![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
D. Cell Theory |
The fundamental principle of Biology. IT states that all living things organisms are composed of cells, and all living cells arise from pre-existing cells through cell division |
|
|
D. Prokaryotic Cell |
A unicellular organism that lacks a membrane bound nucleus, mitochondria, and other membrane bound organelles |
|
|
D. Eukaryotic Cells |
An organism whose cells contain a nucleus surrounded by a membrane and whose DNA is bound together by proteins into chromosomes |
|
|
What are two other names for Plasma Membrane? |
Cell Membrane and Plasmalemma |
|
|
All cells are surrounded by a _________ __________. Structure of the Plasma Membrane? |
All cells are surrounded by a plasma membrane. |
|
|
What is the structure of a plasma membrane? |
Phospholipid bilayer and in which are embedded protein and cholesterol molecules |
|
|
Structure of - Endoplasmic Reticulum |
a network of interconnecting flattened sacs, tubes and channels, and is continuous with the nuclear envelope |
|
|
Rough E.R. and smooth E.R. are ___________ with eachother. |
continuous |
|
|
Structure of the Nucleus |
this is the repository of information in the form of DNA and is surrounded by the nuclear envelope |
|
|
Mitochondria - structure and function |
S - consists of an outer and inner membrane, with folds called cristae F - uses enzymes to help make ATP for cellular respiration |
|
|
Structure and Function of - Chloroplasts |
S - enclosed by an inner and outer membrane F - The contain chlorophyll; The stroma and thylakoid membranes play important roles in photosynthesis |
|
|
S and F - Golgi apparatus |
S - flattened membranous sacs F - modifies and packages proteins for secretion or for destinations in the cell. |
|
|
Define cyclosis in plant cells, and why it occurs |
cyclosis is a directed steaming of the cytosol inside the cell. It occurs to transport materials and organelles around the cell. |
|
|
Define Plasmolysis |
the shrinking of the cytoplasm away from the cell wall due to exosmosis |
|
|
List 4 ways that plant cells and animals cells differ |
1. plant cell has cell wall, animal cell does not 2. plant cell has large vacuole, animal cell has small or no vacuole 3. plant cell has chloroplasts, animal cell does not 4. Animal cells have a flagella, plant cells do not, unless they are gametes |
|
|
All cells are bounded by a selectively ____________ ____________ _____________ that regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell. |
Permeable Plasma Membrane |
|
|
Name 3 things that biological membranes are composed of |
phospholipid bilayers proteins carbohydrates |
|
|
Carbohydrates attach to ________ or _________ molecules on the outside surface of the membrane |
lipid or protein |
|
|
The colour of the Beet root is due to __________ ___________ , ____________(red-violet) and _______________(yellow-orange), which are dissolved in the cell sap of the _______________. |
The colour of the Beet root is due to betalain pigments , betacynin(red-violet) and betaxanthin(yellow-orange), which are dissolved in the cell sap of the vacuoles. |
|
|
What happens to a beet cell when it is put in hot water? |
the membrane and tonoplast that hold in the colour pigments pass the plasma membrane of the cell
|
|
|
What device can quantify the relative amount of betacyanin pigments that leak from beet cells? |
A spectrophotometer |
|
|
The amount of light absorbed from the beet pigment is proportional to the ________________ of pigments that have been leaked out of the cell. |
Concentration |
|
|
When a beet is previously frozen, why might it leak more pigment than a room temperature beet? |
The frozen beet cells crystallize and puncture the cell membrane |
|
|
What is the difference between discrete and continuous data? |
Discrete Data have finite values. Continuous data technically have an infinite number of steps, which form a continuum. |
|
|
Plants occur both in aquatic and terrestrial environments. Most of these plants, especially those that live on land, are __________ plants |
Vascular |
|
|
Name 3 types of vascular plants |
Ferns Conifers Flowering plants |
|
|
Most of the non-vascular plants are found in ___________ and __________ environments. |
aquatic and moist |
|
|
Varied habitats for plants provide challenges such that special adaptations for ____________, _____________ and __________ absorption, and ________________ serve the plants in their survival. |
Varied habitats for plants provide challenges such that special adaptations for attachment, nutrient and water absorption, and reproduction serve the plants in their survival. |
|
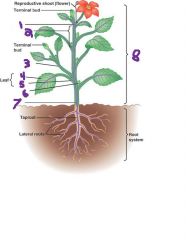
|
1. node 2. internode 3. vegetative shoot 4. blade 5. petiole 6. axillary bud 7. stem 8. shoot system |
|
|
What are the functions of the following? 1. Apical Bud 2. Node 3. internode 4. vegetative shoot 5. blade 6. petiole 7. axillary bud |
1. Develops leaves 2. leaf attachment 3. stem segments between nodes 4. makes leaves, not flowers 5. surface area for photosynthesis 6. joins the leaf to the stem at the node 7. forms lateral shoots(branches) |
|
|
Name the 3 Tissue systems of plants |
Dermal, Vascular, and Ground |
|
|
What are the cell types in: 1. Dermal tissues 2. Vascular tissues 3. Ground tissues |
1. epidermal cells 2. xylem and phloem 3. parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma |
|
|
