![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Aerobic respiration typically has a net yield of _____ atp |
36 |
|
|
Which fuel type provides renewable sources of energy? |
Biofuels |
|
|
Lactate fermentation _____ |
Generates NAD+ |
|
|
Light energy _____ |
Can be converted into chemical energy |
|
|
The process of carbon fixation involves ______ |
Extracting carbon atoms from an inorganic source and incorporating them into an organic molecule |
|
|
The enzyme-mediated reactions of the Calvin-Benson cycle _____ |
Build sugars in the stroma |
|
|
For each glucose molecule, glycolysis yields a net production of _____ |
2 nadh 2 atp 2 pyruvic acid |
|
|
What similarities do aerobic respiration and fermentation share? |
They both begin with glycolysis |
|
|
The electrons in photosystem are replaced by______ |
Breaking down water molecules |
|
|
How did the emergence of abundant levels of oxygen in earths atmosphere first affect life? |
The formation of free radicals caused many cells to die out. |
|
|
The H+ gradient generated during the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis facilitiates the formation of atp by ______ |
Providing energy to fuel atp synthase |
|
|
The vast majority of producers obtain their carbon for photosynthesis from _____ |
Atmospheric carbon dioxide |
|
|
CAM plants ______ |
Store C4 products in vacuoles |
|
|
When you eat more protein than your body needs to build molecules, Amino acids are broken down. Molecules derived from the carbon backbones of amino acids enter which stage of aerobic respiration? |
Krebs cycle |
|
|
A pigment is an organic molecule that _____ |
Selectively absorbs light |
|
|
Which statement best describes a coupled reaction? |
An exergonic reaction powers an endergonic reaction |
|
|
Which law of thermodynamics explains inputs and outputs in chemical reactions? |
The first law of thermodynamics |
|
|
Atp stores energy in the form of ____ |
Chemical bond energy |
|
|
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that helps living things extract energy from food. From this we know that glycolysis ____ |
Consists of a series of chemical reactions. Uses a number of enzymes Involves the modification of a series of substrates Proceeds by means of each enzyme leaving a succeeding reaction to a different enzyme. |
|
|
The portion of an enzyme that attaches to the substrate is the ____ |
Active site |
|
|
Which action is an example of active transport? |
Calcium pumps in muscle cells transporting calcium against te concentration gradient. |
|
|
Bacteria enter your body througg a cut on you finger. Your immune system cells kill off the invaders by ingesting them. This is an example of
|
Phagocytosis |
|
|
Which of the following is not a function of the proteins in the plasma membrane? |
Keeping the membrane fluid at low temperatures |
|
|
Osmosis refers to the net movement of _____ across a _____. |
Water Semipermeable |
|
Front (Term) |
Simple diffusion - no energy or protein Facilitated diffusion -transporters Osmosis- aquaporin
Active transport - requires energy |
|
|
______ and _____ are important not so much for the ATP produced in them, but for the yield of electrons that are used in ——- |
Glycolysis Krebs cycle Etc |
|
|
At most, how many molecules of atp can be produced per glucoses molecule in aerobic cellular respiration? |
36 |
|
|
Which stage, or stages, or aerobic respiration occur in the mitochondria? |
The krebs cycle And the etc |
|
|
When NADH passes its electrons to the etc, it is _____ |
Oxidized |
|
|
In photosynthesis, energy from the sun is being _____ while in the cellular respiration, energy is being ______ |
Stored in carbohydrates ... released from storage in food |
|
|
Stomata are the _____ on leaved that not only let water wrapper out, but let _____ in. |
Pores Carbon dioxide |
|
|
Two important products of the light reactions in photosynthesis are |
ATP NADPH |
|
|
The ultimate product of photosynthesis is te organic molecule. |
The sugar G3P |
|
|
Cells use pseudopodia or false feet to surround and engulf whole cells, fragments of them, or other large organic materials. |
Phagocytosis |
|
|
What is membrane crossings? |
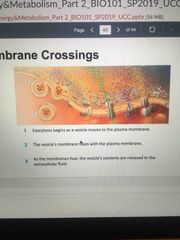
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Chemical reactions that transfer electrons between reactants are called ______ |
Redox reactions |
|
|
In _____, a substance loses electrons or is ____. |
Oxidation Oxidized |
|
|
In _____, a substance gains electrons or is ____. |
Reduction Reduced |
|

Which equation is this? |
Cellular respiration. Fuel is oxidized and O2 is reduced |
|
|
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: In it empty state, this molecule exists as _____ |
NAD NAD+ |
|
|
Through a redox reaction, NAD+ picks up one hydrogen atom and another single electron from food, thus becoming _____ |
NADH |
|
|
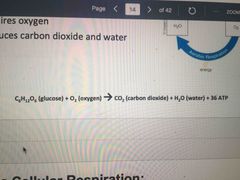
Requires oxygen and it’s more efficient producing atp. |
Aerobic respiration |
|
|
Does not require energy and it’s less efficient producing atp.
