![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
main function of the Nervous system?
|
to immediately detect changes in environment and adapt to maintain homeostasis
|
|
|
CNS consists of________ and _______
|
brain and spinal cord.
PNS |
|
|
PNS neurons can be_________ (towards CNS) or_________ (away from CNS)
|
afferent, efferent
|
|
|
ANS has two branches – sympathetic (‘fight or flight’) and parasympathetic (‘relax time’) Give an example of each
|
Sypathetic - Releases adrenaline when in crisis, increase breathing, heart rate.
Parasympathetic - slows everything back down to normal |
|
|
nervous tissue = _______ + _________
|
neurons + glia
|
|
|
________ bring info in, _____ sends info out
|
dendrites bring info in, axon sends info out
|
|
|
action potential
|
when a neuron ‘fires’, or sends a nerve impulse, it is called an action potential
|
|
|
________are electrical currents sent down the length of the axon; ____________are released at tip
|
APs are electrical currents sent down the length of the axon; neurotransmitters are released at tip
|
|
|
a neuron’s charge on the inside is different than outside because of_____ and _____ ions
|
a neuron’s charge on the inside is different than outside because of Na+ and K+ ions
|
|
|
Why are some axons myelinated?
|
axons are myelinated to help increase speed of action potentials
|
|
|
myelin is made of ______________ and made by cells wrapped around the ___________
|
myelin is made of phospholipids and made by cells wrapped around the axon
|
|
|
Why can't brain and spinal cord damage be repaired?
|
brain and spinal cord damage usually cannot be repaired because neurons cannot grow back
|
|
|
damage to___________can sometimes be repaired
|
motor neurons
|
|
|
The brain
Four main parts: |
brain stem; cerebellum; diencephalon, cerebrum
|
|
|
Name a function of the Brain stem
|
regulates heart rate, breathing, blood pressure
|
|
|
Name the parts of the Brain stem
|
three parts: midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
|
|
|
Cerebellum
‐ two main functions |
‘muscle’ and ‘movement’
maintains muscles, posture and balance; fine‐tuning all motor signals sent by cerebrum and learning of motor skills |
|
|
Diencephalon - Describe
|
2‐part relay center that integrates sensory info and motor commands
|
|
|
What reflexes are found in the Diencephalon?
|
visual and auditory startle reflexes are here
|
|
|
Name 2 parts of the Diencephalon
|
thalamus and hypothalamus
|
|
|
Cerebrum - Describe
|
the central processing center
|
|
|
Functions of the cerebrum
|
connects with other parts of brain, involved in higher thought
processes (learning, memory, speech, etc.) |
|
|
Physical features of the cerebrum
|
gray matter and white matter
‐ two hemispheres and four lobes ‐ left hemisphere – more ‘logical’ thinking (speech, calculation, etc.) ‐ right hemisphere – facial recognition, emotional interpretation ‐ corpus callosum bridges both hemispheres, allows crosstalk |
|
|
set of ____ cranial nerves extend from brain
|
12
|
|
|
____ pairs of spinal nerves extend from spinal cord
|
31
|
|
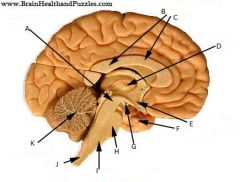
Identify
|
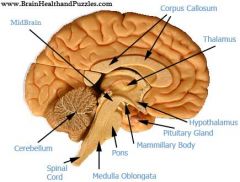
|
|
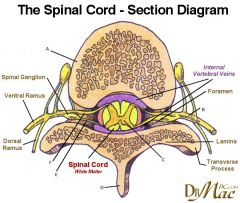
Identify
|
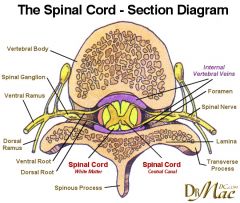
|
|
Identify
|
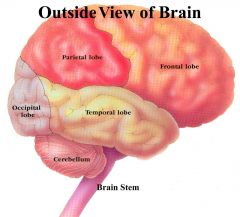
|

