![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
40 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Phylogenetic Tree
|
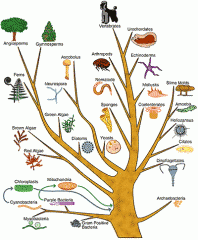
branching diagram depicting hypothesis about evolutionary relationships
|
|
|
INgroup
|
species or group of species whose evolutionary relationship are determined to be closer
|
|
|
Outgroup
|

species or group of species from an evolutionary lineage that is known to have diverged early from other groups
Ex: Reptiles |
|
|
Convergent Evolution
|

when similar environments pressures and natural selection produce similar adaptations in organisms from diffrent evolutionary lineages
Ex: Sharks and Dolphines |
|
|
Homologies
|
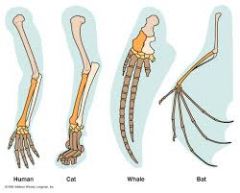
similarities in organisms due to shared ancestry
|
|
|
Homoplasies
|
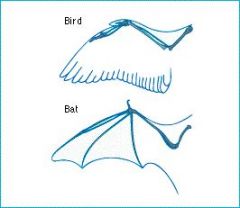
analogous structures that evolve independently in the absence of convergent evolution
|
|
|
Analogies
|

similarities in arrangement and shape of physical structure due to convergent evolution rather than shared ancestry
Ex: Australian vs European Mole Ex: Bray wolf vs Tasmanian Wolf |
|
|
Unikonts
|
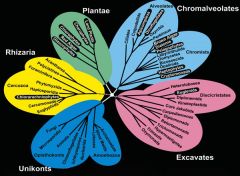
*consist of species of ameba, most of which have lobe-like pseudopodia
*Also includes fungi and animals |
|
|
Archaeplastids
|

includes red and greed algae as well as terrestrial plants
|
|
|
Green Algae
|

Occur symbiotically with other organisms as in lichens
(fungi + algae) |
|
|
Terrestrial Adaptations
|
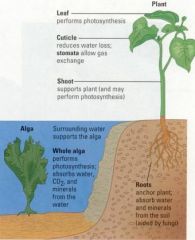
1) Overcame Dehydration
2) Overcame unfiltered sunlight 3)Benefited from abundance of CO2 4) Benefited from mineral rich soil 5) Benefited from scarcity of herbivores (plant eater) and pathogens (disease- causing agent) |
|
|
Green Algae-Morphological Similaries
|

1) Multicelular Eukaryotes
2)Photosynthetic autorophs 3)Chloroplasts with chlorophyll A and B 4)Cell Walls made of Cellulose |
|
|
Alternation of Generations
|
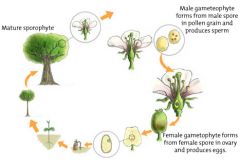
when life cycles alternate between two multicellular bodies with each generation producing the other
|
|
|
Sporophytes
|
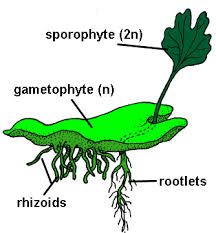
make spores by meiosis that form gametophytes that make the sperm and egg which fertilizes to make the sporophyte
|
|
|
Gametophytes
|
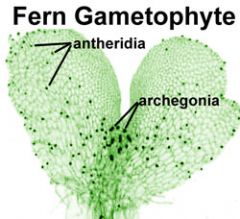
stage in which haploid (n) gametes are produced by mitosis (to maintain the haploid amount)
|
|
|
Bryophytes
|

*Gametophyte generation is Dominant
*Seedless, non-vascular (no xylem and Phloem) plants |
|
|
Ferns
|
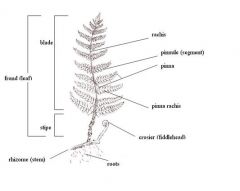
* Sporophyte generation is dominant
*Seedless vascular (xylem and phloem) plants |
|
|
Heterospory
|
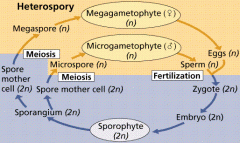
difference in spores
|
|
|
Megasporangia
|
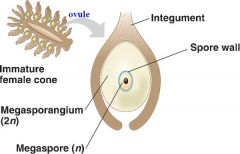
(in mega-sporophylis ) produce mega-spores that give rise to female gametophytes
*1 mega spores is produced |
|
|
Microsporangia
|
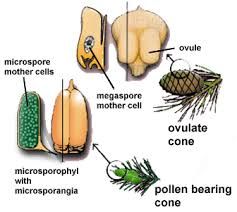
( in microsporoporphylis) produce microspores that give rise to male gametophytes
*many microspores are produced |
|
|
Monocots
|
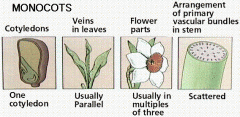
1) Single cotyledon
2) Parallel Lear Veins 3) Scattered Vascular Tissue 4) Fibrous root system |
|
|
Dicots
|

