![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Far right: parenchyma cells
second from right: Primary Phloem fibers Centered red cells: tracheary elements |
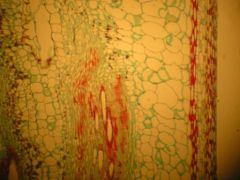
Identify the far right red cells, the ones second to the right, and the centered red cells?
|
|
|
This is a longitudinal section. Far left, epidermis, cortex, phloem, xylem, pith...
|
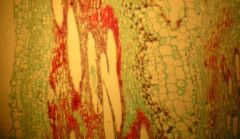
Identify the cell on the far left leading to the right.
|
|
|
From top to bottom: Epidermis, cortex, pith, (vascular bundle) external phloem, vascular cambium, seconday xylem (large cells), primary xylem (smaller cells), primary phloem fibers, parenchyma, collenchyma, epidermis (maybe stoma).
|
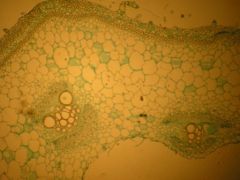
Identify all parts of the cell.
|
|
|
the LARGE empty areas is the pith, then there is a vascular bundle from top to bottom: external phloem, vascular cambium, large secondary xylem, primary xylem, primary phloem, primary phloem fibers, parenchyma, collenchyma, epidermis, (at times a stoma).
|

Describe the cell?
|
|
|
From left to right: Epidermis, exodermis, companion cells, mature sieve tube elements (above it is a slime plug, companion cells, exodermis, epidermis...
|

Identify the cell parts?
|
|
|
Epidermis, collenchyma, parenchyma, sclerenchyma-fibers (1st bundle of red fibers), vascular cambium, seconday xylem, xylem ray, primary xylem, pith
|

Identify the cells from top to bottom?
|
|
|
Reticulate, helical, annular
|

Identify these tracheray elements form left to right?
|
|
|
Pith, external phloem, vascular cambium, large secondary xylem, primary xylem, internal phloem...
|
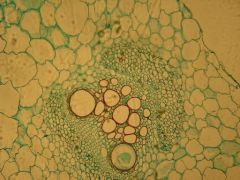
Identify the vascular bundle from left to right?
|
|
|
Protoderm (outer most part of leaf around head/horns), procambium (inner dark trail of cells), ground meristem (inner open clear areas), axillary bud primordia (dark shoulderblads area), leaf primordia (horns), SAM (top center)
|
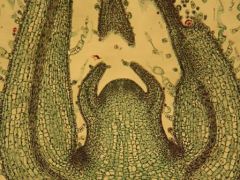
Identify the shoot tip from left to right?
|
|
|
Procambium (trail), w/a visible bud primordium
|
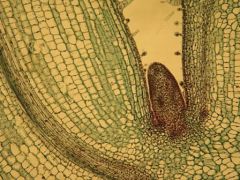
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a Helianthus stem cs, outer part is epidermis (maybe trichomes present extending outward from the surface), maybe guard cells and stomata present in the epidermis, the epidermis is covered by a waterproofing cuticle, next is cortex (several layers thick w/collenchyma and parenchyma cells), inside the cortex is a ring of vascular bundles (each has a cluster of red-staining phloem fibers called the vascular bundle cap), a region of green stained phloem, a region of xylem composed of tracheary elements (vessel members and tracheids) and parenchyma. The region between the vascular bundles is called PITH RAYS. In the center is the PITH...
|

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a a Leaf cs.
the procambium is in the center, then ground meristem, and on the outer ring is the protoderm... |

Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a root: epidermis is onthe outside, cortex, (star shape) primary xylem, and the area inbetween the star is the grean colored cells is the primary phloem...
|
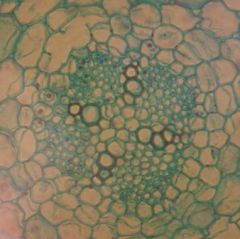
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
This is a root tip ls: it has root hairs, root cap (inner part of tip), promeristem (inner tuning point in the middle), right/left side is the apical meristem, end of apical meristem (5-8 cells back is the) procambium, inch back is the Ground Meristem, another inch back and to the outside is the Protoderm...
|
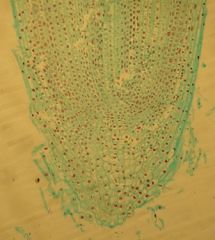
Identify the slide?
|
|
|
this is a root cs the outermost part is the epidermis, which gives rise to root hairs, w/in the epidermis is the cortex (made up of parenchyma cells used for food storage, the inner most part of the cortex right before the vascular cylinder is called the endodermis, the inner most part of the cell is the xylem used for conducting water and minerals (this is usually shaped like a 4 or 5 armed arrangment), inbetween these arms is the phloem (green in color used for conducting food), inside the endodermis is the pericycle, which becomes meristomatic and produces lateral roots...
|

Identify this slide?
|
|
|
This is a Branch root cs: the root primordia is developing in the center and will eventually break out which will develop a rootcap and apical meristem, and then the primary meristems appear, this later forces some parenchyma cells to differentiate into xylem and phloem that combine to become the vascular cylinders...
|

Identify the slide?
|

