![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Tripartite tubular hairs |
stramenophiles |
|
|
2 unequal flagella |
heterokonts (labryinthulids, thraustochytrids) (most bacteriovore flagellates) |
|
|
cell surface underlain by abutting sacs |
alveolata |
|
|
single posterior flagellum |
opistokonts |
|
|
freshwater |
crptomonads |
|
|
ciliates |
microplankton important phytoplankton/flagellate grazer
|
|
|
important ciliates |
loricate, tintinnids (condom) aloricate mesodoinium rubrum (phototroph) |
|
|
dinoflagellates |
microplankton, diverse lifestyles |
|
|
Sacrodines 1 |
marine amoeba (radiolaria and acantharia) important for silica shells and strontium sulfate
everywhere |
|
|
holoplankton |
whole life suspended in water (acantharia) |
|
|
Foraminifera |
top 1000m calcium shell ooze (pink sand) very susceptible to acidification |
|
|
Choanoflagellates |
silicate collar, chitin shell, important bacteriovores |
|
|
sponge |
stacks of choanaflagellates first multicellularity in animals |
|
|
Microbial abundance |
Viruses 10^7/8 Bacteria 10^5/6 Hnan 10^3 Ciliates 10^0
|
|
|
to develop multicellularity |
need permeable membrane and thus inner (Cyto)skeleton
perhaps due to new toxin (oxygen from cyanobacteria) in environment
probably happened only once |
|
|
Bacterivory |
even large protests eat them, though dilute control bacteria pop as much as viruses |
|
|
cytostome |
mouth, necessary for phagocytosis
protists effectively digest by controlling pH |
|
|
endocytosis |
invagination of plasma membrane, molecules absorbed by active transport or active diffusion |
|
|
phago vs pinocytosis |
solid food vs liquid |
|
|
filter feeding mostly |
producing currents to bring particles to cytostome using flagella and cilia |
|
|
I max |
feeding rate much higher in smaller organisms; more per weight |
|
|
size structures |
trophic levels flagellates eating bacteria largest consumption |
|
|
dilution response technique |
assuming saturation of nutrients, place increasing amounts of sample ins ams amounts of blank water.
water dilutes sample; nutrients still saturate but predators dispersed. Growth rate greater can be measured
less manipulation then applying tracers but can't use everywhere |
|
|
filter out all but bacteria and HNAN |
oscillate with smaller troughs until bacteria and flagellate balanced |
|
|
Food Chain |
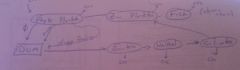
|
|
|
trophic cascade |
remove predators of prokaryotes and competition removed they grow
but remove predators of predators of prokaryotes and prokaryotes shirnk
remove predators of predators of predators of prokaryotes, population of pro ^ |
|
|
prokaryotes dominant consumers of |
DOM |
|
|
prokaryote respiration |
(co2 production) primary biogeochemical loss term for oceanic DOC |
|
|
most bacteria are |
free living |
|
|
all known ecological interacts |
occur at <5 uM(primary production, viral infection, herbivory...) |
|
|
bacteria have limited potential for |
remineralization (combined with grazers yield more inorganic P and N) |
|
|
protists including |
bacterivores are important food mesozooplankton (copepods...appendicularians) |

