![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a) this is muscle tissue that is made up of fibers that contract
b) it is skeletal muscle c) attached to bones d) Striated muscles moves the skeleton e) it is multi-nucleate, it is unbranched, the activity is voluntary, which means it is required to recieve signal from motor neuron, it is striation (hoizontal lines) |

a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) this is muscle tissue
b) it is cardiac muscle c) heart d) it pumps blood e) characteristics: 1 or 2 nuclei, it has branched or intercalated discs form direct cytoplasmic connection end to end, activity is "non-voluntary", meaning that signal from motor neuron is not required |
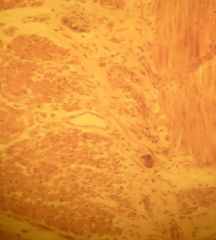
a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) this is muscle tissue that is made up of fibers that contract
b) it is cardiac mucle tissue c) located at the heart d) function to pump blood e) characteristics: 1 or 2 nuclei, branched; intercalated discs form direct cytoplasmic connection end to end, activity is "non-voluntary" meaning that signal from motor neuron is not required |
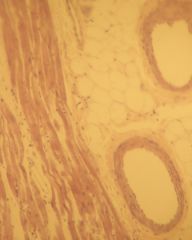
a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) this is muscle tissue and it is made up of fibers that contract
b) it is smooth muscle tissue that lines the wall of blood vessels and digestive tract c) located in intestines, arteries, other d) function is to move food, help regulate blood pressure, etc. e) characteristics: single nucleus, unbranched, activity is "non-voluntary", meaning that signal from motor neuron is NOT required |

a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) this is muscle tissue that is made up of fibers that contract
b) it is cardiac mucles tissue c) located at the heart d) function to PUMP BLOOD e) characteristics: 1 or 2 nuclei, branched, intercalated discs form direct cytoplasmioc connection end to end |
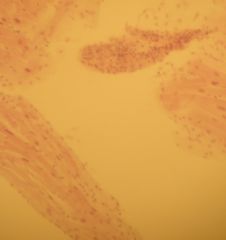
a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) this is nervous tissue, consists of cells with projections that transmit electrical signals
b) nerve tissue, that consists of nerve cells, which are called neurons located in all parts of the body, from brain, back, feet, etc d) function is to send electrochemical signals, which are produced by changes in the permeability of the neurons plasma membraneto ions. e) neurons recieve support from support cells that also supply neurons w/nutrients |
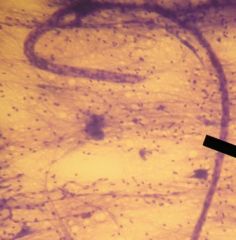
a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) this is nervous tissue
b) neuron (large star shaped figure) cell bodies, inside the cell is a single nucleus and nucleolus is usually visible, w/in the cell body is darkly stained small/thin NEUROFIBRILS extending from the chain of SCHWANN CELLS, extending from the cell bodiy is single, long AXONS w/DENDRITES on the ends, the LONG CHAIN of SCHWANN CELLS are connected by "NODES OF RANVIER", each Sch. cell has a nucleus and at the end is a axon w/axon terminals. |
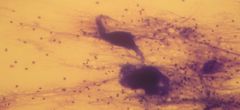
a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) this is nervous tissue
b) these are PURKINJE neurons c) located in the cerebellum d) function is ? e) it has a cell body w/dendrites |
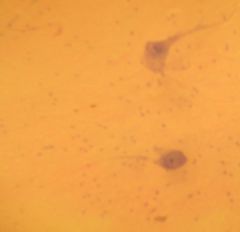
a) Identify the slide
b) What type of tissue c) Where is it located d) What is its function e) Anything extra add here |
|
|
a) This is a slide of a sponge
b) ALL sponges are suspension feeders, meaning that their cells beat in a coordinated way to produce a water current that flows through small pores in the outer body wall, into chambers inside the body and out through a single layer opening. c) ADULT SPONGES ARE SESSILE but may produce larvae that swim w/the aid of flagella d) they have asexual reproduction, meaning fragments fall off and are able to produce a new individual e) some form radial symmetric tubes, in addition some like this one has branched spicules |

a) Identify this slide
b) how do they feed c) how do they move around d) how do they reproduce e) what is is shape or any extra additive features |
|
|
a) this is a sponge w/an asconoid body structure
b) in all sponge types, the body is designed to facilitate feeding. Water is pulled into the pores and canlas by the beating of the choanocytes flagella. It moves into the spongocoel and is eventually forced out through the osculum. As the water passes across the choanocytes, food particles (microscopic algae, bacteria, and organic debris) adhere to the cells and are eventually taken into food vacuoles for intracellular digestion. c) movements is limitted, they are sessile d) asexual reproduction occurs e) the opening is the OSCULUM, the many little lines are the SPICULES, the dark cells inside are OSTICA |

a) Identify this slide
b) how do they feed c) how do they move around d) how do they reproduce e) what is is shape or any extra additive features |
|
|
This is a sponge w/an Ascon body type (Asconoid body structure) and the opening here is the Osculum, which is formed by little small spicules
|

