![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

Synthesis
|
combination of two or more entities that together form something new; alternately, it refers to the creating of something by artificial means.
|
|
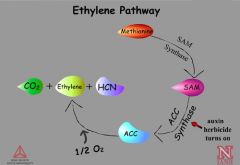
Biosynthesis
|
multi-step, enzyme-catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products
|
|

Descomposition
|
process by which organic substances are broken down into a much simpler form of matter.
|
|
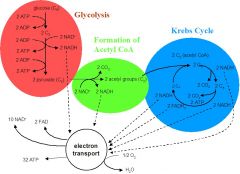
Cell respiration
|
set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products.
|
|
Aerobic
|
takes place in the presence of oxygen and is the more efficient way of producing energy.
|
|
|
Anaerobic
|
oxygen is not present so the Krebs cycle and the cytochrome system stages are not able to occur.
|
|
|
Fermentacion
|
metabolic process that converts sugar to acids, gases and/or alcohol. It occurs in yeast and bacteria, but also in oxygen-starved muscle cells, as in the case of lactic acid fermentation.
|
|
|
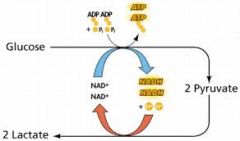
Glycolysis
|
is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C6H12O6, into pyruvate, CH3COCOO− + H+. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy compounds ATP and NADH.
|
|
|
Krebs cycle
|
A
|
|
|
ETS
|
occurs in the cristae of the mitochondria, where a series of cytochromes (cell pigments) and coenzymes exist. These cytochromes and coenzymes act as carrier molecules and transfer molecules.
|
|
|
NADH & FADH2
|
The role of NADH and FADH2 is to donate electrons to the electron transport chain. They both donate electrons by providing an hydrogen molecule to the oxygen molecule to create water during the electron transport chain.
|
|
|
Pyruvate/ pyruvic acid
|
Pyruvic acid is an organic acid, has a carboxylic acid and a ketone functional group, and is the simplest of the alpha-keto acids.
|
|
|
Lactate/lactic acid
|
is a chemical compound that plays a role in various biochemical processes and was first isolated in 1780 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Scheele.
|
|
|
Alcoholic ( fermentation)
|
is a biological process in which sugars such as glucose, fructose, and sucrose are converted into cellular energy and thereby produce ethanol and carbon dioxide as metabolic waste products.
|
|
|
Mitochondrion
|
is a membrane bound organelle found in most eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
Matrix
|
is the material in animal or plant cells, in which more specialized structures are embedded, and a specific part of the mitochondrion that is the site of oxidation of organic molecules.
|
|
|
Cristae
|
A
|
|
|
Citochromes
|
are membrane-bound hemeproteins containing heme groups and are primarily responsible for the generation of ATP via electron transport.
|
|
|
Faculative aerobes
|
Microorganisms that can live in the presence of free energy.
|
|
|
Obligate anaerobes
|
microorganisms that are killed by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen (21% O2).
|
|
|
Hydrolysis
|
means the cleavage of chemical bonds by the addition of water. Where a carbohydrate is broken into its component sugar molecules by hydrolysis, this is termed saccharification.
|