The arrangement of plant parts and distribution of tissue systems is different in the two subgroups of __________________. The ___________ and the _____________. |
angiosperms, monocots, eudicots |
|
|
The plant body composed of primary tissue develops from a seed via growth regions, called __________________. |
meristems |
|
|
What are non-woody plants called? |
herbaceous |
|
|
The dermal tissue system is protected by what? |
cuticle |
|
|
Function of - Roots |
anchor to substrate and absorption of water and solutes |
|
|
Leaves are generally flat, exposing a large surface area to light, and ideally adapted for photosynthesis. Both surfaces are lines with flat ___________ cells and perforated with a ___________ that allows for __________ exchange and ____________ _________ ______. |
epidermal evaporation water loss |
|
|
(Leaves cont'd) Between the epidermal layers is the ___________ tissue made up of _____________ cells and generally called the _______________. |
Ground
parenchyma mesophyll |
|
|
1. Plants must have _________ to survive 2. plants lose a vast amount of ______ through _______ ______ _______. 3.plants must conserve ______ so they will not _____ and die. 4. plants must get most of this water from the ______ via absorption by the _________. 5. the water has to be transported from the ______ to the ________. |
1. water 2.water, evaporation water loss 3. water, wilt 4. soil, roots 5. roots, leaves |
|
|
Transport in plants involves _______ different levels. |
three |
|
|
Explain the three different levels of transport in plants. |
1. the uptake and release of solutes by individual cells. 2. short-distance transport of substances from cell to cell. 3. long distance transport of sap within xylem and phleom in the whole plant |
|
|
Physiological processes that take place in plants, such as photosynthesis and respiration, require ___________ either as a __________ or a ____________. |
water, reactant, medium |
|
|
What pushes water upward against gravity in root pressure? |
osmotic uptake |
|
|
____________ cells that surround the stomatal pore continuously regulate ____________________ and _____________ . |
Guard, photosynthesis, transpiration |
|
|
Function of the Stomata |
Allow for the passage of gases in leaves Allow escape of water vapour in leaves |
|
|
Name 4 factors that influence stomatal opening |
1. light 2. CO2 concentration 3.Water balance 4. circadian rhythm |
|
|
The majority of living organisms are dependent on the process of ________________ to transform the ____________ ____________ of the sun into usable _____________ ____________. |
photosynthesis radiant energy chemical energy |
|
|
Organisms that undergo photosynthesis are called _____________ |
phototrophs |
|
|
What is the general formula for photosynthesis? |
6CO2 + 6H20 + Light >< C6H1206 + 602 |
|
|
The photosynthetic pigments are responsible absorbing the light that is used in photosynthesis. The major photosynthetic pigments are called the _____________. |
Chlorophyll |
|
|
How does the intensity of light affect the rate of photosynthesis? |
Increase in light intensity = increase in photosynthesis rate |
|
|
Osmoregulatory processes control the ___________ and _______ balances in organisms living in _______________, ________________, or _______________ environments. |
water, salt, hypertonic, hypotonic, terristrial |
|
|
_______________ plays a key role in homeostasis. |
osmoregulation |
|
|
Another function of osmoregulation is keeping the _____________ of ________________ from building up and poisoning the body fluids. |
by-products, metabolism |
|
|
Define 1. isosmotic 2. hypoosmotic 3. hyperosmotic |
1. solutions of equal solute concentrations 2. solution with a lesser concentration of solute 3. solution with the greater concentration of solute |
|
|
Animal cells swell and may _________ if they are in an hypoosmotic environment. |
burst |
|
|
Many marine invertebrates are osmoconformers. Osmoconformers are ___________ with their environment, and do not need to actively change their _____________. |
isosmotic, osmolarity |
|
|
Animals that are not isosmotic with their environment are called ___________________. |
osmoregulators |
|
|
Animals such as the bony fishes which are hypoosmotic to their envirnoment must continuously take in water to balance _____________ _______. |
osmotic loss |
|
|
Excess water in a freshwater paramecium is eliminated out of the body by two ________________ ___________________. |
contractile vacuoles |
|
|
What happens to the rate of contraction in a freshwater paramecium's vacuoles after adding drops of salt water solution to its environment? |
it increases |
|
|
Describe the route blood takes in the mammalian pulmonary circuit starting from the right ventricle and ending in the right ventricle. (11 steps) |
1.contraction of the right ventricle pumps blood into the lungs 2. via the pulmonary arteries 3. flowing through capillary beds in the left and right lungs. It loads O2 and unloads CO2. Oxygen rich blood returns from the lungs via the lumonary veins into 4. the left atrium. Next the oxygen rich blood flows into the 5. left ventricle, which pumps O2 rich blood out to the body tissues through the systemic circuit. Next, blood leaves the left ventricle 6. via the aorta, which conveys blood to arteries leading throughout the body. The first branches leading from the aorta are the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart muscle itself. 7. Then, branches lead to capillary beds in the heads and arms. The aorta then descends into the abdomend |

