![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
64 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Age of the Earth |
4.5 billion years old |
|
|
first life on earth |
3.5 billion years ago |
|
|
oldest definite eukaryotic microfossil |
1.5 billion years ago |
|
|
first multicellular organism |
900 million years ago |
|
|
first dinosaurs |
200 million years ago |
|
|
first homo sapiens |
160,000 years ago |
|
|
compound microscope |
uses light and glass lenses to see small structures. different colors are visible (max magnification=2000x) |
|
|
electron microscope |
uses a beam of electrons instead of light to see small structures. produces black and white images only |
|
|
transmission electron microscopes |
used to view the inside of objects (max magnification= 1,000,000x) |
|
|
scanning electron microscope |
used to view the surface of objects (max magnification= 100,000x) |
|
|
inner membrane |
1 membrane that makes up the nuclear envelope |
|
|
outer membrane (connected to the ER) |
1 membrane that makes up the nuclear envelope |
|
|
Nuclear pores |
the nuclear envelope contains many of these pores |
|
|
nuclear pore |
permits certain molecules to pass through the nuclear envelope |
|
|
transport vesicles |
bud from ER and delivers products to the Golgi (cis face) |
|
|
secretory vesicles |
bud from Golgi and fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell (transface) |
|
|
lysosomes |
bud from the Golgi; contain powerful enzymes used to digest imported substances or worn-out organelles |
|
|
food vesicles |
bud from plasma membrane; used to take substances into the cell; fuse with lysosomes for digestion of the imported substances |
|
|
peroxisomes |
bud from themselves by growing and dividing; break down fatty acids and amino acids, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is produced by this breakdown and and is toxic to cells. peroxide in liver cells break down alcohol and other toxins |
|
|
fission |
breaking apart |
|
|
fusion |
coming together |
|
|
mitochondrion |
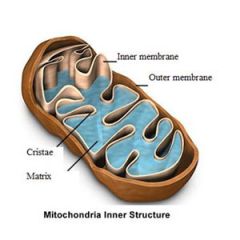
|
|
|
chloroplast cell |
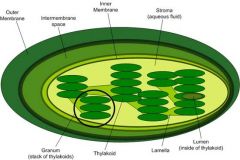
|
|
|
Plant Cell |
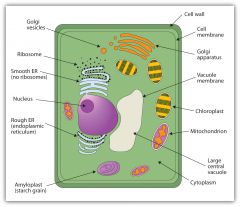
|
|
|
Animal Cell |
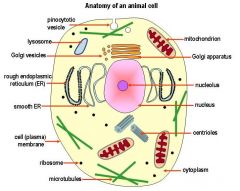
|
|
|
Phosophlipid
|

|
|
|
phosophlipid bi-layer |
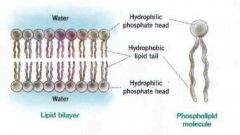
|
|
|
plasma membrane
|
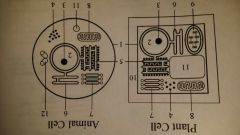
Plant Cell, Animal Cell, Bacteria
controls movement of substances into and out of the cell |
|
|
nucleus (nuclei)
|
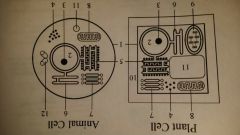
Plant Cell, Animal Cell
isolates and stores DNA (genetic material) |
|
|
nucleolus (nucleoli)
|
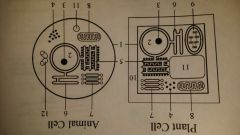
Plant Cell, Animal Cell
Makes ribosomes |
|
|
ribosomes
|
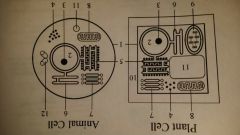
Plant, Animal, Bacteria
makes protein |
|
|
rough endoplasmic reticulum
|
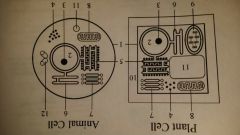
Plant, Animal cell
has many ribosomes temporarly attached to the outer surface. provides surface for making secretion proteins. i.e of secretion proteins: enzymes. hormones, and anitbodies |
|
|
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
|
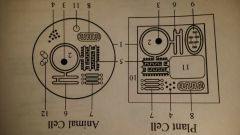
plant, animal cell
has no attachment ribosomes. makes and transports lipids and carbohydrates |
|
|
golgi apparatus (enzymes, antibodies, hormone)
|
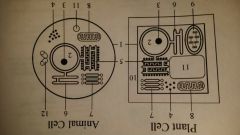
plant, Animal cell
discover by Camillo Golgi. a stack of separate compartments. products recieved from ER are processed and packaged for delivery. each sac in the stack contains different enzymes |
|
|
mitochondrion (mitochondria)
|
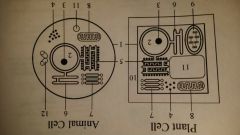
