![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
5 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the four cases of isocline dynamics? |
1. cyclic dynamics (excitable) 2. stable equilibrium dynamics (excitable with oscillatory decay) 3. stable equilibrium dynamics (non-excitable) 4. resource goes to carrying capacity (K) |
|
|
Explain the isocline "cyclic dynamics" |
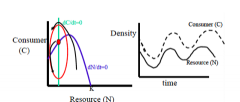
- its excitable & unstable - happens when the consumer isocline lies left to the peak of resource isocline - population capable of living off low resources - consumer density usually higher than resource - it is top heavy (bigger C block over N block) - strong IS & high A (attack rate) |
|
|
Explain "stable equilibrium (excitable)" |
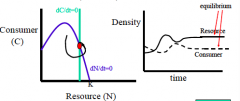
- its excitable with oscillatory decay - happens when consumer isocline is to right right of the resource isocline (but not close to K yet) - moderate top heavy (C block on top is a little smaller than N on bottom) - moderate IS & moderate A (attack rate) |
|
|
Explain "stable equilibrium (non-excitable)" |
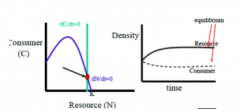
- non excitable - occurs when consumer isocline lies WELL to the right of the resource isocline - is relatively close to carry capacity (N=K) - dynamics lose excitability - bottom heavy (C block on top is much smaller than N on bottom) - low IS & low A (attack rate) |
|
|
Explain "resource goes to carrying capacity" |
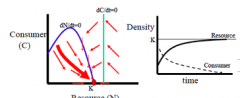
- consumer near/meets extinction - consumer isn't efficient at all - consumer isocline isn't even on the resource isocline anymore, its completely to the right of the curve - bottom heavy (No C block on the N) - weak IS & very low A (attack rate) |

