![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
84 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
5 stages of development |
gametogenesis, fertiliaation, cleavage, gastrulation, organogenesis |
|
|
Isolecithal, mesolecithal, telolecithal, centrolecitha |
low, medium, large amount of yolk. Central yolk |
|
|
Vitelline membrane |
hardens and becomes fertilization membrane |
|
|
are dividing cells undergoing cleavage |
blastomere.
blastomere surrounds blastocoel (fluid filled cavity) |
|
|
holoblastic vs incomplete cleavage |
all of cytoplasm becomes cells vs not all |
|
|
protostomes |
spiral cleavage, mosaic and determinate so cytoplasmic speciation = death on removal of blastomere, mouth first, SCHIZOcoely |
|
|
Dueterostomes |
radial cleavage, indeterminate and blastomere removal = twins, anus first, enterocoely |
|
|
Gastrula |
stage with more germ layers where blastula forms and stomach/mouth/anus... then schizo or enterocoely |
|
|
Ectoderm/Endoderm |
outer layer, inner bulge that defines gastrulation |
|
|
Archentron |
aka Gastrocoel, middle of endoderm/gastrula |
|
|
Morula |
16 and 32 cell stage before blastula forms with blastocoel |
|
|
Coelem |
gut formed by surrounding mesoderm |
|
|
Types of Protostomes |
Lophotrochozoa, Ecdysozoa |
|
|
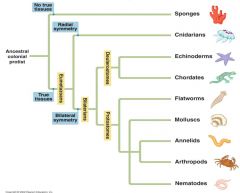
Porifera have no ______ ______ and are ________ ________ contain all organisms Eumetazoans contain ________ _________ Protostomes and Duetrostomes are _____________
Cnidarians have __________ _________ |
|
|
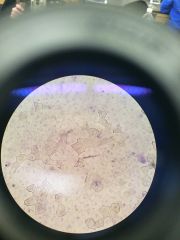
name, ID basement membrane |
Squamous Epithelium 400x, basement membrane is thin sheet of fibers that serves for attachment and stabilization |
|
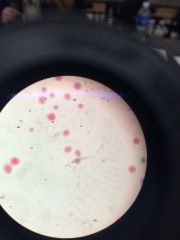
|
Fertilized/Ripe eggs have fertilization membrane which is not perfect and bigger than vitalline membrane AND can have polar bodies |
|

|
Bipinnaria with developed stomach and anus |
|
|
epithelial cells are avascular which means: |
they have no vessels. |
|
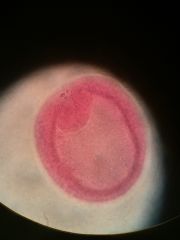
Define this |
early stage gastrulation, NO LONGER a blastula |
|
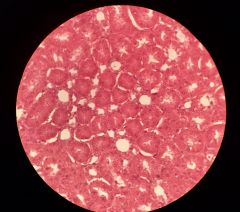
|
Epithelial, Cuboidal 400x, has glands, nuclei are small and purple. White middle is duct, basement membrane is around layer of cells surrounding duct |
|
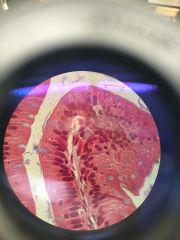
|
Epithelial, Columnar, **Goblet Cells are purple and secrete mucus. (have Microvilli borer) |
|
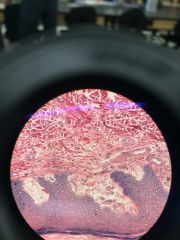
|
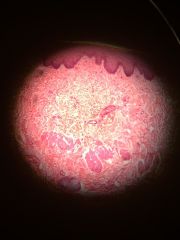
Stratified Squamous again. |
|
|
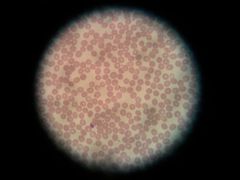
Connective--Blood. large purple=luekocyte, small purple=platelet. |
|
|
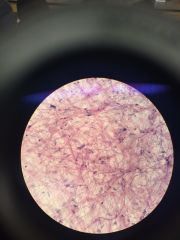
Loose Connective Tissue. Thick Bundle: non-elastic fibers thin: elastic fibers clear: where it connect, ground substance.
thin can bend: elastic |
|
|
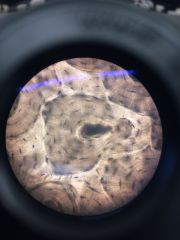
Connective. Bone. Haversian Canal. Lacunae (thick in rings) Lamellae (thin rings on which lacunae lie) Canalaculi (fibers going opposite way) |
|
|
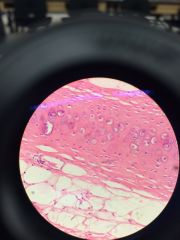
Connective. Hyaline Cartilage. matrix = pink lacunae = circles w/ purple in (chondrocyte) |
|
|
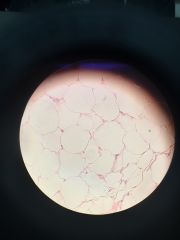
Connective. Adipose tissue |
|
|
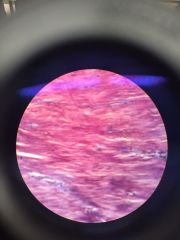
Muscle. Smooth. |
|

