![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gout
|
is caused by an increase in uric acid production.
|
|
|
ADA deficiency (Adenosine Deaminase deficiency)
|
accounts for 15% of all SCIDs patients. ADA is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of adenosine to inosine in the breakdown of AMP.
|
|
|
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
|
is due to a deficiency in HGPRT (Hypoxanthine-Guanine Phosphoribosyl Transferase).
|
|
|
Ribose-5-Phosphate
|
Produced from Pentose Phosphate Pathway and is used in the synthesis of both ATP and GTP.
|
|
|
PRPP synthetase
|
is the first step in the conversion of Ribose-5-phosphate to PRPP (Phosphoribosyl-1-Pyrophosphate).
|
|
|
IMP-Inosine monophosphate
|
is the branch point in the purine nucleotide pathway.
|
|
|
PRPP synthease is regulated by AMP
|
True, ADP and ATP as well.
|
|
|
PRPP synthease is regulated by GMP
|
True
|
|
|
PRPP synthease is regualted by GTP
|
True
|
|
|
PRPP synthease is regulated by ADP
|
True
|
|
|
HGPRT
|
is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of Guanine to GMP and is deficient in Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome.
|
|
|
APRT
|
is the enzyme responsible for the conversion of adenine to AMP.
|
|
|
High Uric Acid levels
|
are a common sign of gout.
|
|
|
CPS-II
|
is responsible for the conversion of glutamine, carbon dioxide, and ATP to carbamoyl phosphate.
|
|
|
Ribonucleotide reductase
|
is responsible for the removal of the 2' OH group from the ribose sugar.
|
|
|
Thymidylate Synthase
|
is responsible for the conversion of dUMP to dTMP.
|
|
|
Severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome (SCIDs)
|
Results in a genetic loss of adenosine deaminase
|
|
|
Nucleotide Metabolism
|
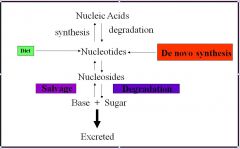
Nucleotide Metabolism
|
|
|
Purine Synthesis
|
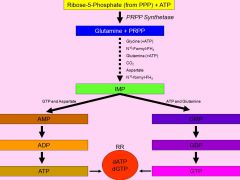
|
|
|
Purine Metabolism Regulation
|
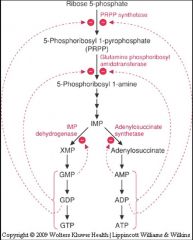
|
|
|
_____ causes hyperuricemia, uric aciduria, juvenile onset of uric acid stone formation, gouty arthritis, and self mutilation.
|
Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome
|
|
|
Purine Breakdown
|
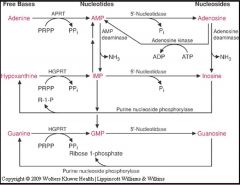
|
|
|
Uric Acid Formation
|
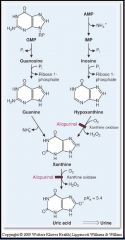
|
|
|
An overproduction of purines causes _____, in which excess uric acid crystals lodge in small capillaries, especially in joints and toes.
|
gout
|
|
|
adenosine deaminase
|
adenosine→inosine; deletion or mutation results in SCIDS
|
|
|
Infants with an inherited _____ deficiency have profound lymphocyte depletion, lack both cellular and humoral immune function.
|
adenosine deaminase (ADA)
|
|
|
Pyrimidine Synthesis
|
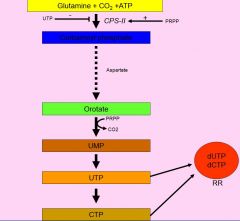
|
|
|
how many rings do pyrimidines have?
|
one
|
|
|
Ribonucleotide Reductase
|
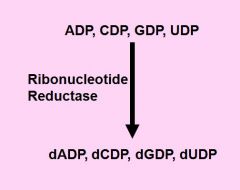
|
|
|
TTP Synthesis
|
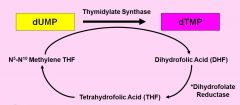
|
|
|
pyrimidine degradation
|
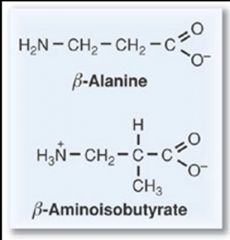
|

