![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How many pairs of electrons can carbon share?
|
4
|
|
|
What is the general role of enzymes?
|
make reactions go faster, lower the activation energy of a reaction
|
|
|
What are the 5 categories of reactions that are mediated by enzymes?
|
rearrangement
cleavage condensation electron transfer functional group transfer |
|
|
rearrangement
|
a type of organic compound converted to another by changes in internal bonds
|
|
|
cleavage
|
molecule separted into two smaller compounds
|
|
|
condensation
|
covalent bonding between 2 small molecules - become bigger
|
|
|
electron transfer
|
electron splitting off from one molecules to another
|
|
|
functional group transfer
|
functionalgroup split off and transferred to another
|
|
|
saturated vs unsatured
|
saturated - all carbons have all their binding sites taken
|
|
|
4 types of fats
|
phospholipids
sterols fatty acids triglyceride |
|
|
amino acid
|
a small organic compounds having an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and an R group
|
|
|
peptide bond
|
the kind of covalent bond linking one amino acid to another
|
|
|
polypeptide chain
|
three or more amino acids joined in a linear chain
|
|
|
primary structure
|
sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain
|
|
|
proteins
|
most diverse of all large biological molecules, some speed reactions, organism structure, nutritious, move substances, communication, defend against pathogens
|
|
|
secondary structure
|
twists, bends, loops, folds of polypeptide - formed by hydrogen bonds between R groups
|
|
|
domain
|
a polypeptide chain, or part of it, that has become a structurally stable unit -
|
|
|
tertiary structure
|
third level of protein organizations - makes the protein a functional molecules
|
|
|
quaternary structure
|
fourth level of protein organization - globular - multiple polypeptide chains
|
|
|
heme group
|
a large organic molecule with an iron atom at its center
|
|
|
glycoproteins
|
proteins with a sugar group attached
|
|
|
lipoproteins
|
proteins with a lipid group attached
|
|
|
denaturation
|
breaking weak bonds in larage molecules (such as protein) to disrupt three dimensional shapes such that they no longer function
|
|
|
ATP
|
adenonine triphosphate
|
|
|
DNA
|
deoxyribose nucleic acid
|
|
|
RNA
|
ribose nucleic acid
|
|
|
coenzymes
|
nucleotides necessary for enzyme function
|
|
|
nucleic acids
|
?
|
|
|
base pairing
|
?
|
|
|
?
|
?
|
|
|
Functional groups - name and identify
|
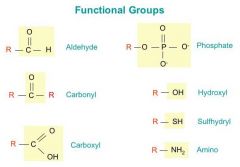
functional groups
|
|
|
Where are hydroxl groups found? Do they dissolve in water?
|
in alcohols (eg. sugars, amino acids) - water soluble
|
|
|
Where are methyl groups found? Do they dissolve in water?
|
in fatty acid chains - insoluble in water
|
|
|
Where are carbonyl groups found? Do they dissolve in water?
|
in sugars, amino acids, nucleotides - water soluble
At end of chain - aldehyde In middle of change - ketone |
|
|
Where are carboxyl groups found? Do they dissolve in water?
|
in amino acids, fatty acids -
water soluble - highly polar - acts as an acid (ie releases H+) |
|
|
Where are amino groups found? Do they dissolve in water?
|
in amino acids and certain nucleotide bases -
water soluble Acts as weak base (accepts H+) |
|
|
Where are phosphate groups found? Do they dissolve in water?
|
in nucleotides (eg. ATP) also in DNA, RNA, many proteins, phospholipids -
water soluble, acidic |
|
|
What are functional groups?
|
lone atoms or clusters of atoms that are covalently bonded to carbon atoms of organic compounds
|
|
|
What is a saccharide?
Monosaccharide? Polysaccharide? Oligosaccharide? |
sugar
1 chain (monomer) multiple chains (polymers) short chain of sugar monomers |
|
|
What is sucrose?
|
Disaccharide - fructose and glucose monomers
|
|
|
What are the three most common polysaccharides (complex carbohydrates)
|
cellulose, starch, glycogen
|
|
|
cellulose
|
glucose chains are stretched side to side - resist hydrolysis
|
|
|
starch
|
an angle to the next - coil like a staircase with hydroxyl groups to the outside - hydrolyzed easily for energy (plants)
|
|
|
glycogen
|
storage unit in animals - found in liver and muscles in particular
|
|
|
chitin
|
ni9trogen containing unit attached to glucose units - forms hard body parts and exoskeletons or many animals
|
|
|
What are the different types of lipids
|
fats
triglycerides |
|
|
What is a fat?
|
one, two or three fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule
|
|
|
What is a fatty acid?
|
backbone of as many as 36 carbon atoms, a carboxyl group at one end, and hydrogen atoms at most or all of the remaining carbons.
|
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
|
unsaturated - one or more double bonds (between two carbons)
saturated all single bonds |
|
|
What is the most abundant lipids in the body and what are they made up of?
|
triglycerides - 3 fatty acid tails linked to a glycerol
|
|
|
What are phospholipids?
What is their most important use? |
glycerol backbone, 2 nonpolar fatty acid tails, and a polar head.
Lipid bilayer for cell membrane. |
|
|
What are waxes?
|
long-chain fatty acids tightly packed and linked to long-chain alcohols or carbon rings - plant cuticle, and eg. beeswax, birds secrete to make feathers waterproof
|
|
|
What are sterols?
|
no fatty acids
cholesterol, hormones |
|
|
What is an amino acid?
|
small organic compound with an amino group (-NH3) a carboxyl group (COO-), a H atom and an R group - building blocks of proteins - 20 kinds
|
|
|
What is a peptide bond?
|
condensation reaction joins the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of the next in line
|
|
|
What are the levels of protein organization?
|
primary structure - sequence of amino acids
secondary structure - chain twists, bends, loops, and folds (hydrogen bonds) tertiary structure - further bending, etc. gives protein it functional molecule ("domain") quaternary - two or more polypeptide chains (eg. Hemoglobin) |
|
|
What are glycoproteins?
|
saccharides attached to a polypeptide chain
|
|
|
What is an example of a mutation in protein structure that results in a disease?
|
Sicke cell disease.
|
|
|
denaturation
|
polypeptide chains lose their 3 dimensional shape and can no longer function - heat, changes in pH
|
|
|
What are nucleotides?
|
one sugar, at least on e phosphate group, and one nitrogen containing base - eg. DNA and RNA, and ATP
|
|
|
What are the roles of nucleotides?
|
energy transfer (transfer of phosphate group) eg ATP
coenzymes (necessary for certain enzympe reactions) monomers for nucleic acids |
|
|
What are nucleic acids?
|
Formed by a covalent bond getween the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate group of the next
|
|
|
What are the 4 bases used in DNA?
|
adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
|

