![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
41 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)

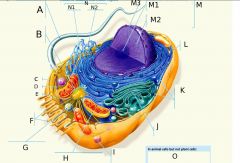
A?
|
Flagellum
|
Motility structure present in some animal cells, composed of a cluster of microtubules within an extension of the plasma membrane
|
|
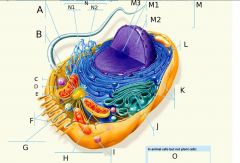
B?
|
Centrosome
|
region where the cell's microtubules are initiated; contains a pair of centrioles.
|
|
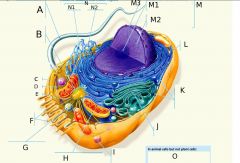
C?
|
Microfilaments
|
Two intertwined strands of protein.
Function: Maintenance of cell shape (cytoskeleton). Changes in cell shape. Muscle contraction. Cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis). Cell motility (amoeboid movement). Formation of cleavage furrow during cell division. |
|
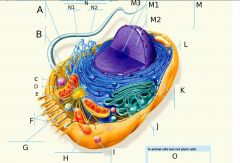
D?
|
Intermediate Filaments
|
Structure: Fibrous proteins (such as keratin) supercoiled into cables
Function: Maintenance of cell shape (cytoskeleton). Anchorage of nucleus and other organelles. Nuclear lamin type forms meshwork that stabilizes inner membrane of nuclear envelope |
|
E?
|
Microtubules
|
Function: Maintenance of cell shape (cytoskeleton). Cell motility (major component of cilia and flagella). Chromosome movement in cell division. Organelle movements.
|
|
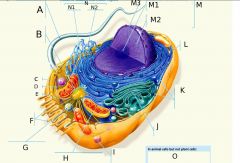
F?
|
Microvilli
|
Structure: Cylindrical projection. Long and skinny. High SA/V ratio Functions: Increase the cell's surface area
|
|
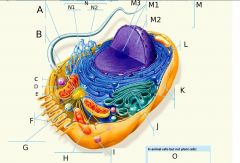
G?
|
Peroxisome
|
Function: Both produce and destroy H2O2
Peroxisome: Breaks down fatty acids into smaller molecules that are used as fuel for cellular respiration; detoxify alcohol and other drugs Glyoxysomes: Converts fatty acids to sugars Single-membrane-bound spherical sac with no internal structure May contain a large crystal |
|
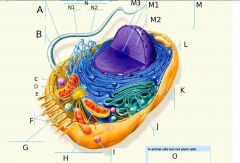
H?
|
Mitochondria
|
Performs Cellular Respiration*
Enclosed by 2 membranes: Outer membrane smooth, inner membrane folded into cristae Inner membrane encloses the matrix that contains ribosomes and DNA |
|
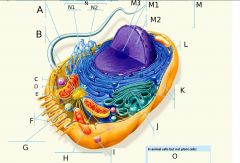
I?
|
Lysosome
|
Function: Digest macromolecules used for food or help defend the body by digesting potentially dangerous bacteria. Recycle cell’s own organic material
Structure: Membrane-enclosed sac of hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes Internal pH of 5 |
|
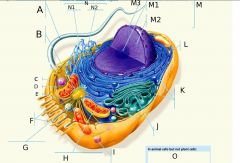
J?
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
Function: Modified, stored, and packaged for other destinations. Manufactures some polysaccharides
Important in the processing of proteins for secretion. Structure: Stack of flattened membranous sacs (cisternae) Has distinct polarity with receiving and shipping ends |
|
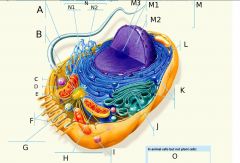
K?
|
Ribosomes
|
Function: Site of protein synthesis
Structure: Composed of 2 subunits, one large, one small Each subunit is an aggregation of proteins and rRNA |
|
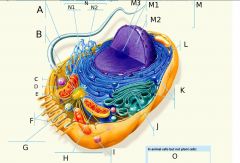
L?
|
Plasma Membrane
|
|
|

M?
|
Nucleus
|
Function: Stores genetics information Controls protein synthesis, which occurs in the cytoplasm
Structure: Enclosed by 2 membranes called the nuclear envelope Pores in the nuclear envelope Contains DNA in chromosomes Contains the nucleolus |
|
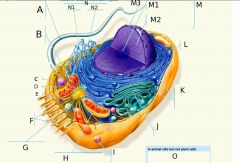
M1?
|
Nucleolus
|
Function: Synthesis of rRNA rRNA and proteins assembled into ribosomal subunits (large and small)
Structure: Roughly spherical Mass of densely stained granules and fibers adjoining parts of the chromatin |
|
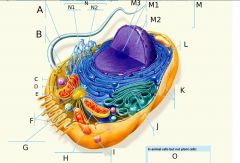
M2?
|
Chromatin
|
Function: The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes.
