![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is matter?
|
the "stuff" of the universe (anything that has mass and takes up space)
|
|
|
What are the states of matter?
|
solid, liquid, gas
|
|
|
What is matter made up of?
|
atoms
|
|
|
What is an atom?
|
the smallest stable units of matter
|
|
|
What type of charge does a proton have?
|
positive charge
|
|
|
What type of charge does a neutron have?
|
neutral charge
|
|
|
What type of charge does an electron have?
|
negative charge
|
|
|
What forms the nucleus?
|
protons and neutrons
|
|
|
What is an electron cloud?
|
electrons that travel around nucleus at a high speed
|
|
|
What are elements?
|
pure substance composed of atoms of only 1 kind
|
|
|
What are elements determined by?
|
their atomic number
|
|
|
What identifies an element?
|
the number of protons
|
|
|
Define atomic weight
|
actual mass of an atom (expressed in daltons)
|
|
|
What is one dalton?
|
the weight of a single proton or a single neutron
|
|
|
Define mole
|
element's atomic weight in grams or a compound's molecular weight (sum of atomic weights) in grams
|
|
|
What is the formula for Avogadro's number?
|
6.02 x 10²³
|
|
|
One mole contains ________
|
same number of particles
|
|
|
Define molecules
|
2 or more atoms held together by chemical bonds
|
|
|
Define compounds
|
2 or more different types of atoms chemically bonded
|
|
|
What are the three types of chemical bonds?
|
ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds
|
|
|
Define valence shell
|
outermost energy level containing chemically active electrons
|
|
|
Define the Octet rule
|
except for the first shell which is full with 2 electrons, atoms interact in a manner to have 8 electrons in their valence shell
|
|
|
What is an ionic bond?
|

attraction between cations and anions
|
|
|
Define ions
|
charged atoms resulting from the gain or loss of electrons
|
|
|
Define an anion
|
gained one or more electrons = negative charge (e.g. Cl-)
|
|
|
Define a cation
|
lost one or more electrons = positive charge (e.g. Na+)
|
|
|
Ionic bonds form between atoms by the _____ of electrons
|
Ionic bonds form between atoms by the transfer of electrons
|
|
|
Ionic compounds form _____ instead of _____
|
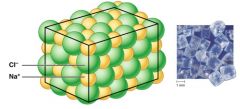
Ionic compounds form "crystals" (dry state) instead of individual molecules
|
|
|
When placed in water, ionic compounds _____ and the component anions and cations _____.
|
When placed in water, ionic compounds dissolve and the component anions and cations separate.
|
|
|
Define covalent bonds
|
strong electron bonds
|
|
|
Covalent bonds are formed by the _____ of two or more electrons.
|

Covalent bonds are formed by the sharing of two or more electrons.
|
|
|
Define nonpolar molecules
|

electrons shared equally between atoms
-shared electrons spend the same time around each nucleus |
|
|
Define polar molecules
|

electrons shared unequally
-shared electrons spend more time orbiting one nucleus vs. the other |
|
|
Define electronegative
|

atoms that "attract" more e- to orbit around their nucleus
|
|
|
Define electropostive
|

atoms that have low e- attraction
|
|
|
Atoms with six or seven valence shell electrons are _____.
|
electronegative
|
|
|
Atoms with one or two valence shell electrons are _____.
|
electropositive
|
|
|
What is an example of an ionic bond?
|
a
|
|
|
What is an example of a polar covalent bond?
|
H - O - H
(water) |
|
|
What is an example of a non polar covalent bond?
|
O = C = O
(carbon dioxide) |
|
|
What are hydrogen bonds?
|

