![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
54 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
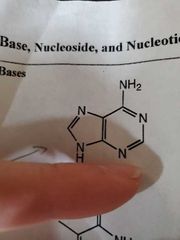
Adenine |
|
|
|
|
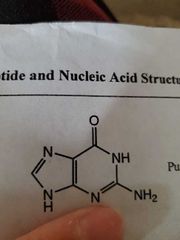
Guanine |
|
|
|
|
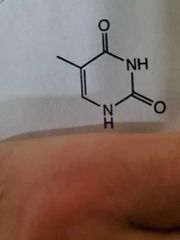
Thymine |
|
|
|
|
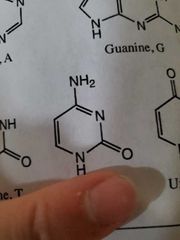
Cytosine |
|
|
|
|
Uricle |
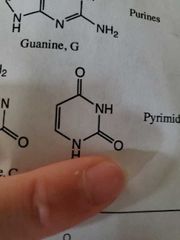
|
|
|
|
Deoxy vs normal |
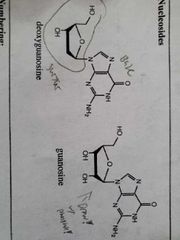
|
|
|
|
Major grove vs minor grove |
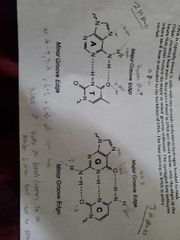
|
|
|
|
Animo acid base structure |

|
|
|
|
Deoxythymidine_3_monophosphate And the 5 version |

|
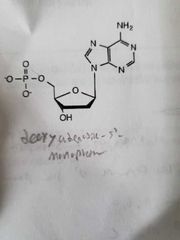
|
|
|
What determinee form of biomolecules -5 things |

|
|
|
|
Electrostatof cling in molecules |

|
|
|
|
Hydrophobic effect and what its driven by |

|
|
|
|
Hydrolisys |

|
|
|
|
Oxidation reduction |

|
|
|
|
What is thermodynamic spontaneity |

|
|
|
|
Wgst spontaneous process drives non spontaneous processes? |

|
|
|
|
Work and heat |

|
|
|
|
1st and 2nd law of thermo Spontaneous reactionsc are ones that |

|
|
|
|
What is entropy |

|
|
|
|
What makes a spontaneous math wise |

|
|
|
|
Whata delta g And equation |

|
|
|
|
Enfo thermic vs exo thermic in h |

|
|
|
|
Pos vs neg delta g |

Pos fo go from a b to a A Neg to lower grade |

|
|
|
Pos and neg H |

Enthalpy Neg = more stable in final state Less energy Bonds made |
|
|
|
Pos and neg delta s |

Pos = final state less ordered Neg = final state more ordered |
|
|
|
Weakest time strongest interaction d |

Strong = covalent Week = London London |
|
|
|
DNA structure Sugar type? What strands? |

|
|
|
|
3 things they stabilise dna molecule |

|
|
|
|
Protein binding is used to regulate.... |

|
|
|
|
Replication Leading, lagging. 5 prime end. |

|
|
|
|
Transcription |

|
|
|
|
Synthesis and trna |

|
|
|
|
Restriction enzymes and strands/overhang What are base pairs . Y or R? |

|

|
|
|
Gel electrophoresis Larger strands? Charge? 2 materials? |

|

|
|
|
Henderson hasselbalch equation |

|
|
|
|
Blood buffers |

|
|
|
|
Buffer system blood and oh blood |

7.35 to 7.45 |
|
|
|
To high and to low ph blood And causes |

|
|
|
|
Amino acid combined |

|
|
|
|
Lower pka equals |

Lower affiliation |
|
|
|
Protien functions |
Enzymes, transporter |
|
|
|
Nuclsix acid |
RNA and dna |
|
|
|
Lipids |

|
|
|
|
Carbs 3 |

|
|
|
|
Why is one bond stronger than another ? Equations! |

|
|
|
|
Dif between ph and pka |

|
|
|
|
PH calculation Poh cal |
Ph = -log[h+] Poh =log[oh] Ph + poh = 14 |
|
|
|
RNA vs dna sugar |

|
|
|
|
DNA melting curve |

|
|
|
|
What does dna melting mean? |
Strand separation of the dna similar to protein denaturing in that only the imfs are affected. No covalent bonds are broken. |
|
|
|
Melting dna mean |

|
|
|
|
R = |
Purine (AG) |
|
|
|
Y = |
Prymadine (TC) |
|
|
|
Give me seq to copy strand |

|
|

