![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
112 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which biogeochemical cycle does not have an atmospheric component?
|
phosphorous
|
|
|
What are the nonliving aspects of an ecosystem called?
|
abiotic factors
|
|
|
Which type of macromolecule stores genetic information?
|
nucleotides
|
|
|
What structure do all cells have?
|
cell membrane
|
|
|
Which organelle is called the “powerhouse of the cell”?
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
The process of the plasma membrane pumping excess sodium out of a cell into an environment where there is a lower concentration of sodium is called?
|
active transport
|
|
|
What polymer makes proteins?
|
amino acids
|
|
|
Which chemical do all organic compounds contain?
|
carbon
|
|
|
What are organisms at the top of an ecological pyramid are called?
|
apex predators
|
|
|
Which process increases genetic diversity within a population?
|
sexual reproduction
|
|
|
If a cell has 20 chromosomes, how many chromosomes do the daughter cells have mitosis?
|
20
|
|
|
What is the first phase of mitosis called?
|
prophase
|
|
|
What is the role of the spindle fibers in mitosis?
|
separate/ pull apart chromosomes
|
|
|
What ability have cancer cells lost?
|
to control cell growth
|
|
|
What is it called when cells specialize during development?
|
cell differentiation
|
|
|
Which type of organism does cancer affect?
|
all multicellular organisms
|
|
|
What is an advantage of having a cell’s DNA bundled into separate chromosomes?
|
each daughter cell will get the same number of genes
|
|
|
What must a cell do first to divide successfully?
|
duplicate its genetic information
|
|
|
What is the role of external regulatory proteins in the cell cycle?
|
direct cells to speed up or slow down the cell cycle
|
|
|
What are the problems that cells face if they grow too large?
|
can't retain enough nutrients, expelling waste, more demands the cell places on DNA
|
|
|
What can be said about the genetic information of two chromatids of a chromosome?
|
each get one new copy of genetic information. game genetic info (DNA)
|
|
|
What does the process of mitosis ensures equal distribution of?
|
chromosomes
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of living organisms?
|
movement, reproducing, responds to the environment, growth and development
|
|
|
How are sister chromatids attached to each other?
|
at the centromere
|
|
|
What are the ratios of offspring when hybrid tall pea plants are crossed?
|
50 heterozygous tall, 25 homozygous tall, 25 homozygous short
|
|
|
What is the outward appearance of a genetic trait called?
|
phenotype
|
|
|
How is the inheritance of two gene traits that are unrelated explained?
|
independent assortment
|
|
|
How is the inheritance of two gene traits that are related explained?
|
gene linkage
|
|
|
How many chromosomes are found in a sperm cell in comparison to a body cell?
|
half
|
|
|
When does crossing over occur in the cell cycle?
|
when homologous chromosomes line up in pairs
|
|
|
How do you get a 9:3:3:1 genetic inheritance ratio?
|
dihybrid cross
|
|
|
Why did Mendel remove the male parts of the pea plants he was crossing?
|
so that the plant wouldn't asexually reproduce
|
|
|
Roan cattle, which have a combination of red and white hairs, are an example of
|
___codominant alleles_____ inheritance.
|
|
|
What type of inheritance is characterized by two different colors producing a third color?
|
incomplete dominance
|
|
|
What is the ratio of offspring expected in a heterozygous incomplete dominant cross?
|
25:50:25
|
|
|
Science differs from other disciplines because science relies on
|
______testing explanations_______________.
|
|
|
What is a theory?
|
A system of ideas intended to explain something
|
|
|
Which characteristic of living things is explained by migration?
|
responding to the changes of an environment
|
|
|
The variable that is deliberately changed in an experiment is called the
|
independent variable
|
|
|
The three particles of an atom are
|
Protons, Neutrons, Electrons.
|
|
|
The pH of stomach acid is
|
1.5, below 7
|
|
|
What does a catalyst do?
|
speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction
|
|
|
What are the two types of carbohydrates?
|
simple and complex
|
|
|
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
|
DNA and RNA
|
|
|
Enzymes that are biological catalysts are
|
proteins
|
|
|
The initial lens on a microscope used to locate the specimen is the
|
scanning objective lens
|
|
|
The lowest level of environmental complexity that includes living and nonliving factors is the
|
ecosystem
|
|
|
How do most primary producers make their own food?
|
with energy from the sun/ biochemical energy; light energy, carbs
|
|
|
Human burning of fossil fuels moves carbon through the carbon cycle includes which other processes?
|
Biological, geological, physical/chemical
|
|
|
The interconnected feeding relationships in an ecosystem make up a food
|
web/chain
|
|
|
What is the total amount of living tissue within a trophic level called?
|
biomass
|
|
|
Know the terms: carnivore, consumer, autotroph, herbivore, producer and decomposer
|
Carnivore- organism obtaining energy by eating animals./ Herbivore- organism obtaining energy by eating plants./ Decomposer- organism that breaks down and obtains energy from dead organic matter./ Consumer- organism relying on other organisms for it's energy/ Autotroph/producer- organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds.
|
|
|
How are the movements of energy and nutrients through living systems different?
|
nutrients recycle and energy has one flow
|
|
|
Why are most food chains only 4-5 steps long?
|
Only a small portion of the energy transferred in a trophic level is stored in the bodies of organisms in the next level
|
|
|
What are some abiotic factors?
|
water, sunlight, wind, rocks, dirt, etc.