Occurred first in evolution. |
Anaerobic respiration |
|
Front (Term) |
Aerobic respiration |
|
|
Aerobic has 3 stages: |
Glycolysis Krebs cycle Electron transport chain |
|
|
Where does Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, and etc take place: |
Cytosol Matrix Inner membrane |
|
|
Glycolysis yields _____ is ATP per molecule of glucose, as does the Krebs cycle |
Two net molecules |
|
|
The net yield in te ETC is a maximum of about _____ |
32 ATP |
|
|
Glycolysis begins with a single molecule of glucose, the ultimate products are |
2 atp 2 NADH which moves to etc 2 pyruvic which moves to Krebs |
|
|
Intermediate step: |
1 CO2 1 NADH 2 acetyl coA |
|
|
Krebs cycle: |
2 FADH 6 nadh 2 ATP 4 CO2 2 acetyl coa |
|
|
On reaching the ETC, the electron carriers ____ and ____ are oxidized by molecules in the chain. |
Nadh fadh2 |
|
|
The last electron acceptor in the ETC is ______. |
Oxygen |
|
|
In the inner compartment, _____ accept the electrons from the ETC and hydrogen ions, this forming ... |
Oxygen Water |
|
|
ETC yields: |
26-28 atp H2O |
|
|
ATP production by cellular respiration: GLUCOSE ——> |
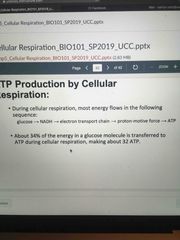
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Uses an electron transport chain with a final electron acceptor different from O2, usually sulfate or nitrate. |
Anaerobic respiration |
|
|
Uses substrate level phosphorylation instead of an electron transport chain to generate atp |
Fermentation |
|
|
Two types of fermentation: |
Alcoholic Lactic acid |
|
|
Pyruvate is concerted to ethanol in two steps... |
Alcoholic fermentation |
|
|
In alcoholic fermentation, the first step releases _____ from ____, and the second step reduces the resulting acetaldeyde to ethanol. |
CO2 Pyruvate |
|
|
Human muscle cells use ____ to generate atp when O2 is scarce. |
Lactic acid fermentation |
|
|
_____ is the process that converts solar energy into chemical energy. |
Photosynthesis |
|
|
Produce organic molecules from CO2 and other inorganic molecules. |
Autotrophs |
|
|
Obtain organic material from other organisms. |
Heterotrophs |
|
|
3 types of photosynthesis |
Plants Algae Bacteria |
|
|
Equation for photosynthesis |
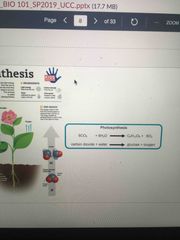
Back (Definition) |
|
|
The site for photosynthesis |
Chloroplast |
|
|
Green pigment within chloroplast |
Chlorophyll |
|
|
Microscopic pores that can open and close, letting carbon dioxide in and oxygen and water vapor out. |
Stomata |
|
|
Connected sacs im the chloroplast. (May be stacked in Colomums called GRANUM) Contains chlorophyll. |
Thylakoid membrane |
|
|
Dense interior fluid |
Stroma |
|
|
Can all plants do photosynthesis? |
Not all cells in plants are photosynthetic |
|
|
Energy radiating from the sun travels through space in waves and is organized in packets called |
Photons |
|
|
Energy radiating from the sun travels through space in waves and is organized in packets called |
Photons |
|
|
Distance between the crests of two successive waves |
Wavelength |
|
|
The main photosynthetic pigment |
Chlorophyll A |
|
|
Absorbs light from ____ and ____ regions of visible light and reflects and transmits green light. |
Chlorophyll a
Red and blue |
|
|
Accessory pigments include. |
Chlorophyll b Carotenoids Xanthophylls |
|
|
Photosynthesis is a _____ process in which h2o is oxidized and CO2 is reduced. |
Redox |
|
|
Photosynthesis is an ______ process, the energy boost is provided by light. |
Endergonic |
|
|
Photosynthesis occurs in two stages: |
Light dependent reaction
Light independent reaction (Calvin cycle) |
|
|
In the first stage (light reactions), electrons derived from water are energetically boosted by ____ |
Power of sunlight |
|
|
In light reactions electrons physically move in this process: |
Pass along through electron carriers End up as NADPH NADPH carries electrons to second stage of photosynthesis |
|
|
Light reactions first stage, photosynthesis works through a pair of molecular complexes |
Photosystem II and I |
|
|
Molecules that absorb and transmit solar energy. |
Antennae |
|
|
Accept both this energy and electrons derived from water. |
Reaction center |
|
|
A part of the reaction centers, to which te electrons move after being energetically boosted. |
Primary electron acceptors |
|
|
Key processes in light reactions: |
Water is split, yielding both electrons and oxygen. The water is transferred to a different molecule, the initial electron receptor. ATP is produced |
|
|
In the second stage ______, the electrons brought together with carbon dioxide and a sugar. |
Calvin cycle |
|
|
Carbon dioxide fixation Energizing the sugar Exit the product RuBP regeneration |
The Calvin cycle |
|
|
____ can be used for energy or plant growth. Some will be used to make glucose, starch, cellulose. Some to keep the cycle going |
G3p |
|
|
Allow plants to live where water is scarce. |
Waterproof cuticles |
|
|
Gaps that open between guard cells in plant surfaces. |
Stomata |
|
|
Use only the Calvin cycle to fix carbon. Conserve water; oxygen interferes with sugar, sugar production becomes less as temperature rise |
C3 plants |
|
|
Plants that minimize photorespirqtoon by fixing carbon twice, in two cell types. |
C4 plants. |
|
|
C4 plants that conserve water by fixing carbon twice, at different times of days |
CAM PLANTS |

