
|
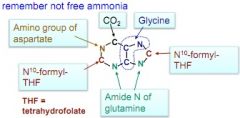
draw out the building blocks of purines. there are 5
|
|
|
|
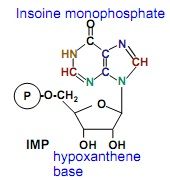
basic structure that leads to all purines
|
|
|
|
how many steps are in purine synthesis? What is the first and last step?
|
11 steps. 1st step is PRibosePP + Gln. last step is IMP --> AMP and GMP
|
|
|
what is the first structure that all other parts add to in purine synthesis?
|
everything is built up off of a ribose
|
|
|
What is a key difference in bacterial and animal synthesis of purines?
|
bacteria use up one more molecule of ATP
|
|
|
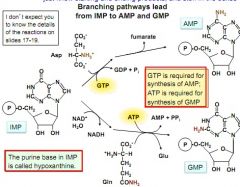
getting from IMP to GMP or AMP
|
|
|
|
purine regulation
|
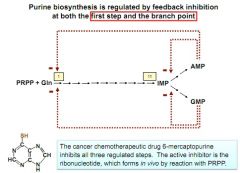
|

