![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
hypothesis |
A "guess" based on logical inferences and informed, creative imagination |
|
|
experiment |
Results of experiments must be repeatable |
|
|
theory |
A theory may eventually prove to be untrue and need to be revised |
|
|
biology |
The study of the living world |
|
|
homeostasis |
The way organisms keep their internal conditions fairly constant |
|
|
a population |
A group of organisms of the same type that live in the same place |
|
|
ionic bond |
Transferring electrons |
|
|
covalent bond |
Sharing electrons |
|
|
valence electrons |
Electrons available to form bonds |
|
|
water |
most abundant compound in living things |
|
|
solvent |
The liquid in which a solid is dissolved |
|
|
solute |
The solid which is dissolved in a solvent |
|
|
pH |
-pH above 7--basic -pH below 7--acid |
|
|
emmigration |
Moving out of a population |
|
|
immigration |
Moving into a population |
|
|
catalyst |
A substance that speeds up a chemical reaction |
|
|
prokaryotes |
A one-celled organism that does not have a nucleus |
|
|
eukaryotes |
An organism whose cells have nuclei |
|
|
demography |
Scientific study of human populations |
|
|
nucleus |
Contains chromosomes which contain DNA, the genetic material of a cell |
|
|
osmosis |
Diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane |
|
|
diffusion |
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration |
|
|
cell wall |
Only found in plant cells |
|
|
abiotic factor |
Nonliving factor that affects an ecosystem |
|
|
biotic factor |
"Living-thing" influence on organisms within an ecosystem |
|
|
levels of organization in a multicellular organism |
Cell, tissue, organ, organ system |
|
|
isotonic solutions hypertonic solution hypotonic solution |
-the concentration of both solutions is the same -the specified solution is more concentrated than the other -the specified solution is less concentrated than the other |
|
|
autotroph |
Organism that makes its own food (plants) |
|
|
heterotroph |
Organism that obtains its energy from the food it eats |
|
|
ATP (adenosine triphosphate) |
A major chemical compound that cells use to store and release energy |
|
|
ATP/ADP |
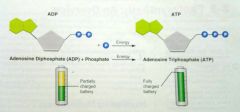
|
|
|
the photosynthesis equation |
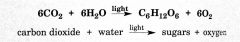
|
|
|
chloroplast |
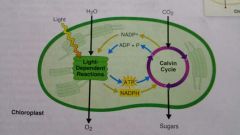
|
|
|
chloroplast |
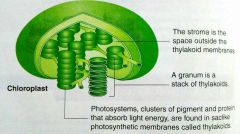
|
|
|
cellular respiration equation |

|
|
|
cellular respiration |
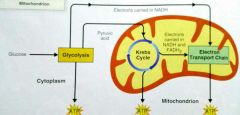
|
|
|
cell cycle |
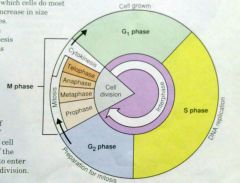
|

