![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
38 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a glycoprotein?
|
protein w/ one or more covalently attached carbohydrate groups
|
|
|
What is the process of covalently attaching carbohydrates to proteins called?
|
glycosylation
|
|
|
Where does glycosylation occur?
|
ER and golgi
|
|
|
Why are carbohydrate groups useful to glycoproteins?
|
-targeting to organelles a/o membranes
-recognition & adhesion -resistance from proteolysis |
|
|
N-glycosidic bonds
|
carbohydrate sugars attached to N of arginine
|
|
|
O-glycosidic bonds
|
carbohydrate sugars attached to O of serine or threonine
|
|
|
Sugar added to billirubin is called _____. Sugar added to lipid is called ____.
|
glucuronide, glycolipid
|
|
|
Disaccharides, polysaccharides and glycosaminoglycans are examples of sugars added to _____.
|
other sugars
|
|
|
Sugars must be _____ to add them to anything.
|
Sugar Activation:
Glucose-1-phosphate + UTP → UDP Glucose |
|
|
What can you do with activated sugars?
|
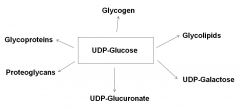
|
|
|
What is used to conjugate billirubin?
|
UDP-glucuronate
|
|
|
Addition of glucuronate to bilirubin adds a _____ charge making it more _____; the rxn is catalyzed by _____.
|
negative, hydrophilic (for excretion), glucuronyltransferase
|
|
|
Crigler Najjar syndrome
|
-severely impaired or absent glucuronyltransferase activity
-rare - ↑ indirect BR -Type I most severe; kernicterus and death w/o Tx -Type II less severe than I |
|
|
Gilbert's syndrome
|
-Mildly reduced expression of glucuronyltransferase
-common in U.S. - slightly ↑ indirect BR levels, but not detrimental -may see increased drug sensitivity to certain drugs |
|
|
Lactose synthesis
|
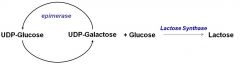
|
|
|
Beacause _____ can be converted to galactose, you do not need dietary galactose to make lactose.
|
glucose; occurs only in lactating mammary gland
|
|
|
What chemical properties of GAGs are responsible for the consistency of mucous secretions and synovial fluid?
|
Lots of negative charge causes them to repel one another and attract water.
|
|
|
What is a proteoglycan?
|
-Proteoglycans are GAGs covalently attached to a core protein
-high carbohydrate content -often sulfated |
|
|
Is hyaluronic acid a proteoglycan?
|
No; it is not attached to a core protein so it is just a GAG
|
|
|
Proteoglycan carbohydrate chains are composed of repeating _____ units.
|
disaccharide
|
|
|
Chondroiton sulfate, Dermatan sulfate and Heparan sulfate are components of _____.
|
proteoglycans
|
|
|
Heparan sulfate containing proteoglycans are expressed on the surface of _____ cells where they facilitate the activity of ______.
|
endothelial cells, anti-thrombin
|
|
|
What differentiates glycoproteins from proteoglycans?
|
-GPs have more protein, less carbohydrate
-GP carb components are shorter, less charged, and branched |
|
|
How are glycoproteins targeted to lysosomes?
|
-GPs get phosphorylated on mannose residues, which targets them for lysosomes
|
|
|
I-cell disease
|
-Deficiency in enzyme which targets lysosomal enzymes for lysosomes
-Lysosomal enzymes get secreted instead -Proteins buildup in lysosomes because there is a shortage of lysozomal enzymes needed to degrade them- inclusions |
|
|
glycolipids
|
-lipid and carb components
-derived from ceramide and are called glycosphingolipids -important for cell surface recognition and signalling |
|
|
Cerebrosides have ___ sugar(s) while gangliosides have ___ sugar(s).
|
one, two or more
|
|
|
Cerebrosides and Gangliosides
|
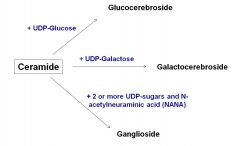
|
|
|
_____ are sulfated glycosphingolipids, important in the maintenance of myelin.
|
sulfatides
|
|
|
_____ on RBC cell membranes are determinants of blood type.
|
glycolipids
|
|
|
Lysozomal storage diseases
|
-Deficiency in any one of the enzymes required for lysosomal degradation of PGs, GLs & GPs
-muccopolysaccharidoses -sphingolipidoses -glycoproteinoses -I-cell disease |
|
|
_____ (such as dermatan sulfate or heparan sulfate) are detected in the urine w/ mucopolysaccharidoses.
|
mucopolysaccharides (GAG components)
|
|
|
Hurler and Hunter syndromes belong to what class of disorders?
|
mucopolysaccharidoses
|
|
|
T/F: Hunter syndrome is X-linked.
|
True
|
|
|
What are the 4 sphingolipidosis diseases?
|
-Fabry
-Gaucher -Tay-Sachs -Niemann-Pick "fuck golf, try nintendo" |
|
|
What is the most common sphingolipidosis disease?
|
Gaucher
|
|
|
Which sphingolipidosis is X-linked?
|
Fabry
|
|
|
Which sphingolipidoses are much more common in peeople of Ashkenazi Jewish descent?
|
Gaucher, Tay-Sachs & Niemann-Pick
|

