![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Why are cells small |
Surface area increases in the cell while the total volume remains constant. The nutritional need of the cell is dictated by the volume and the satisfaction of those needs is dictated by surface area |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Contains the genome which contains most but not all DNA * has double membrane |
|
|
|
Nuclear envelope |
Contains pore complexes that allows passage of materials through the envelope to the nucleus |
|
|
|
Nuclear lamina |
Protein scaffolds that give the nucleus its shape |
|
|
|
Endomembrane system |
The system of membranes inside the cell |
|
|
|
Parts of the endomembrane system |
1)endoplasmic reticulum 2) rough endoplasmic reticulum 3)smooth endoplasmic reticulum 4)Golgi apparatus 5) lysosomes 6) cytosol |
|
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Flattened membrane sacs that ship and receive for the cell |
|
|
|
Lysosomes |
Vesicles that contain digestive enzymes |
|
|
|
Cytosol |
The region of the cell inside the plasma membrane but outside of the organelles |
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton |
Contained in the cytosol. Contains three networks of protein fibers( microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules) that help to give the cell its shape, organize contacts, and control processes. |
|
|
|
Cell Junction |
Holds the cell together |
|
|
|
Three types of cell Junctions |
1) tight junctions- waterproof seals 2) Desmosomes- rivets attach to intermediate filaments 3) Gap Junction- channels that run from one cell to another |
|
|
|
Types of semi-autonomous organelles |
Mitochondria chloroplasts |
|
|
|
What characteristics makes the mitochondria and chloroplast semi-autonomous organelles |
1) they have their own DNA 2) they make their own proteins 3) they divide independently through binary fission |
3 points |
|
|
Endosymbiosis Theory |
The theory that states that an early ancestor of eukaryotic cells engulfed and oxygen using non photosynthetic prokaryotic cell |
|
|
|
Organelles |
The membrane enclosed structures within eukaryotic cells |
|
|
|
Nucleoid |
In a prokaryotic cell DNA is concentrated in this region |
|
|
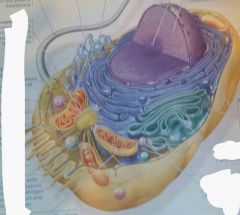
all the parts of an animal cell |
|
|
|
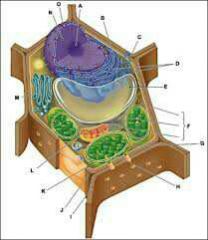
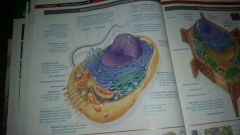
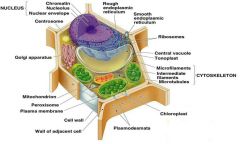
All the parts of a plant cell |
|
|
|
|
Peroxisome |
-organelles with various specialized metabolic functions that produces hydrogen peroxide as a by-product and then converts it to water *in plant and animal |
|
|
|
Centrosome |
Region where the cells microtubules are initiated; it contains a pair of centrioles *animal |
|
|
|
Flagellum |
Motility structure present in some animal cells composed of a cluster of microtubules within an extension of the plasma membrane |
|
|
|
Ribosomes |
Complexes that make proteins; free in the cytosol or bound to the rough endoplasmic reticulum or nucular envelope |
|
|
|
Plasmodesmata |
- cytoplasmic channels through cell walls that connect the cytoplasms of adjacent cells *plant |
|
|
|
Cell wall |
Outer layer that maintains cell shape and protect cell from mechanical damage made of cellulose, other polysaccharides, and protein *plant |
|
|
|
Central vacuole |
Prominent organelle in older plants cells; functions include storage, breakdown of waste products, and hydrolysis of macromolecules; enlargement of the vacuole is a major mechanism of plant growth |
|
|
|
Cristae |
The inner membrane of the mitochondria convoluted with infoldings |
|
|
|
Mitochondrial Matrix |
The second compartment of the mitochondria enclosed by the inner membrane containing many different enzymes as well as the mitochondria DNA |
|
|
|
Thylakoids |
Flattened interconnected sacs inside the chloroplast that form another membranous system |
|
|
|
Granum |
Stacks of thylakoids |
|

