![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
98 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is Genetics |
the study of how genetic info. is passed from gen. to gen. |
|
|
|
What are the points for the cell theory? |
all living things are made of one or more cells cells are smallest units of life, new cells come from pre-existing ones |
|
|
|
What is DNA |
genetic info. that one inherits from their parents. |
|
|
|
what happens during metaphase? |
.spindle fibers attach to centromere of sister chromatids .sister chromatids line up at the equator of the cell |
|
|
|
what happens during anaphase |
.each centromere seperates causing sister chromatids to seperate .each chromatid migrates to the opposite pole .one complete set of chromosomes is on each pole |
|
|
|
what happens during telophase |
.chromosomes unwind into chromatin .spindle fibres break down .nuclear membrane forms around new chromosomes .nucleolus forms within new nucleus |
|
|
|
what's the point of cytokenesis.??????? |
cytoplasm divides and creates daughter cells |
|
|
|
which phase of mitosis does this happen migration of sister chromatids to poles |
anaphase |
|
|
|
which phase of mitosis does this happen condensation of chromatin into chromosomes |
prophase |
|
|
|
which phase of mitosis does this happen formation of nuclear membrane |
telophase |
|
|

what phase is this??? |
prophase |
|
|
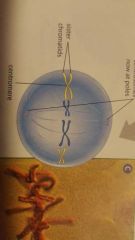
what phase is this? |
metaphase |
|
|
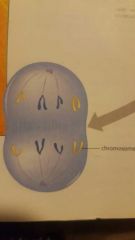
what phase is this? |
anaphase |
|
|
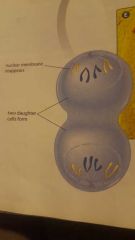
what phase is this?? |
telophase |
|
|
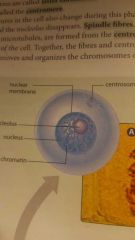
what phase is this |
inerphase |
|
|
|
what does homologous mean? |
cells preform the same functions |
|
|

what is this called? |
karyotype |
|
|
|
whats a gamete |
male or female reproduction cell |
|
|
|
whats a zygote |
a cell formed by the fusion of 2 gametes |
|
|
|
how do you determine the number of gamete cells in an organism. |
diploid(2) |
|
|
|
how many chromosomes are in a gamete if there are 78 diploid chromosomes |
78(2) = 156 |
|
|
|
what phase of meiosis are most like mitosis? |
metaphase bc. they both line up at the equator |
|
|
|
what term matches this statement produces haploid cells from diploid cells |
meiosis |
|
|
|
if a horse has 64 somatic chromosomes whats its diploid number? |
64 |
|
|
|
if a horse has 64 somatic chromosomes whats its haploid number? |
32 |
|
|
|
if a horse has 64 somatic chromosomes how many chromosomes are present in a normal gamete? |
32 |
|
|
|
if a horse has 64 somatic chromosomes how many chromosones are present at prophase 1 |
64 |
|
|
|
what process produces haploid and diploid cells |
fertilization |
|
|
|
what 2 outcomes does meiosis achieve that mitosis doesn't |
unique offspring and 4 daugher cells instead of 2 |
|
|
|
what parts of the body does meiosis take place?????? |
reproduction organs |
|
|
|
what does DNA that's double stranded mean |
it's called a double helix |
|
|
|
during cell division (___) is DNA replicated |
mitosis |
|
|
|
What is it called when there's a chain of nucleotides? |
polynucleotide |
|
|
|
what is a chain of DNA's (polynucleotide) 3 main parts |
phosphate group nitrogenous base pentose sugar |
|
|
|
which sugar doesn't have Oxygen on the 5th carbon |
deoxyribose |
|
|
|
wht are the 2 nitrogenous bases and how many rings do they have and what are their 2 bases (2 in each) |
pyrimidine. single ring. cytosine and thymine purine. 2 ring. adenine and guanine |
|
|
|
what are the complimentary base pairings? |
adenine-thymine guanine-cytosine |
|
|
|
describe genome!! |
dna sequence of an organism |
|
|
|
describe chromatin |
uncoiled undensed dna |
|
|
|
describe chromosome |
coiled dna |
|
|
|
what are the 3 main stages of the cell cycle? |
interphase mitosis cytokenesis |
|
|
|
the cell cycle is for the ___ and cell division of ___ ___ |
growth, somatic cells |
|
|
|
how many daughter cells are produced after one complete cell cycle |
2 new daughter cells |
|
|
|
how long does one cycle of the cell cycle take |
12- 24 hours |
|
|
|
whats the function of the cell cycle |
growth repair and maintenance |
|
|
|
what's the purpose of interphase |
cell grows and makes genetic info. and prepares for division |
|
|
|
what are the 3 stages of interphase and what happens in each |
G1: synthesizes new molecules S: DNA is copied in the form of chromatin G2: synthesizes more proteins that prepare for cell division |
|
|
|
What happens during mitosis stage of cell cycle |
the copied gm. seperates and prepares for 2 new daughter cells |
|
|
|
what are the 4 main phases of mitosis |
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase |
|
|
|
what happens during prophase in mitosis? :) |
.chromatin condenses into chromosomes .chromosome arms are sister chromatids and are joined at center by Centromere .nucleus disappears .spindle fibres formed at poles |
there are 4 points |
|
|
Describe Gametogenesis |
the production of gametes (sex cells) through meiosis |
|
|
|