weak forces between atoms of adjacent water molecules
|
|
|
Define metabolism
|
all chemical reactions under way in cells and tissues at any given time
|
|
|
What is an example of a decomposition reaction (catabolism)?
|
AB → A + B
|
|
|
What is an example of a synthesis reaction (anabolism)?
|
A + B → AB
|
|
|
What is an example of a exchange reaction (reversible)?
|
AB ⇋ A + B
|
|
|
Define hydrolysis
|
catabolic reactions involving water
-complex molecule is broken down and components of water molecule (H and OH are added to the resulting fragments) |
|
|
Define dehydration synthesis (condensation)
|
anabolic reactions involving water
-formation of a complex molecule by the removal of water |
|
|
Define energy
|
the power to do work
|
|
|
Define work
|
a change in mass or distance
|
|
|
What are the forms of energy?
|
kinetic energy, potential energy, and chemical energy
|
|
|
What is kinetic energy?
|
energy of motion
|
|
|
What is potential energy?
|
stored energy
|
|
|
What is chemical energy?
|
potential energy stored in chemical bonds
|
|
|
What is an inorganic compound?
|
generally don't contain carbon and hydrogen as primary structural components
|
|
|
What are some examples of inorganic compounds in the body?
|
water, salts, inorganic acids and bases, CO₂ and O₂
|
|
|
What is an organic compound?
|
carbon and hydrogen are primary structural components, covalently bonded and large
|
|
|
What are the four main classes of organic compounds in the body?
|
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
|
|
|
What is solubility?
|
water's ability to dissolve a solute in a solvent to make a solution ("universal solvent")
|
|
|
What is a chemical reactivity?
|
most body chemistry uses or occurs in water
|
|
|
Catabolic reactions ___ bonds
|
Catabolic reactions break bonds (catabolic reaction)
|
|
|
Anabolic reactions _____ bonds
|
Anabolic reactions form bonds (dehydration synthesis)
|
|
|
What is high heat capacity?
|
water's ability to absorb and release heat
|
|
|
What is lubrication?
|
moisten and reduce friction
|
|
|
Chemical reactions in our body depend on _____
|
Chemical reactions in our body depend on water
|
|
|
H₂O molecules form _____ around ions and small polar molecules to keep them in solution
|
H₂O molecules form hydration spheres around ions and small polar molecules to keep them in solution
|
|
|
What is a hydrophilic compound?
|
"react with water" (water loving)
-organic molecules with polar covalent bonds → also attract water -hydration spheres form... and carry these molecules into solution |
|
|
What is a hydrophobic compound?
|
"do not react with water" (water fearing)
-organic molecules lacking polar covalent bonds (nonpolar) -no hydration spheres formed... molecules don't dissolve |
|
|
_____ molecules are electrically attracted to polar H₂O molecules (they can interact with & thus dissolve in H₂O) → hydrophilic (water loving)
|
Polar molecules are electrically attracted to polar H₂O molecules (they can interact with & thus dissolve in H₂O) → hydrophilic (water loving)
|
|
|
_____ molecules cannot enter into a "charge interaction" with H₂O & therefore cannot dissolve in it → hydrophobic
|
Nonpolar molecules cannot enter into a "charge interaction" with H₂O & therefore cannot dissolve in it → hydrophobic
|
|
|
_____ molecules cannot dissolve in lipids or permeate phospholipid bilayer → lipophobic
|
Polar
|
|
|
_____ molecules dissolve in lipids and can permeate phospholipid bilayer → lipophilic
|
Nonpolar
|
|
|
Hydrophobic molecules are "water fearing" and therefore cannot dissolve in water
|
True
|
|
|
Lipophilic molecules can dissolve in water
|
False
|
|
|
Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic
|
True
|
|
|
Polar molecules are lipophilic
|
False
|
|
|
Water is a non polar molecule
|
False
|
|
|
Polar molecules can dissolve in water
|
True
|
|
|
What is a salt?
|
ionic compound with cations other than H- & anions other than OH-
|
|
|
All ions are _____.
|
electrolytes
|
|
|
What is an electrolyte?
|
substances that conduct an electrical signal current in solution
|
|
|
Using the pH values
|
"saves space"
|
|
|
What is an acid?
|

solute that dissociated in solution and releases H+ (proton donors) → pH lower than 7.0
|
|
|
What is a base?
|

solute that removes H+ from solution (proton acceptors) → pH higher than 7.0
|
|
|
What is pH?
|
the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+) in a solution
|
|
|
What is acidosis?
|
excess H+ in body fluid (low pH)
-damages cells and tissues -alters proteins -interferes with normal physiological functions |
|
|
What is alkalosis?
|
excess OH- in body fluid (high pH)
-also causes problems but rarely |
|
|
What is a buffer?
|
mixture of molecules that minimize changes in [H+], stabilizes pH physiological buffers: bicarbonate, phosphate, proteins
|
|
|
When pH is high -->
|
H+ ions are released to lower pH
|
|
|
When pH is low -->
|
H+ ions are bound to raise pH
|