1) Double cotyledon
2) Net-like leaf Veins 3) Ringed vascular tissue 4) Taproot system |
|
|
Xylem
|
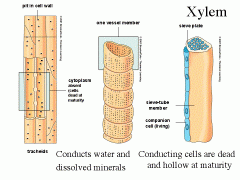
transports water and dissolved materials upwards, from roots to shoots (xylem is closer to the center)
|
|
|
Phloem
|
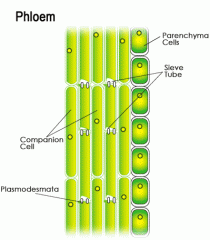
transports organic nutrients from leaves downward to roots, also to growth (leaves and fruit)
|
|
|
Meristems
|
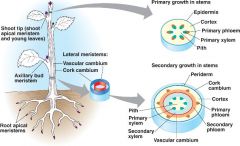
perpetually embryonic tissues (never stop growing)
|
|
|
Apical Meristems
|
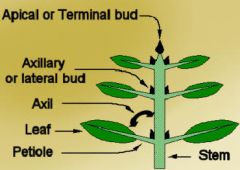
Located in tips of roots and buds of Shoots
|
|
|
Lateral Meristems
|
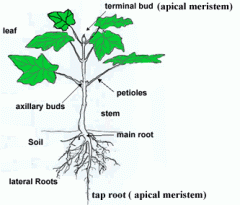
located along the length of roots and stems
|
|
|
Root Cap
|
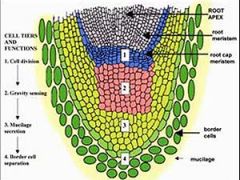
Protected the root tip as the root grows, also secretes slime
|
|
|
Zone of maturation
|
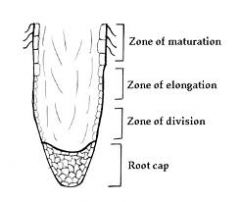
Area where cells complete differentiation and growth
|
|
|
Zone of elongation
|
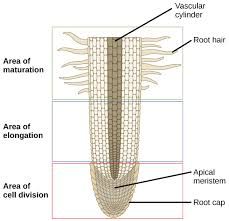
Area Root Lengthening, pushing root tip into soil
|
|
|
Zone of Cell Division
|
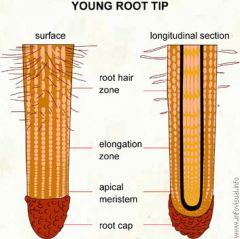
area of new root cell production including root tip (newest cells)
|
|
|
Stele
|
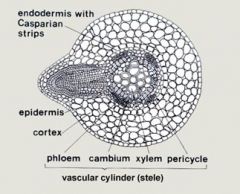
Vascular cylinder composed of the xylem and phloem in most plants
|
|
|
Pericycle
|
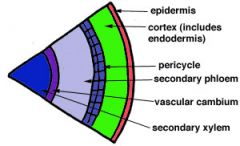
cells which lateral roots arise, the out-most cells in stele
|
|
|
Shoot apical Meristems (SAM)
|
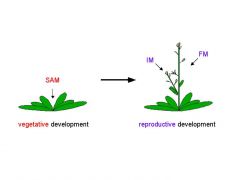
Dome shaped mass of cells at shoot top
|
|
|
Leaf Primordia
|
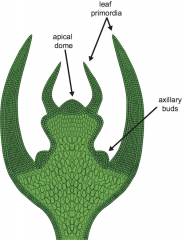
finger-like leaf projections along the sides of the SAM
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|