where does meiosis occur in males? females? |
testes ovaries and oviducts |
|
|
|
how does meiosis work in males? |
starts with spermatogonium and produces 4 non-identical haploid sperm cells |
|
|
|
how long does it take for a sperm to be created? |
about 74 days |
|
|
|
whats the diploid cell meiosis starts with in females? males? |
oogonium spermatogonium |
|
|
|
when does egg production start in females? |
before they're born |
|
|
|
what happens after telophase 1 and 2 in oogenesis? |
only one of the cells receives the majority of the cytoplasm. 1 egg cell and 3 polar bodies are produced |
|
|
|
what is non-disjunction? |
the failure of chromosomes or tetrads to seperate during anaphase. |
|
|
|
what does non-disjunction result in? |
deletion or addition of a chromo. in a gamete |
|
|
|
what is trisomy? |
if a gamete with an extra chromosome is fertilized by a normal gamete. extra chromo. is called trisomy |
|
|
|
what what is monosomy |
if a gamete with a missing chromo. is fertilized by a normal gamete. single copy of chromosome called monosomy |
|
|
|
what does trisomy 21 result in? |
down syndrome |
|
|
|
why does Klinefelters disease happen? |
when there is are 2 X chromosomes and a Y chromosome |
|
|
|
How does Turner syndrome occur? |
when an individual gets only 1 sex chromosome, and X, from mom |
|
|
|
Which parent gives which sex chromosome |
mother X father X or Y |
|
|
|
are you male or female if you have an X and Y chromosome? X and X? |
male female |
|
|
|
what's the purpose of meiosis? |
to create reproductive cells, gametes. |
|
|
|
what happens to the chromatid number prior to meiosis |
doubles |
|
|
|
unlike mitosis, meiosis produces ___ _________ haploid cells |
4 non-identical |
|
|
|
do meiosis and mitosis have the same stages? |
ye |
|
|
|
why do the meiosis stages happen twice? |
to reduce the chromosome number from diploid to haploid |
|
|
|
what happens during prophase 1 that's the same as mitosis? What's different? |
same .nuclear membrane dissolves .chromatids are attached to centromere .centrioles move to poles different homologous chromosomes join together and form a tetrad or bundle of 4 chromosomes. |
|
|
|
what happens during tetrad formation in prophase 1 |
non-sister chromatids exchange genes and create unique alleles. Called crossing over. |
|
|
|
What happens during Anaphase 1 that doesn't during anaphase it mitosis |
centromere does not split apart |
|
|
|
what happens at the end of telophase 1? |
two cells immediately go to next round of meiosis!!! |
|
|
|
what's the only difference between meiosis 1 and 2? |
the phases are occurring in 2 cells at the same time |
|
|
|
what are some of the differences between mitosis and meiosis?? |
mitosis- asexual, meiosis- sexual mitosis-2 daughter cells produced meiosis-4 "" "" "" mitosis-1 division, meiosis-2 divisions mitosis- located everywhere except reproductive organs, meiosis- reproductive organs |
|
|
|
disadvantages of mitosis and meiosis |
mitosis- difficult to adapt, not much diversity meiosis- slow |
|
|
|
what are congenital defects? |
clinical health problems visible at birth |
|
|
|
what are 2 examples of environmental agents that can affect a baby at birth? |
alchohol/drug abuse getting certain viruses while preggers |
|
|
|
genetic defects occur when??? |
chromosomes line up in meiosis |
|
|
|
what's an example of a chromosomal genetic disorder? |
down syndrome |
|
|
|
why are errors in meiosis dangerous? |
cause chromo. copied during interphase will have their daughter cells carry out the mutation |
|
|
|
what are the 4 changes in chromosomal structure |
deletion duplication inversion translocation |
|
|
|
explain deletion |
part of the chromosome is lost |
|
|
|
what are prenatal testings? |
tests preformed on fetuses looking for genetic abnormalities |
|
|
|
what are the two technologies to get desirable traits when breeding |
selective breeding artificial insemination |
|
|
|
what are the three reproductive technologies for plants or animals |
selective breeding artificial insemination embryo transfer |
|
|
|
what are the 3 types of cloning |
gene therapeutic reproductive |
|
|
|
explain how gene cloning happens |
a fragment of DNA containing desired gene is cut by enzymes and inserted into vector |
|
|
|
explain what therapeutic cloning is!!! |
produces genetically identical cells. grows to new tissues or organs |
|
|
|
what does reproductive cloning do |
produces genetically identical organisms |
|
|
|
which stem cells can be used in the hope of repairing damaged organs |
embryotic stem cells adult stem cells induced pluripotent stem cells |
|
|
|
what does GMO stand for? |
genetically modified organisms |
|
|
|
what are some applications of transgenic organisms |
can study diseases produce medical proteins can be developed to be organ doners for humans |
|
|
|
what are 3 concerns with transgenic organisms |
enviornmental threats health threats social and economic |
|
|
|
whats a vector |
carrier of DNA to be cloned |
|
|
|
what are the 2 cells used in somatic transfer |
somatic body cell egg cell |
|

