![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
94 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Branches of anatomy |
Gross anatomy(body structure) microscopic anatomy(tissue study) surface anatomy (all organs studied together) |
|
|
|
Anatomical terminology |
Based on ancient Greek or Latin, provides standard nomenclature worldwide |
|
|
|
Chemical level |
Atoms form molecules |
|
|
|
Cellular level |
Cells an their functional subunits |
|
|
|
Tissue level |
Group of cells preforming a common function |
|
|
|
Organ level |
Discrete structure made up of more than one tissue |
|
|
|
Organ system |
Organs working together for common purpose |
|
|
|
Organism level |
Result of all simpler levels working in Union |
|
|
|
Organism |
Human |
|
|
|
Intugumentary system |
External body covering, protects deeper tissue from injury, sunthesizes vitamin D |
|
|
|
Skeletal system |
Protects and supports body organs, provides framework for muscles, blood cells form with in bone |
|
|
|
Muscular system |
Allows manipulation of environment, Locomotion, facial expressions, maintains posture,produces Heat |
|
|
|
Nervous system |
Fast acting control system responds to internal and external changes |
|
|
|
Endocrine system |
Glands secrete hormones that regulate growth reproduction and nutrition use |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular system |
Blood vessels transport blood blood carries oxygen and carbon dioxide carries nutrients and waste |
|
|
|
Lymphatic system/immunity |
Picks up excess fluids leaked from blood vessels mounts attacks against foreign objects |
|
|
|
Respiratory system |
Keeps blood supplied with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
Digestive system |
Breaks down food into smaller units and indigestible foodstuffs eliminated as feces |
|
|
|
Uranary system |
Eliminates nitrogenous wastes regulates water electrolyte and acid-base balance |
|
|
|
Reproductive systems |
Overall function is to produce offspring testes produce sperm & male sex hormone ovaries produce eggs and female sex hormone |
|
|
|
Anatomical position |
Visual refrence point |
|
|
|
Planes |
Frontal- dividing front and back Median-dividing left and right Transverse- dividing upper and lower |
|
|
|
Cell main components |
Plasma membrain- outer boundary Cytolasm- contains most organelles Nucleus-controls cellular activities |
3 |
|
|
Plasma membrain |
Outer boundary structure of membrane fluid mosaic model provides barrier against substance outside cell determines which substance enters or leaves the circle |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Contains most organelles |
|
|
|
Nucleus |
Control cell activity |
|
|
|
Membrain transport |
Simple diffusion-tendency of molecules to move down their concentration gradient Osmosis- diffusion of molecules across membrain Intergral proteins- use ATP as every source |
|
|
|
Facilitates diffusion |
Movement of molecules down their concentration gradient through an integral protein |
|
|
|
Active transport |
Moves molecules across the plasma membrane against their concentration gradient |
|
|
|
Endocytes |
mechanisms by which particles enter cells phagocytosis- cell eating pinocytosis-cell drinking |
|
|
|
Exocytosis |
Mechanism that moves substances out of the cell |
|
|
|
Cytoplasm |
Life internal to plasma membrane consists of centrioles organelles and inclusions |
|
|
|
Cytosol |
Consist of water ion and enzymes |
|
|
|
Ribosomes |
Constructed of proteins and ribosomal RNA not surrounded by a membrane |
|
|
|
Endoplasmic reticulum |
Network within the cytoplasm |
|
|
|
Rough ER |
Ribosomes stud the external surface |
|
|
|
Smooth ER |
Tubules in a branching Network |
|
|
|
Golgi apparatus |
Stack of three to 10 disk shaped envelopes (UPS) |
|
|
|
Lysosomes |
Membrane wall sacs containing digestive enzymes digests unwanted substances |
|
|
|
Peroxisomes |
Membrain walled sacks of oxidase enzymes the trash removal system |
|
|
|
Mitochondria |
Generates most of the cells energy, most complex organelles powerhouse |
|
|
|
Stages of mitosis prophase |
Prophase first and longest stage of mitosis-cromatin threads condense onto chromosomes |
|
|
|
Metaphase |
Second stage, chromosomes Custer at the middle of the cell centrosomes are aligned along the Equator |
|
|
|
Anaphase |
Chromosomes are pulled apart |
|
|
|
Telophase |
Cells pull apart |
|
|
|
Cytokinesis |
Completes the division of the cell into 2 daughter cells |
|
|
|
Developmental aspects of cells |
Aging genetic theory proposes that aging is programmed by genes |
|
|
|
Tissue |
Cells that work together to preform a common function |
|
|
|
4 basic types of tissue |
