![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Saprobic (fungi) |
Living off of dead material |
|
|
|
Hyphae (fungi) |
Long branched filaments of a fungus |
Basic body plan of a true fungus |
|
|
Mycelium (fungi) |
All of the vegetative hyphae |
|
|
|
Zygomycota (fungi) |
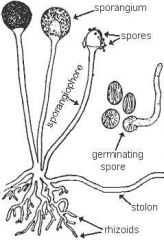
Conjugating fungi; have filamentous growth form. Have haploid (n) septate hyphae |
Includes mucor and Rhizopus, 2 common bread molds. |
|
|
Stolons (fungi) |
Unbranched hyphae |
|
|
|
Gametangium (fungi) |
Two hyphae of different mating types fuse |
|
|
|
Zygospore (fungi) |
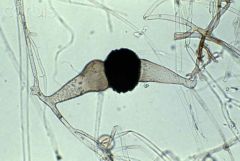
When a zygote enlarges and thickens. Can tolerate extreme conditions and remain dormant for months. Undergo MEIOSIS when conditions are favorable to become a new haploid mycelium. |
|
|
|
Ascomycota (fungi) |
Largest and most diverse fungal phylum. Characterized by an ascus. |
|
|
|
Ascus (fungi) |
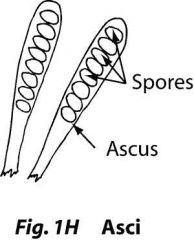
Saclike structure with produces ascospores via MEIOSIS. |
|
|
|
Saccharomyces cerevisae (fungi) |
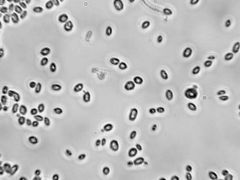
Unicellular yeasts, live in moist places, absorb nutrients from surroundings. Needed in bread making. |
Baker's and Brewer's yeast. |
|
|
Buds (fungi) |
Protrusions on cells; formed asexually, break loose and become new yeast cells. Yeast cells are haploid that has a short diploid stage and rarely conjugated. |
|
|
|
Penicillin (fungi) |
First antibiotic. |
|
|
|
Conidiophores (fungi) |

Specialized reproductive hyphae that have large objects called conidiospores, also called conidia. Resistant haploid cells with huge numbers. Easily dispersed. |
|
|
|
Ascomycota sexual phase (fungi) |
Occurs in cup shaped cluster of hyphae. On the cups are small round chambers called ascocarps form. Asci form in ascocarps. Two haploid nuclei fuse and go through MEIOSIS and CELL DIVISION to form 8 haploid ascospores in one ascus. |
|
|
|
Asci (fungi) |
Contains ascospores. |
|
|
|
Basidiomycota (fungi) |
Club fungi, has large and noticeable species, many edible mushrooms. Economically important. Can cause damage to agriculture and TREES. |
|
|
|
Mushroom (fungi) |
Fruiting structure that forms when conditions become favorable for reproduction. Biomass mostly underground in form of a diffuse mycelium with millions of absorptive hyphae. |
Portion we eat. |
|
|
Basidiomycete hyphae development (fungi) |
Develop from minute haploid spores. Hyphae grow, branch, and extend through soil via CELL DIVISION. |
|
|
|
Basidiomycete sexual reproduction (fungi) |
Two hyphae of opposite mating types MEET, they can form a protoplasnic bridge to exchange nuclei. Nucleus of each hypha divides by MITOSIS and one of two nuclei made will go across bridge. Each hypha can end up with two haploid nuclei that do not fuse. |
|
|
|
Dikaryon (fungi) |
When two nuclei do not fuse but live as a double nuclear cell. Dikaryon continues to divide but both nuclei must divide at the same time to stay as a dikaryon. This causes growth of absorptive portion of fungus and hyphae can grow upward and break through ground as a mushroom. |
|
|
|
Basidiocarp (fungi) |
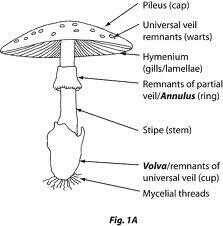
Fruiting body of a fleshy fungus. |
|
|
|
Stipe (fungi) |
Stalk like structure. |
|
|
|
Pileus (fungi) |
Fleshy cap, often umbrella shaped. |
|
|
|
Basidiocarp development part 1 (fungi) |
Begins as small round mass of hyphae called a button. Button is closed and covering underside of button is a thin tissue called a veil. Hyphae in button grow fast and pileus begins to form. |
|
|
|
Basidiocarp development part 2 (fungi) |
Thin veil is torn free from pileus and remains around the stipe as a ring of tissue called the annulus if placed high on stipe or volva if placed low. Tearing the veil reveals thousands of gills which are site of spore formation. On each gill are microscopic basidia. Each basidium starts as a dikaryon however haploid nuclei fuses to form diploid zygote which undergoes MEIOSIS to form 4 haploid nuclei in each basidium. Each nuclei ends up in a small pouch that become haploid basidiospores. Life cycle ends with basidiospore release. |
|
|
|
Gill (fungi) |
Site of spore formations, contains basidia, color+arrangement important for taxonomy. |
|
|
|
Lichens (fungi) |
"Kind" of living thing, mutualistic partnership with unicellular green algae and fungi. Algae provides food via photosynthesis, fungus provides framework that shelters algae. Lichens are extremely tolerant and can survive on bare rocks. |
Fungal partner may only be Ascomycete or Basidiomycete |
|
|
Crustose Lichen (fungi) |

Form a crust-like coating over solid surfaces. |
|
|
|
Foliose Lichen (fungi) |

Leaf-like, flattened growth form, adhering closely to substrate. |
|
|
|
Fruticose Lichen (fungi) |

Erect or pendulous, hanging, appearing like a small bush |
|
|
|
Rhizopus nigricans conjugation (fungi slides) |
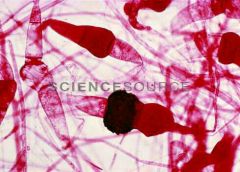
|
|
|
|
Saccharomyces Methylene Blue smear (fungi slides) |
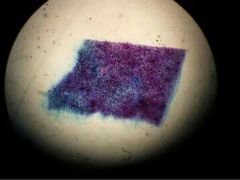
|
|
|
|
Peziza apothecium (fungi slides) |
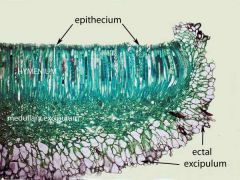
|
|
|
|
Claviceps purpurea mature stroma perithecia (fungi slides) |
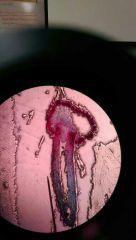
|
|
|
|
Boletus c/s (fungi slides) |
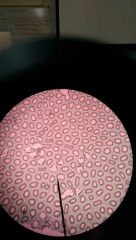
|
|
|
|
Penicillium mycelium condiophpres (fungi slides) |
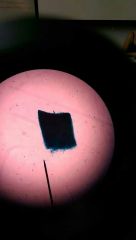
|
|
|
|
Coprinus mushrooms (fungi slides) |
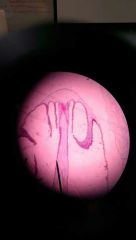
|
|
|
|
Lichen teased (fungi slides) |
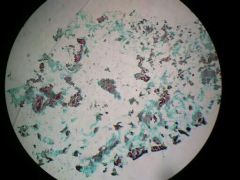
|
|
|
|
Lichen Ascomycete (fungi slides) |
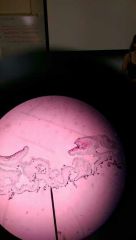
|
|