|
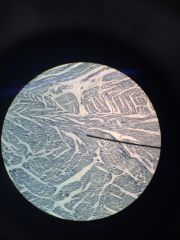
Striated muscle. (skeletal muscle) very thin vertical lines nucleus = ovals (can be red or purple) sacolemma = gaps where nucleus resides |
|
|
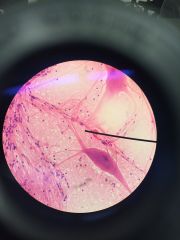
nervous tissue. cell body, nucleus, nerve processes = dendrites and axons |
|
|
Cardiac muscle is similar to striated muscle but with gaps called intercalated disks. |
|
|
The 3 types of Dueterostomes are |
Chordates and hemichordata/echinodermata |
|
|
Echinodermata has 3 things |
Pentaradial Symmetry (like star fish) Calcareous endoskeleton Water vascular system |
|
|
What are the 6 types of Lophotrochozoa Protostomes? |
PREMAB Platyhelmines Rotifera Ectoprocta Brachiopoda Mollusca Annelida |
|
|
Two types of Ecdysozoa? |
AN ecdysozoa. Nematoda & Arthropoda |
|
|
Porifera |
(metazoa) sponges -2 layers of cell separated by mesohyl. Pinacocytes line canals Choanocytes filter food Archaeocytes can phagocytize larger particles |
|
|
Cnidaria |
(eumetazoa) either 1) free-swimming medusa or sessile polyps -diploblastic acoelemates with an incomplete gut and no excretory or respiratory system
cnidae: capsule organelles. nematocysts sting. |
|
|
Bilateria |
triploblastic: have endoderm, ectoderm, mesoderm
Dueterostome (chordates, hemi, echinoderms) Protostome (lophotrochozoa, ecydsozoa) |
|
|
Lophotrochozoa |
crown of ciliated tentacles for feeding called lophophore trochophore larvae stage
PREMAB |
|
|
Platyhelminthes |
(Eumetazoa, Bilateria, Protostomia, Lopho)
flatworms acoelemate (no central body cavity)
classes: Turbellaria (flatworms) Tremataoda and Monogenea (flukes) Cestoda (tapeworms) |
|
|
Rotifera |
(Eumetazoa, Bilateria, Protostomia, Lopho)
psuedocoelem |
|
|
Mollusca |
(Bilateria, Protostomia, Lopho)
coelemates- true body cavities mantle- encloses gills and secretes shell 3 main body parts: head, foot, visceral mass |
|
|
Classes of Phylum Mollusca |
Gastropoda: snails, slugs, intricate shells Polyplacophora: Chitons Bivalvia: clams, oysters Cephalopoda: squids, octopus |
|
|
Annelids and 3 classes |
(bilateria, protostomia, lopho)
long like worms, large coelem
Oligochaeta: earthworms Polychaeta: marine worms Hirudinia: leeches |
|
|
What is the clitellum |
Part of the earthworm that is not ringed.
earthworm-oligochaete-lopho-proto |
|
|
Ecdysozoa and 2 phylums |
(Eumetazoa, bilateria, protostomia)
Arthropodia, Nematoda |
|
|
Phylum Nematoda |
Ecdysozoa
parasitic round worms secrete nonliving cuticle and shed as juvenile Eutely |
|
|
Eutely |
set number of cells at maturity |
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda
and 4 subphylum |
(ecdysozoa, protostomia)
chitinous exoskeleton cuticles harden into sclerites
MCCH Myriapoda, Chelicerata, Crustacea, Hexapoda |
|
|
subphylum Myriapoda |
(Arthropoda, Ecdysozoa, Proto)
millipedes and centipedes |
|
|
subphylum chelicerata |
spider and horseshoe crab
chelicerae: 2 fang arms on front prosoma: behind head opsothoma: rear abdomen |
|
|
subphylum crustacea |
(arthropoda, ecydysozoa, proto)
lobsters, crabs, shrimp
head then cephalothorax then abdomen |
|
|
subphylum hexapoda |
6 legs, grasshopper, fly, praying mantis
head then prothorax then mesothorax then metathrox then abdomen |
|
|
Dueterostomes |
Eumetazoa, Bilateria
Chordata, Echinodermata, hemidorata |
|
|
5 classes of Echinodermata |
ACHOE
Asteroidea (sea stars) Crinoidea (other stars) Ophiureoidea (other stars) Echinoidea (sea urchins and sand dollars) Holutheroidea (sea cucumbers) |
|
|
Class Asteroidea |
(asteroids are shooting stars) (Dueterstomia, Echinodermata)
madrepoite (circle on outside) mouth (on bottom) central disk (middle) |
|
|
Phylum Chordata
and 5 characteristics DNPEP |
(Bilateria ,Dueterostomes)
Dorsal nerve cord Notochord Paired pharyngeal slits Endostyle (thyroid) Postanal tail |
|
|
3 subphylums of Chordata |
Cephalochordata (lancelets) Urochordata Vertebrata (humans) |
|

