![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
prokaryotes
|
no nucleus
|
|
|
eukaryotes
|
nucleus
|
|
|
golgi bodies
|
modifies proteins for export
|
|
|
phospholipids
|
glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group
-2 nonpolar hydrophobic tails -Polar hydrophilic head -Can form bilayer for membranes |
|
|
competitive inhibitor
|
reduces the activity of an enzyme
binding enzyme's active site in place of the substrate cock blocks |
|
|
hypertonic
|
-more solute inside than out
-solution causing a cell to lose water |
|
|
hypotonic
|
-less solute outside than in
-a solution causing a cell to take in water |
|
|
isotonic
|
equal solute
|
|
|
ribosomes
|
-RNA and protein in 2 subunits
-PROTEIN SYNTHESIS |
|
|
Enzyme
|

-a catalyst
-speeds up chemical reactions |
|
|
catalysts
|
increases rate of a chemical reaction without permanent chemical changing
|
|
|
what do enzymes do?
|
speed ⬆ chemical reactions
by ⬇ the activation energy |
|
|
receptor proteins
|
proteins that communicate with other cells
|
|
|
marker proteins
|
-in membrane
- analyzes any invaders (find friend from foe) |
|
|
channel proteins
|
transport protein that provides a tube-like opening in the plasma membrane through which particles can diffuse
|
|
|
activation energy
|
energy needed to start a reaction
|
|
|
endergonic
|
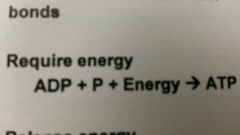
Require energy
ADP + P + Energy ➡ ATP |
|
|
exergonic
|

Release energy
ATP ➡ ADP + P + Energy |
|
|
ATP
|
-Adenosine Tri-Phosphate
-the main energy molecule in cells |
|
|
how is ATP energy formed
|
the breaking of the unstable bonds
|
|
|
types of active transport
|
-Pumps
Sodium Potassium Pump: (3 Na+out/2 K+ into the cell; important in nerve transmission) -Endocytosis Phagocytosis Pinocytosis -Exocytosis |
|
|
types of passive transport
|
-Diffusion
-Osmosis -Facilitated Diffusion- usage of a membrane spanning protein (to help move larger molecules?) |
|
|
passive transport
|
diffusion of a substance across a biological membrane, with no expenditure of energy
|
|
|
active transport
|
movement of a substance
across a membrane against its concentration gradient, helped by transport proteins that REQUIRE ENERGY |
|
|
Endocytosis
|

cellular uptake of molecules or particles THROUGH FORMATION OF NEW VESICLES
from the plasma membrane |
|
|
Exocytosis
|
materials out of the cytoplasm
by vesicle-plasma membrane fusion |
|
|
Pinocytosis
|

takes FLUID and dissolved solute
into small membranous vesicles |
|
|
Phagocytosis
|
cell engulfs macromolecules, other cells, or particles into its cytoplasm
ENGULF STUFF INTO CYTOPLASM |
|
|
energy
|
the ability to do work
|
|
|
composition of cell membrane
|
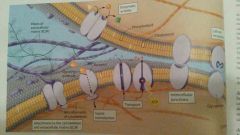
|
|
|
diffusion
|
down the concentration gradient
more ➡ less concentrated |
|
|
active site
|
part of an enzyme where a substrate molecule attaches
|
|
|
concentration gradient
|
the difference in the amount of solute in certain amount of space in a solution
|
|
|
substrate
|
the specific substance or reactant that an enzyme acts on
|
|
|
chemical energy
|
energy stored in bonds in molecules
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion
|
transport proteins that help
transport molecules across a biological membrane |

