![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
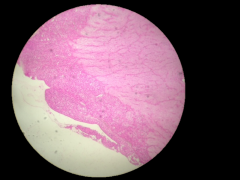
What gland is this? Where is it located? |
Pituitary; In sella turcica of sphenoid brain (skull) |
|
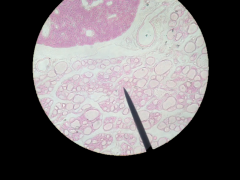
What gland is this (bottom cells)? Where is it located? |
Thyroid; bottom of neck |
|
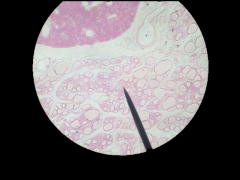
What gland is this (top cells)? Where is it located? |
Parathyroid; Posterior surface of thyroid |
|
What gland is this? Where is it located? |
Adrenal; Top of kidneys |
|
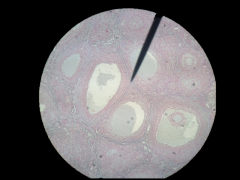
What gland is this? Where is it located? |
Ovaries; Female reproductive organs |
|
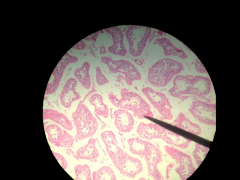
What gland is this? Where is located? |
Testicles; Male reproductive organs |
|
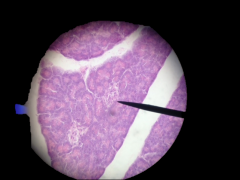
What gland is this? What is the name of these cell groups? Where is this gland located? |
Pancreas; Islets of langerhan Cells; Top of small intestine |
|
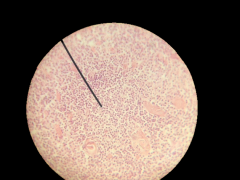
What gland is this? Where is it located? |
Thymus; Top of heart |
|
What gland is this? Where is it located? |
Pineal; Posterior end of corpus callosum/ diencephalon |
|
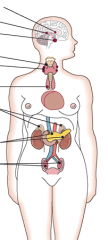
Name the glands (top to bottom, from A to I) |
A: Hypothalamus B: Pineal C: Pituitary D: Parathyroid (Posterior) E: Thyroid F: Thymus G: Adrenal H: Pancreas (Islets of Langerhans) I: Ovary (Testes in males) |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the (posterior) pituitary gland? What do they do? |
None! It only stores oxytocin and Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the (anterior) pituitary gland? What do they do?
|
Growth hormone (GH) for regulating growth, Thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) for stimulating thyroid (duh), Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) for sex cell production, Luteinizing hormone (LH) for sex hormone release, Adrenocorticotropic (ACTH) for stiulating the adrenal cortex, and Prolactin for breats milk secretion |
|
|
What is the name of hormones that regulate other endocrine gland secretions? |
Tropic hormones aka Tropins |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the hypothalamus? What do they do? |
Anti-diuretic hormone (ADH) for water resorption regulation, oxytocin for childbirth, and releasing hormones (RH) for regulating hormone secretions from the anterior pituitary gland |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the pancreas? What do they do? |
Insulin (via beta cells) for decreasing blood glucose levels, glucagon (via alpha cells) for increasing blood glucose levels |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland? What do they do?
|
Thyroid hormone for maintaining blood temperature and calcitonin for decreasing blood calcium levels |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the parathyroid? What do they do?
|
Parathyroid hormone for increasing blood calcium levels |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the adrenals? What do they do?
|
Corticosteroids: cortisol for blood glucose regulation and aldosterone for blood mineral content (via the cortex); Catecholamines: epinephrine and nor-epinephrine for stress response(via the medulla) |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the thymus? What do they do?
|
Thymosin for increasing immunity and combating disease |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the pineal? What do they do?
|
Melatonin for sleep/wake regulation |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the ovaries? What do they do?
|
Estrogen for development of female sex characteristics and progesterone for implantation of fertilized egg onto uterus (pregnancy hormone) |
|
|
What hormones are secreted by the testis? What do they do?
|
Testosterone for the development of male sex characteristics |
|
|
Blood type A has which antigens on it's red blood cell membrane? What type of antibodies are in the blood plasma? |
A protein/antigens; B antibodies |
|
|
Blood type B has which antigens on it's red blood cell membrane? What type of antibodies are in the blood plasma? |
B proteins/antigens; A antibodies |
|
|
Blood type AB has which antigens on it's red blood cell membrane? What type of antibodies are in the blood plasma? |
A and B proteins/antigens; No antibodies |
|
|
Blood type O has which antigens on it's red blood cell membrane? What type of antibodies are in the blood plasma?
