![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
TSA |
Trypyic Soy Agar, broth-soy based plate |
|
|
|
EMB |
Eosin Methylene Blue, selectively stains for gram negative bacteria |
|
|
|
MSA |
Manitol Salt Agar, grows hardy bacteria that can survive on salt which is known to kill many living things. |
|
|
|
Alcohols |
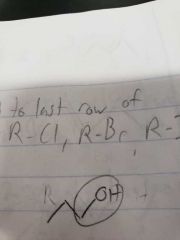
R-OH |
|
|
|
Esthers |

R-O-R |
|
|
|
Aldehydes |
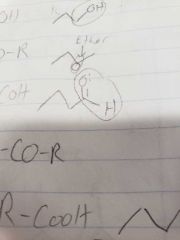
R-COH |
|
|
|
Ketones |
R-CO-R |
|
|
|
Carboxylic Acid |
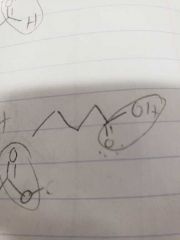
R-COOH |
|
|
|
Esters |

R-COO-R |
|
|
|
Amines |
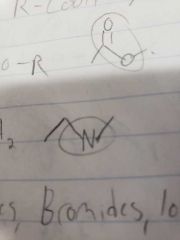
R-NH2 |
|
|
|
Halogen |
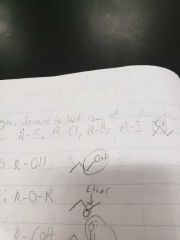
Second to last row of periodic table |
|
|
|
Halogen Naming |
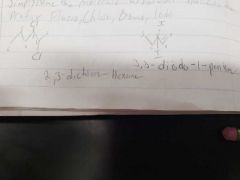
Fluorides, Chlorides, Bromides, Iodides Name the molecule as normal but add the prefix Fluoro, Chloro, Bromo, or Iodo |
|
|
|
Alcohol Naming |
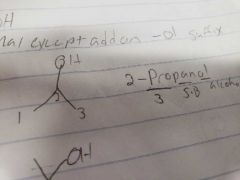
R-OH, Normal except add an -ol suffix |
|
|
|
Esthers |

R-O-R, name the two R groups with -yl endings, end name in -ether |
|
|
|
Aldehydes |
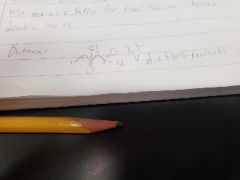
R-COH. A carbon to a double oxygen bond with a hydrogen at the end. Name as normal but add -al as a sufficient. Do not use as suffix for non-carbon based bonds. |
|
|
|
Ketones |
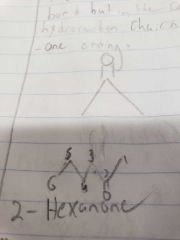
R-CO-R. A carbon to oxygen double bond but in the center of a hydrocarbon. -one ending. |
|
|
|
Carboxylic Acid |

Carbon double bond w/ the same carbon bonded to an OH group. -anoic acid ending. |
|
|
|
Cyclo |
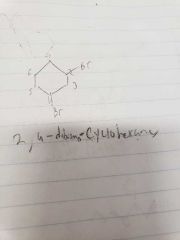
Prefix for the beginning of a ring |
|
|
|
Esters |
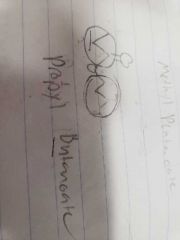
Carbon to oxygen double bond with a carbon to oxygen single bonded to another single bonded carbon. Name by giving short branch -yl suffix and long branch -anote. |
|
|
|
Amines |

Name the R group with -yl endings and add the word amine |
|
|
|
Four Types of Bacteria |

Cocci, Streptococci, Staphylo, Diplo |
|
|
|
Antibiotics |
Kill bacteria. Mention this in that one question you know the one. |
|
|
|
Catalase Test |
A test used to detect the presence of the enzyme catalase in bacteria. Catalase serves to neutralize bacterial effects of hydrogen peroxide. |
|
|
|
Methyl Red |
Metabolic test run used to determine what kind of fermentation pathway used. |
|
|
|
Secondary Messengere |
Small, non-protein based molecules or ions that carry the signal to target organelle. |
|
|
|
cAMP |
Adenozene Mono Phosphate. Acts as secondary messenger. |
|
|
|
Cyclic AMP |

|
|
|
|
Calcium Ions |
Common secondary messenger. |
|
|
|
Protein Phosphorylation Cascade |
A series of proteins called kinase add a phosphate to the next protein in line, activating it and sending the signal to the target. |
|
|
|
Steps to Protein Phosphorylation Cascade |
1. Relay molecule activates inactive protein kinase 1, turning it into active protein kinase 1. 2. Active protein kinase 1 transfers phosphate from its ATP to inactive molecule or protein kinase, activating it. 3. Active protein kinase 2 catalyzes (speeds up) the Phosphorylation of protein kinase 3. 4. Active protein kinase finally phosphorylates a protein that will bring about the cell's response to the signal given off. 5. Enzymes called protein-phosphates catalyze the removal of phosphate groups from the active proteins, making them inactive and available for reuse. |
|
|
|
Enhancers |
Transcription factors that increase the rate of the process |
|
|
|
Inhibitors |
Transcription factors that block transcription |
|
|
|
Hormones |
Induce transcription. Once inside the cell, the hormone attaches to a protein that takes it into thee muscle where transcription can be stimulated. |
|
|
|
Termination of response |
Reversal of ligand binding. Once the signal is degraded or released, the response will end. |
|
|
|
G Protein Signalling |
1. Signalling molecule + inactive g protein bind to a coupled receptor 2. GTP is created, activating the g protein. 3. The receptor moves across the membrane to |
|
|
|
Electronegativity Chart |

|
|

