![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
16 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
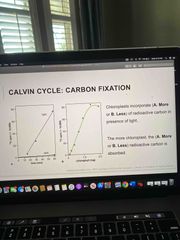
Front (Term)
|
A. More A. More |
|
|
Antenna complex |
Several hundred chlorophyll a molecules Collects light energy to funnel it to... |
|
|
Reaction center |
2 chlorophyll a molecules Converts light energy to chemical energy |
|
|
What pigment do you expect to find at the reaction center |
Chlorophyll A |
|
|
Where does the photosystems happen |
Thylakoids membrane |
|
|
Photo system II |
Functions only in concert with PS I Passes high energy electron to the electron transport chain Peak absorbance 680nm |
|
|
Photo system I |
Can function alone but usually works with PS II catalyze the generation of NADPH Peak absorbance 780nm |
|
|
What happens to the thylakoids space (etc) |
H GOES INTO T SPACE BECAUSE ACIDIC ph goes down |
|
|
What does the atp pump work |
Due to gradient of high concentration H in t space 3 H binds and the rotor turns |
|
|
Where is atp synthesis |
Stroma |
|
|
Non cyclic transport |
Electron is carried to the enzyme ferredoxin NADP reductase (FNR) that reduces nadp to nadph |
|
|
Cyclic electron transport |
Electron are transferred to a proton pump, cytochrome and the. Returned to p700 |
|
|
Which wavelengths of light are most responsible for photosynthesis |
Blue and red |
|
|
Where is chlorophyll located in the chloroplast which |
Thylakoid |
|
|
Which of the following pigments forms the center of the reaction center |
Chlorophyll A |
|
|
Which is not a way in which the electron transport of respiration and photosynthesis are similar |
Both require water |