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a sponge w/an syconoid body structure. in the middle open space is SPONGOCOEL, open areas leading into or out of the sponge is called INCURRENT CANAL, closed sections w/in the sponge are called the RADIAL CANAL, little small circular cells are called CHOANOCYTES, inside the inner ring a cave-like section is called an APOPYLE, a small opening leading into a radial canal can be called an OSTIUM, longer cells on the inside are called PINACOCYTES, darker areas on the outside of the sponge is an area of darker cells called the MESOPHYL. The cell on the inside is a Amphiblastula larvae, which is a product of sexual reproduction.
|

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This are tentacles from a HYDRA, a common fresh water hydrazoan.
Id. Class: Phylum Cnidaria |
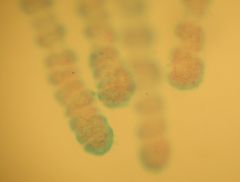
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is an Anterior end of a hydra.
Located are Tenticles, on teh tenticles are Cnidocytes, the top of the hydra is the Hyptostome and the mouth. It is from the Phylum Cnidaria class. |
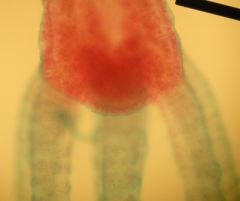
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is an Hydras mid section, the darker area is either the Testis or the Ovary, depending on the location of the lump. Testis are closest to the tentacles, and toward the end is the "BASAL DISC", which would be more closely directed to the Ovary.
|

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
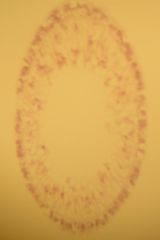
This is a transverse cross section of a female hydra.
The outermost part is the EPIDERMIS, then the GASTRODERMIS, little cells w/in the gastrodermis are MESOGLEA, and the center is the COELENTERON. |
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
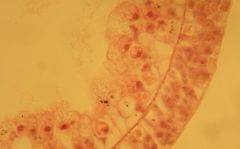
This is a section of a female hydra, from right to left, Epidermis, Mesoglea cells, Gastrodermis, and the inside is the Coelenteron.
|
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
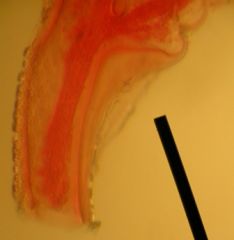
This is a more typical hydrazoan, Obelia.
The area shown is the PERISARC, which is made up of CHITIN - a nitrogen containing polysaccharide whose structure is similar to cellulose. |
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
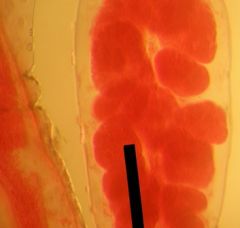
This is a more common hydrazoan, Obelia.
The area shown is a POLYP, called GONANGIUM, reproductive polyp. |
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a POLYP, called HYDRANTH, which is a feeding polyp w/tentacles
|

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is the most common hydrozoan, Obelia.
The area shown is the, Hydranth, feeding polyp w/tentacles |

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a hydrazoan, Obelia, medusa.
Also shown are, Tentacles, center is the MANUBRIUM (mouth is located here on the bottom when in feeding position, side view), the outer large cells are the GONADS, |
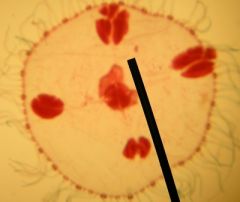
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a from the class Scyphozoa, it is a common moon jelly called Aurelia.
This is a fertilized egg, the PLANULA, that may be retained on the oval armof the medusa |
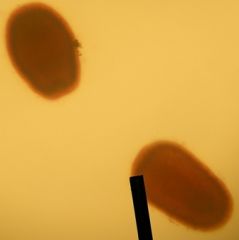
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is close visual of an Aurelia's gastric pouch, the GONAD. W/in each GONAD there are gastric filaments.
These four gonads are branched together w/radial canals. Located on the outside is called circular canals that continue around the perimeter of the body. |
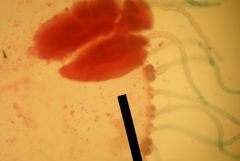
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
this is a moon jelly, Aurelia, from the Class Scyphozoa.
This jelly is known as the scyphistoma, which is the planula larvae metamorphose into a feeding polyp. The Aurelia is similar to the hydra, just that is possesses many more tentacles. The scyphistoma feeds and grows for awhile, then transforms into a reproductive polyp called a strobila |

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is an Aurelia scyphistoma. This is the developing stage in the life cycle of the jellyfish.
|
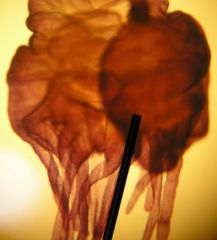
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a Aurelia Strobila. ONLY under favorable condition do the scyphistoma develop into a strobila. It consists of many upside down little medusa's that are popped off rythmically when ready. These new medusa are called EPHYRAE.
|

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a Aurelia Strobila. It has newly developed medusa's developing one on top of another. They are rythmically popped off when ready. The new medusa are called Ephyra.
|

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
this is a Aurelia ephyra larva, which gradually develops into adult jellyfish, it has located on the outer arms sensory organs called RHOPALIA and located in four areas around the center is the GONADS
|
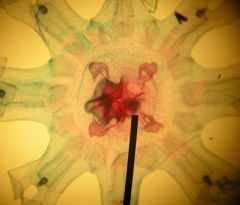
Identify the slide?
|