Plant, Animal Cell
power house of the cell. produces ATP from energy stored in food. ATP powers many cell processes. |
|
|
chloroplast (green)
|
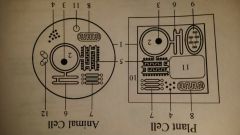
Plant Cell
photosynthesis |
|
|
cell wall
|
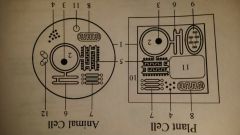
Plant, Bacteria cell
gives structual support and keeps cells from bursting under low salt condition |
|
|
vacuole
|
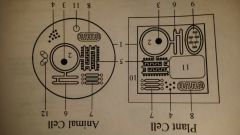
Plant, Animal Cell
the large central vacuole in plant cells pushes all organelles close to the cell surface. this improves membrane transport efficiency and gives structual support to the cell. other vacuoles can be used for storage (fat vacuole_ water disposal (contractile vacuole) and digestion (food vacuole) |
|
|
centriole
|
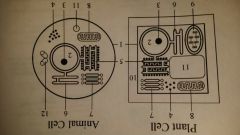
Animal Cell
unknown |
|
|
cytoskeleton
|
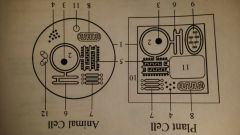
Plant, Animal Cell
a network of protein fibers found in the cytoplasm. used to reinforce, organize, and move cell structures. can be used for cell movement (cell crawling) |
|
|
cilia |
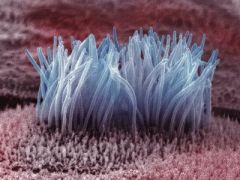
Plant, Animal Cell cell movement or moving liquid over the cell surface |
|
|
flagella (flagellum)
|
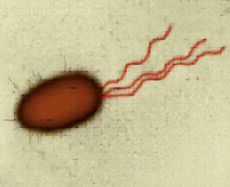
Plant, Animal, Bacteria Cells
cell movement. are fewer in number than cilia and generally longer |
|
|
capsule |
Bacteria allows bacteria to attach to surface and protects then from host defenses |
|
|
nucleiod |
Bacteria Cell an area where the DNA is concentrated inside a prokaryotic cell |
|
|
Factors of passage through the plasma membrane |
size, polarity (lipid solubility), electrical charge |
|
|
what helps passage through the plasma membrane |
|
|
|
what hinders passage through the plasma membrane |
|
|
|
transport proteins |
carrier proteins and channel proteins |
|
|
carrier proteins |
|
|
|
channel proteins |
serve as tunnels for certain substances to cross the membrane |
|
|
gated channels
|
a certain channel protein has gates that open and close to permit or block the passage of specific ions
|
|
|
aquaporins |
specialized channel protines that allow water molecules to cross a cell membrane |
|
|
exocytosis |
(out of cell) vesicles in the cytoplasma membrane fuse with it and have their contents released to the cells surroundings. the vesicles used in this process are called secretory vesicles |
|
|
endocytosis |
(into the cell) a region of the plasma membrane encloses particles at or near the cell surface and then pinches off to form a vesicles that moves into the cytoplasm |
|
|
phagocytosis |
type of endocytosis cell eating transports solids into a cell. food vesicles are formed by this process |
|
|
pinocytosis
|
type of endocytosis
cell drinking transports liquids into a cell |
|
|
receptor- mediated endocytosis |
use receptors found on the membrane surface to bind specific substances and transport them into the cell |
|
|
sodium potassium pump |
(active transport)
|
|
|
Na+K+ pump step 1 |
three sodium ions bind to the cytoplasmic side of the carrier |
|
|
Na+K+ pump step 2 (phosphorylation) |
ATP adds a phosphate group to the carrier protein. this causes the protein to change shape |
|
|
Na+K+ pump step 3 |
with the new shape the sodium ions now face the cell exterior. the ions dont bind as well to the new shape and they are released to the outside |
|
|
Na+K+ pump step 4 |
the new shape will allow two potassium ions to bind from the outside |
|
|
Na+K+ pump step 5 (dephosphorylation) |
the binding of the potassium ions causes the phosphate group to be released. |
|
|
Na+K+ pump step 6 |
once phosphate group is released the protein returns to it's original shape. |

