![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Z-scheme |
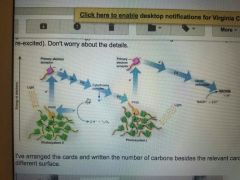
The z-scheme refers to the increase of energy in phototsystem 2 (due to the excitation of electrons) , then thr gradual decrease of energy as the electrons move through the electron transport chain, and another increase at PS1 (as electrons are re-excited) |
|
|
What enzyme phosphorylates glucose the first tim in the glycolisis cycle |
Hexokinase |
|
|
What is the final electron acceptor in the ETC of CR? |
O2/H2O |
|
|
Where does the Krebs Cycle occur? |
Mitochondrial matrix |
|
|
What are the products of Cellular respiration? |
Water, CO2, energy |
|
|
What are the three large parts of cellular respiration? |
Glycolysis, krebs cycle, electron transport chain |
|
|
What are the 4 integral memebrane proteins in the photosynthetic electron transport chain? |
PSII, PSI, CYTB6F, ATP SYNTHASE |
|
|
What are the inputs of photosynthesis? |
CO2, H2O, LIGHT |
|
|
What are the two parts of photosynthesis? |
Light dependent reactions(ETC) and calvin cyle |
|
|
Ad substrate increases, the rate of the reaction..? |
Increases then plateaus |
|
|
What kind of molecule is an enzyme? |
Protein |
|
|
Where do allosteric inhibitors bind? |
Allosteric site/ not the active site |
|
|
What kinf of inhibitor relies on a molecule that binds to the active site, preventing the binding of the substrate? |
Competitive inhibition |
|
|
What is the most abundant naturally occurring enzyme? |
Rubisco |
|
|
What are the axis of a free-energy graph? |
Y-axis: gibbs free energy X-axis: reaction progress |
|
|
What type of macromolecule metabolizes energy the fastest? |
Sugars |
|
|
What are the two broad classes of energy? |
Kinetic and potential |
|
|
What is the primary energy carrier in the cell? |
ATP |
|
|
Where is the energy stored in our molecules? |
Bonds |
|
|
How do cells fix molecules in one place? |
Phosphorylation |
|
|
What kind of reactions occur in glycolysis, allowing it to remain catabolic? |
Coupled reactions |
|
|
If there is a lack of CO2 where does the calvin cycle stop? |
At RUBP |
|
|
Products of the citric acid cycle |
2 CO2 1 FADH2 1 ATP **this happens twice to multiply by two |