|
(Dueterostomia, Chordata, Cephalochordata)
5 parts |
|

|
Cross section of cephalocordata |
|
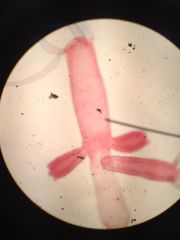
|
polyp
eumetazoa, phylum cnidaria, |
|
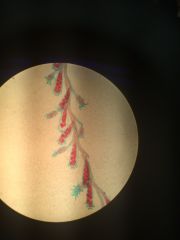
|
polyp and medusa
Hydrozoa Obelia
eumetazoa, cnidarai, hydrozoa |
|
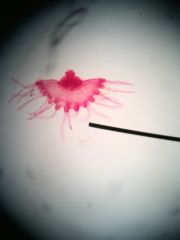
|
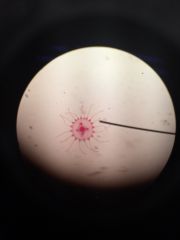
Medusa |
|

|
Flatworm (has eyespots on top of head) angled head
Bilateria, Protostome, Lophotrochozoa, Platyhelminthes, Turbellia
|
|
|

Bilateria, Protostome, Lophotrochozoa, Platyhelminthes, Trematoda
|
|
|
Protostomia, Lophotrochozoa, Platyhelminthes, cestoda
also can be worm like with teeth/head structure |
|

|
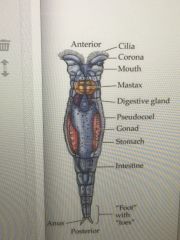
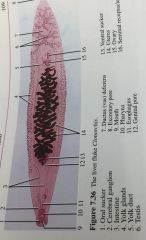
Protostomia, Lopho, Rotifera, |
|

|
Protstomia, Lopho, Mollusca, Polyplacaphora |
|

|
Protsomia, Lopho, Mollusca, Gastropoda |
|

|
Protostomia, Lopho, Mollusca, Cephalopoda
Cephalopods are also squids, octo, cuttle |
|

|
Protostomia, Lopho, Annelids, Polycheates (marine worms) |
|

|

Protostomia, Lopho, Annelid, Hirudinida
leech |
|
|
Dog heartworm is |
Protostomia, Ecdysozoa, Nematode |
|

|
Protostomia, Ecydysozoa, Nematoda |
|

|
Protostomia, Ecydsozoa, Arthropods, Chelicerata |
|
|
Spiders are what subphylum of what |
Chelicerata of Arthropoda |
|

|
Protostomia, Ecdysozoa, Arthropods, Myriapoda centipiede and millipede |
|

|
Protostomia, Ecdysozoa, Arthropoda, HEXAPODA |
|

|
Dueterostomia, Echinodermata, Asteroidea |
|

sea cucumber |
echinodermata, holothuroidea |
|

|
basket star
echinodermata, ophiuroidea |
|

|
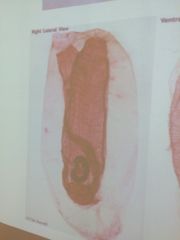
dueterostome, chordota, urochodota
left is tadpole urochordota, here is adult
|
|
|
Coral |
Cnideria Anthozoa |
|
|
telencephalon |
Cerebrum, Olfactory bulbs, Optic nerve, Optic chiasma |