|
|
|
How is energy transferred within the biological community?
|
energy is transferred in trophic levels
|
|
|
Organisms that break down and feed on dead organisms are called?
|
decomposers
|
|
|
What is the sequence of energy flow through a food chain?
|
Primary Producers > Various Consumers One way flow.
|
|
|
What is an organism’s niche?
|
full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way which it uses the conditions
|
|
|
What is a symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is harmed?
|
parasitism
|
|
|
A scientific hypothesis can be tested
|
by during experiments or observations
|
|
|
What is the difference between primary and secondary succession?
|
Primal secession begins on newly exposed surfaces while secondary succession begins on soil.
|
|
|
Orchids growing high on trees to get sunlight for photosynthesis are an example of?
|
Commensalism
|
|
|
Freshwater ecosystems that purify water by filtering pollutants and prevent flooding are
|
wetlands
|
|
|
The first species to repopulate an area affected by volcanic eruption is called
|
pioneer species
|
|
|
What are temperate grasslands in the called?
|
prairies
|
|
|
The arctic is the polar bear’s
|
_______habitat__________.
|
|
|
What is the main function of a vacuole?
|
storage
|
|
|
What is the role of ribosomes?
|
Synthesize proteins.
|
|
|
What are the parts of the cell theory?
|
1: All living things are made up of cells, 2: All living things arise from preexisting cells by division, 3: The cell is the fundamental unit of life.
|
|
|
What is diffusion?
|
Movement of materials of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
|
|
|
During diffusion, if the concentration on both sides of the membrane is the same, the molecules will?
|
Continue to move across the membrane in both directions.
|
|
|
How does diffusion differ from active cell transport
|
Active transport requires cell energy while diffusion does not.
|
|
|
Ridding the cell of materials by discharging the materials in vesicles is called?
|
exocytosis
|
|
|
Organelles that break down lipids, carbohydrates and proteins into small molecules is done by?
|
lysosomes
|
|
|
What are cell membranes made of?
|
lipid bilayer
|
|
|
The movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane is known as
|
osmosis
|
|
|
What is tissue composed of?
|
similar cells
|
|
|
Which cell structures are sometimes found attached to the endoplasmic reticulum?
|
ribosomes
|
|
|
Who first saw chambers in cork?
|
robert hooke
|
|
|
What is the sequence of protein synthesis in a cell?
|
1: Ribosomes 2: ER 3: Golgi Apparatus
|
|
|
Which organelle converts the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that are convenient for the cells to use?
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
Unlike the cell membrane, the cell’s wall is
|
rigid
|
|
|
An animal cell that is surrounded by fresh water will burst because the osmotic pressure causes
|
water to move in the cell
|
|
|
Photosynthesis is to chloroplast as respiration is to?
|
Mitochondria.
|
|
|
Where in the chloroplast is chlorophyll found?
|
thylakoid membrane
|
|
|
What stores information in a cell?
|
DNA
|
|
|
How are carnivores and herbivores alike?
|
both obtain energy by consuming other organisms
|
|
|
Know the reaction of photosynthesis.
|
coming in carbon dioxide and water going out oxygen and glucose
|
|
|
What are characteristics of the nucleus?
|
decides what material comes in and out, stores coded instructions, ribosome assembly takes place.
|
|
|
During a controlled experiment, a scientist isolates and tests
|
______a single variable__________
|
|
|
How do organisms get the energy they need?
|
by breaking down food molecules for energy
|
|
|
What is the symbiotic relationship in which one organism benefits and the other is not affected?
|
commensalism
|
|
|
Why are electron carriers needed for transporting electrons from one part of the chloroplast to another?
|
high energy electrons are highly reactive
|
|
|
What is the role of NADP+ in photosynthesis?
|
electron carrier molecule
|
|
|
Several species of warblers can live in the same spruce tree only because
|
they occupy different niches within the tree
|
|
|
Information gathered from observing a plant grow 3 cm over a two week period is called
|
data
|
|
|
Where do light-dependent reactions take place?
|
thylakoid membrane
|
|
|
Colors seen in images made from electron microscopes are
|
__added to make certain structures easier to see___________
|
|
|
Why is cellular respiration called an aerobic process?
|
it requires oxygen
|
|
|
Know the order of ecosystem taxonomy.
|
individual species, population, community, ecosystem, biome.
|
|
|
Living things adjust to a stimulus by a reaction called
|
_____response_____________
|
|
|
How do living things change during their lives?
|
by growing and developing
|
|
|
Why do leaves appear green?
|
chlorophyll reflects green color
|
|
|
What helps a dog maintain homeostasis?
|
panting
|
|
|
What should a scientist conclude about data that is inconsistent with current scientific understanding?
|
further investigation to find out why
|
|
|
Why do scientists repeat investigations several times?
|
consistent data
|
|
|
What are the steps used by scientists for gathering information and testing hypotheses called?
|
scientific method
|
|
|
What is a decomposer?
|
an organism, especially a soil bacterium, fungus, or invertebrate, that decomposes organic material
|
|
|
How do nutrients move through an ecosystem?
|
using the biogeochemical cycles
|
|
|
Be able to read a Punnett Square
|

|
|
|
Know how to determine the possible gamete combinations from a dihybrid gene cross. |
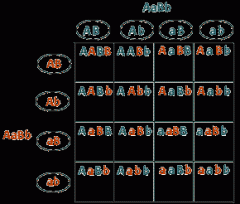
|

