![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Magnesium (macronutrient). What is it's function? |
Chlorophyll component, activates many enzymes |
Chlorophyll & enzymes |
|
|
Micronutrient Mnemonic |
It's Mnemonic Szn! By Cleaning Most Cupboards & Nice Fences. |
|
|
|
Phloem loading is always active or inactive? |
Always active! (ATP) |
ATP is used |
|
|
True/False: phloem unloading is always passive. |
False, it can be active or passive |
|
|
|
What is the direction of flow of Xylem? |
SPAC |
|
|
|
What is the direction of flow of Phloem? |
From Source to Sink |
|
|
|
Xylem is under positive or negative pressure? |
Negative |
|
|
|
Phloem is under positive or negative pressure? |
Positive pressure |
|
|
|
What role do p-proteins play in the phloem transport? |
They're a safety measure. If the plasmodesmata is damaged, they will plug the hole to reduce further damage |
|
|
|
What is the pressure-flow hypothesis? |
The idea that high turgor pressure bear sources causes sucrose to flow to sinks. |
|
|
|
Tracheids |
Long cells, pits, only a primary cell wall |
|
|
|
Vessel elements |
Short, wide, pits, perforations at ends (more efficient at transporting H2O) |
|
|
|
Positive turgor pressure in guard cells means |
Stomata will be open |
|
|
|
Negative pressure/flaccid guard cells means |
Stomata will be closed |
|
|
|
Xylem are alive or dead at maturity? |
Dead |
|
|
|
Phloem are alive or dead at maturity? |
Alive |
|
|
|
Plasmodesmata |
Channels that connect inside of one cell to the inside of the next cell |
|
|
|
Aquaporin |
Protein channels that allow water to cross between cells |
|
|
|
What are the three routes to which water moves through the cortex in roots? |
Symplastic route, transmembrane route, and apoplastic route |
|
|
|
Endodermis function in roots |
Controls ion uptake and prevents ion leakage from the vascular tissue |
|
|
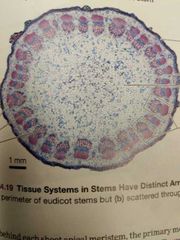
Is this a monocot or dicot? Can it undergo secondary growth? |
Dicot, yes! |
Vascular bundles are arranged by the edges |
|
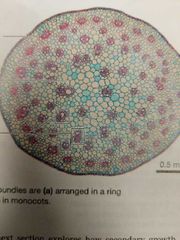
Is this a dicot or a monocot? Can it undergo secondary growth? |
Monocot, no! |
Vascular bundles are scattered throughout the ground tissue |
|
|
Anticlinal growth is responsible for what type of growth? |
Length, primary |
|
|
|
Periclinal growth is responsible for what type of growth? |
Width, secondary |
|
|
|
True/False: Heartwood (at the center) is actively transporting water. |
False! A buildup of sap gives it a darker color |
|
|
|
Protoderm leads to what primary tissue system and which primary tissue (s)? |
Dermal tissue, epidermis |
|
|
|
Ground meristem leads to what primary tissue system and which primary tissue (s)? |
Ground tissue. Parenchyma, collenchyma, sclerenchyma |
|
|
|
Procambium leads to what primary tissue system and which primary tissue (s)? |
Vascular tissue. Xylem and Phloem |
|
|
|
True/False: most plants that do not produce Woody tissues consist entirely of primary growth |
True! |
|
|
|
Parenchyma function |
Synthesis and storage |
|
|
|
Collenchyma function |
Support |
|
|
|
Sclerenchyma function |
Sclereids: protection (hard outer surface of seeds and fruits) Fibers: support |
|
|
|
Casparian Strip |
Tightly packed endodermal cells which secrete a narrow band of wax, made of suberin (waterproof barrier) |
|
|
|
Adhesion |
Molecular attraction between unlike molecules |
|
|
|
Cohesion |
Molecular attraction among like molecules |
|
|
|
Cellulose |
Main material of cell walls |
|
|
|
Flowering plants are (angio/gymno) |
Angiosperms |
|
|
|
Meristem |
Populations of undifferentiated cells that retain the ability to undergo mitosis |
|
|
|
How do meristems persist? |
In mitosis, one duplicate carries on duties as a meristematic cell, while the other differentiates |
|
|
|
Vascular cambium (secondary growth) produces what 2 mature tissues? |
Secondary phloem and secondary Xylem |
|
|
|
Cork cambium (secondary growth) produces what mature tissue? |
Cork! (And bark) |
|
|
|
Modified Leaf Example |
Pea tendrils aid the plant in climbing! |
|
|
|
Modified Stem example |
Thorns provide protection from predators and are a type of stem modification! |
|
|
|
Modified root example |
Storage roots, like sugar beets, store carbs and other nutrients for future use |
|