Epithelial-Covering Connective- support Muscle- support Nervous- control |
|
|
|
Characteristics of epithelial tissue |
Cellularity-cells separated by minimal extracellular material Specialized contacts- cells joined by special junctions Polarity, supported by conection tissue, avascular, regeneration |
|
|
|
Endocrine glands |
Ductless glands that secrete into surrounding tissue |
|
|
|
Exocrine glands |
Ducts cary products to epithelial surface |
|
|
|
Cell junction |
Tight junction-close off intercellular space Adhesive belt junction- anchoring junction Desmosomes-main junctions for binding cells together Gap junctions- passageways between two adjacent cells |
|
|
|
Basal lamina |
Acts as a selective filter determining which molecules from capillaries and enter the epatheliam |
|
|
|
Apical surface features |
Microvilli fingerlike extensions of the plasma membrane |
|
|
|
Connective tissue types |
Cartalage, cinnective tissue proper, bone, |
|
|
|
Intugumentary system |
Skin |
|
|
|
Hypodermis |
Lyes deep in the dermis |
|
|
|
Skin color |
Melanin(most important made from tyrosine), carotene(made from carrots) hemoglobin(allows blood to show through, Caucasian skin) |
|
|
|
Hair layers |
Three layers medulla-central core cortex- surrounds medulla cuticle- outer layer |
|
|
|
Nails |
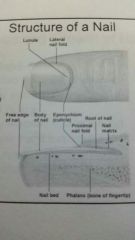
Free edge, body, root, nailfold, cuticle (eponychium) |
|
|
|
Appendage |
Hair follicles, hair bulb, root, arrestor pili muscle (hair standing up) |
|
|
|
Sebaceous glands |
Secrete sebum (oils) -collects dirt softens and lubricates hair and skin |
|
|
|
Sweat glands |
All over body, blood filtrate, 99% water with some salt |
|
|
|
Burns |
First-epadermis second-upper part of dermis third-full thickness of skin |
|
|
|
Skin cancers |
Basal cell carcinoma- not common squamous cell carcinoma-arises from keratinocytes of stratum spinosum Melanoma-most dangerous |
|
|
|
As we age so does akin |
4 months formed 5-6 months covered in downy hairs middle to old age, less elastic, skin inflammation become more common |
|
|
|
Charictoristics of cartalage |
Resilient tissue, consists promarily of water |
|
|
|
Location of cartalage |
Ear, epiglottis, larynx, trachea, nose |
|
|
|
Types |
Hyaline-abundant, provides support throught flexability Elastic- contains many elastic fibers Fibro cartilage- resists strong compression |
|
|
|
Growth |
Adaposal growth-centroblasts in surrounding perichondrium produce new cartalage Interstitial growth- divide and secrete new matrix Stops growing when skeleteon does |
|
|
|
Function of bone |
Function of bone support movement protection mineral storage blood cell formation energy metabolism |
|
|
|
Type of bone |
Long bone short bone flat bone irregular bone |
|
|
|
Structure |
Diaphasis-shaft Epiphysis- ends of bone Blood vessels-well vascularized Medullary cavity-hollow cavity filled with yellow marrow Membranes-fibors |
|
|
|
Anamoy of bone |
Compact bone- dense outer layer Spongy- internal network of bone |
|
|
|
Bone development |
Ossification- bone tissue formation Membrain bones-formed directly from messenchyme Other bones-develope initially from hyaline cartalage |
|
|
|
Bone repair |
Simple and compound fractures - treatment by reduction - close reduction, -open reduction |
|
|
|
Disorders of bones |
Pagets-excessive rate of bone deposits Osteosacroma- form of bone cancer |
|
|
|
Axial |
Skull,vertebrae and bony thorax |
|
|
|
Fasa |
Well |
|
|
|
Foramen |
Hole |
|
|
|
Suture |
Lines |
|
|
|
Appendicular |
Pelvic pectoral girdles, hands and feet |
|
|
|
Disorders |
Hip dysplasia-head of the femur Clubfoot-soles of the feet turn medially |
|
|
|
Joints |
Where bones meet |
|
|
|
Functional classification |
Based on amount of movement |
|
|
|
Synarthroses |
Immovable, common in axial skeleton |
|
|
|
Amphiarthrose |
Slightly movable |
|
|
|
Diarthrose |
Freely moveable |
|
|
|
Structural classicication |
Fibrous, cartalaginous, synovial |
|
|
|
Synovial |
Most moveable type of joint |
|
|
|
Selective synovial joints |
Sternoclavicular -saddle joint Temporomandibular- modified hinge joint Glenohumeral- shoulder joint Elbow-hinge Wrist-stabilized by numerous ligaments Hip-ball and socket Knee-most complex joint, acts as hinge |
|
|
|
Joint injuries |
Torn cartalage-common in knee Sprains- ligaments of reinforcing joint are stretched or torn Dislocation-occurs when bones or joints are forced out of alignment |
|
|
|
Inflammatory and degenerative conditions |
Bursitis-inflamaton of bursa due to injury or friction Tendonitis- inflammation of a tendon sheath Arthritis-osteo-wear and tear-rheumatoid-inflamation-gouty- uric acid build up Lyme disease- inflammatory disease causing pain |
|