|
No proteins/antigens; A and B antibodies |
|
|
Which ABO blood type is the universal recipient? What about universal donor? |
AB is the universal recipient (because it has no antibodies in the blood for other blood types to react with), O is the universal donor (because there are no proteins/antigens on red blood cell membranes for blood antibodies to react with) |
|
|
Explain Rh+ vs. Rh- blood type? |
Rh+ has the Rh protein/antigen on it's red blood cell's membrane, Rh- doesn't, and therefore Rh- has antibodies in the blood for red blood cells with the Rh+ antigen |
|
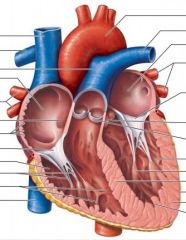
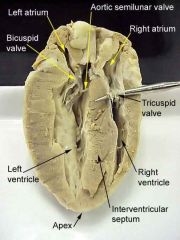
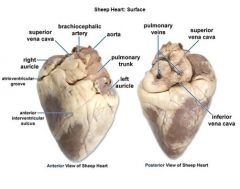
Label: Left side: (top -> bottom; A through L; *F and G are N/A) |
A: Superior vena cava B: Right pulmonary artery C: Pulmonary trunk D: Right atrium E: Right pulmonary veins H: Tricuspid valve I: Right ventricle J: Chordae tendinae K: Trabeculae L: Inferior vena cava |
|
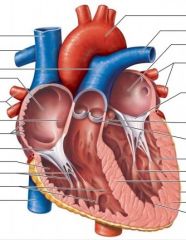
Label: Right side: (top -> bottom; A through M) |
A: Aorta B: Left pulmonary artery C: Left atrium D: Left pulmonary veins E: Bicuspid valve F: Aortic valve G: Pulmonary valve H: Left ventricle I: Papillary muscle J: Inter-ventricular septum K: Epicardium L: Myocardium L: Endocardium |
|
|
You are loved! |
|
|
I am so proud of you! |
|
|
What is blood? |
A liquid connective tissue made of plasma (55%) in which blood cells (45%) travel through to transport nutrients, gases, and ions. |
|
|
Blood cell types |
1. Red: (RBC) aka erythrocytes; transport oxygen and carbon dioxide 2. White: (WBC) aka leukocytes; immunity function by destroying pathogens and parasites and removing old cells 3. Blood platelets: anucleate, incomplete; fragments which initiate blood clotting |
|
|
What is a heart beat? |
An atrial contraction followed by a ventricular contraction |
|
|
What comprises the Lub and Dub sound of a heart beat? |
Lub: Atrio-ventricular valves close (tri and bicuspid) as the ventricles contract Dub: Semilunar valves close (pulmonary and aortic) at the end of ventricular contraction |
|
|
What does systole mean? What does diastole mean? |
Contraction; Relaxation |
|
|
Explain what happens during P wave, QRS wave, and the T wave |
P wave: This is where the atria contract/aredepolarized while the ventricles are relaxed QRS wave: The atria start repolarizing, ventricles are depolarizing, ventricles contract, “Lub” sound takes place, meaning the bicuspidand tricuspid valve are closing. T wave: The ventricles are repolarized and relaxed, “Dubb” sound takes place, thesemilunar valves are closing at this point. |
|
|
Explain the main units of the heart's conduction system |
SA node: pace maker, stimulate atrial contraction; in right atrium AV node: conducts signals to AV bundle; in right atrium near tricuspid valve AV bundle: conducts signals from AV bundle to left and right bundle branches; in inter-ventricular septum Bundle branches: conducts signals from from AV bundle down to purknje fibers; in inter-ventricular septum Purknje fibers: carry electrical signals to outer tissue within ventricle walls |
|
|
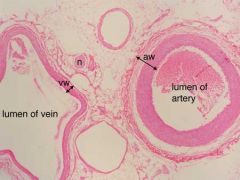
Explain arteries, veins, and capillaries |
Artery: blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart; typically oxygenated blood except pulmonary artery Vein: blood vessels that carry blood toward the heart; typically de-oxygenated blood except the pulmonary and umbilical vein Capillaries: small blood vessels where exchange of molecules occurs between blood vessels and body tissues |
|
|
You are amazing! |
|
|
https://youtu.be/f0wOl4Fz_dI |
You are so smart! |
|
|
https://youtu.be/NJkmlmWv1Ag |
You are so strong! |
|
|
What is pulse? What is blood pressure? |
Pulse is a pressure wave in an artery created byventricular systole
Blood pressure is the measure of pressure acting on the wall of an artery, and is generated by ventricular systole anddiastole |
|
|
What measures blood pressure? |
A sphygmomanometer |
|
|
What is a portal vein? What is the hepatic portal system? |
A portal vein any vein that starts and ends in blood capillaries. The hepatic portal system directs blood from the liver, pancreas, spleen, and small intestine into the liver so that the liver may regulate soluble nutrients and toxins before sending blood into the inferior vena cava. |
|
|
What is the ligamentum arteriosum called before a fetus is born? How is it different? |
Ductus arteriosum; it bypasses the lung function and connects moms lungs to its own |
|
|
Explain how the following structures are different in a fetal pig: umbilical artery & vein, urinary bladder, and ductus venosus |
The umbilical artery takes de-oxygenated blood to the placenta; the umbilical vein takes oxygenated blood from the placenta to the heart; the urinary bladder is closed and connected to mom; and the ductus venosum bypasses the liver function |

