![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
25 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Organic Compounds |
Compounds containing Carbon combining with other elements. (Frequently containing Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Sulfur, or Phosphorus) |
1. Excludes CO2, CO, and H2CO3 2. Constantly contains 1 element and was believed to only be associated with living organisms once. |
|
|
Macromolecules |
Carbon atoms forming in a long string together of complex molecules. |
1. Carbon is the backbone of this molecule 2. (picture) |
|
|
Carbohydrates |
Contain Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen atoms. |
1. All living cells have these 2.Hydrogen and oxygen have the same ratio of 2:1 as water does in this |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
Single sugar molecules that contain between 3-7 carbon atoms.
|
2. Simplest form of a carbohydrate |
|
|
Disacchrides |
A double sugar molecule |
1. Occurs when two simple sugar molecules bond |
|
|
Polysacchrides |
A complex carbohydrate made from several glucose molecules bonding together |
1. Starch and cellulose 2. Usually formed in plants |
|
|
Lipids |
Fats and oils, used for storing things for a long time and building parts of the cell |

1. They store Carbon |
|
|
Fatty Acids & Glycerol |
The building blocks of lipids |
1. Make up simple fats in our diet 2. These are the _______________ which help store energy a and structure cells. |
|
|
Saturated & Unsaturated Fats |
Unsaturated fats contain unsaturated fatty acids (fatty acids where double bonds join some carbon atoms) and saturated fats are the opposite. |
1. Unsaturated tends to be oily at room temp and liquids 2. Saturated fats are solids in room temp |
|
|
Proteins |
Structural parts of cells as well as messengers of the cell. |
1. The Hermes of cells 2. Like the steel beams and columns of a cell |
|
|
Amino Acids |
Small molecules that contain Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen. |
1. Building blocks of protein |
|
|
Peptide Bond |
Covalent bonds between two amino acids |
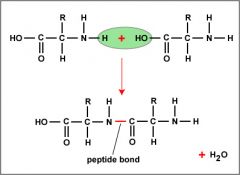
1. Only happen when a chemical bond is formed between the acid group and a molecule the amino group of the other |
|
|
Polypeptide |
More peptide bonds causing a long list of bonded amino acids |
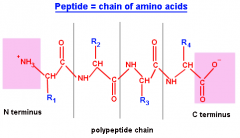
1. Poly means multiple (so think multiple peptide bonds) |
|
|
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, & Quaternary Structures |
The primary structure are the amino acids in the polypeptide chain of a protein. The twists are the secondary structure. Complex folding creates the tertiary structure. The quaternary structure is formed only when there are two or more tertiary structures. |
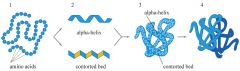
1. A long chain with folds and twists (Think of your headphones in your pocket) |
|
|
Enzymes |
Specialized proteins in all living cells that helps lower activation energy needed for a reaction |
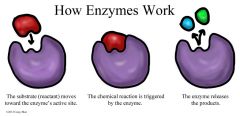
1. Act as catalysts |
|
|
Nucleic Acids |
Macromolecules that control the sequence of amino acids in protein |
1. Put amino acids in their place 2. By ___________ it allows them to control the basic life process |
|
|
Nucleotides |
The simple units that make up nucleic acids |
1. Nucleotides are to nucleic acids as bricks are to a wall 2. These simple units make up ______. |
|
|
DNA |
Nucleotides that have deoxyribose, deoxyribonucleic acids |
1. Like RNA but with deoxyribose 2. A subgenre of nucleic acids |
|
|
Deoxyribose |
Is in nucleotides to form DNA |
1. The thing that makes DNA... well DNA 2. Even smaller than the simple units that make up nucleic acids |
|
|
Double Helix |
Two long chains made of nucleotides which are connected by their deoxyribose sugars. |
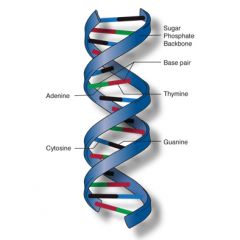
1. Typical shape is what you see as DNA in movies |
|
|
Nitrogen Bases |
A molecule containing nitrogen that has the properties of a base |
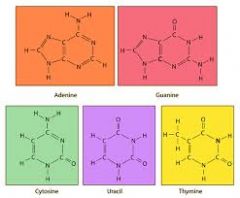
1. Bitter, feel slippery, turns litmus paper blue |
|
|
RNA |
Nucleic acids containing ribose, ribonucleic acids |
1. Ribose puts the R in _______ 2. A subgenre of nucleic acides |
|
|
Ribose |
It is an organic compound. The formula is C5H10O5 |
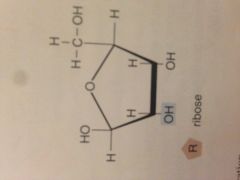
1. Contained in nucleotides to make RNA |
|
|
Single Helix |
One part of a double helix |
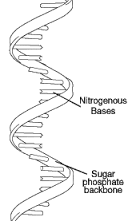
1. While DNA is a double helix RNA is a ________ |
|
|
Gene |
Units of genetic information |
1. What your mom and dad pass down to you 2. DNA forms this like how a chip help forms readable data |