Structure: When the cell is not dividing, this exists in its dispersed form, as a mass of very long, thin fibers that are not visible with a light microscope. |
|
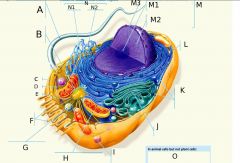
M3?
|
Nuclear Envelope
|
Function: Regulates traffic with the cytoplasm.
Structure: In a eukaryotic cell, the double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, perforated with pores. The outer membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. |
|
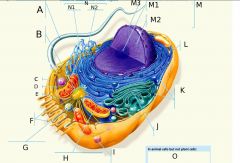
N?
|
Endoplasmic Reticulum
|
An extensive membranous network in eukaryotic cells, continuous with the outer nuclear membrane and composed of ribosome-studded (rough) and ribosome-free (smooth) regions.
|
|
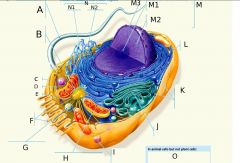
N1?
|
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
|
Structure: Network of membranous sacs called cisternae; ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic surface of the membranes.
Function: Synthesis of proteins that are secreted from the cell Membrane factory |
|
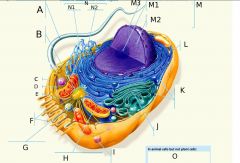
O? 3 Answers
|
1. Lysosomes 2. Centrosomes, with centrioles 3. Flagella (but present in some plant sperm)
|
|
|
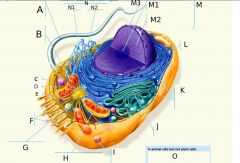
N2?
|
Smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
|
Function: Synthesis of lipids, such as oils, phospholipids and steroids Carbohydrate metabolism Detoxification of drugs
Structure: Network of membranous tubules Membrane lack ribosomes |
|
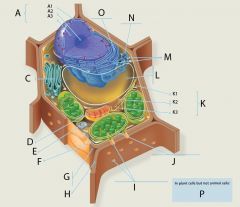
A?
|
Nucleus
|
Function: Stores genetics information Controls protein synthesis, which occurs in the cytoplasm
Structure: Enclosed by 2 membranes called the nuclear envelope Pores in the nuclear envelope Contains DNA in chromosomes Contains the nucleolus |
|
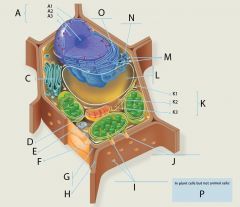
A1?
|
Nuclear Envelope
|
Function: Regulates traffic with the cytoplasm.
Structure: In a eukaryotic cell, the double membrane that surrounds the nucleus, perforated with pores. The outer membrane is continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum. |
|
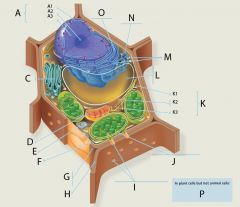
A2?
|
Nucleolus
|
Function: Synthesis of rRNA rRNA and proteins assembled into ribosomal subunits (large and small)
Structure: Roughly spherical Mass of densely stained granules and fibers adjoining parts of the chromatin |
|
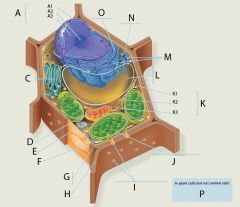
A3?
|
Chromatin
|
Function: The complex of DNA and proteins that makes up eukaryotic chromosomes.
Structure: When the cell is not dividing, this exists in its dispersed form, as a mass of very long, thin fibers that are not visible with a light microscope. |
|
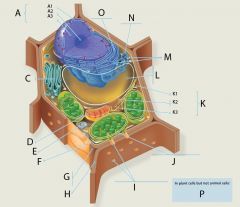
C?
|
Golgi Apparatus
|
Function: Processes and packages proteins after their synthesis and before they make their way to their destination
Manufactures some polysaccharides and attaches them to a protein synthesized in ER to form proteoglycans. Structure: Stack of flattened membranous sacs (cisternae) Has distinct polarity with receiving and shipping ends |
|
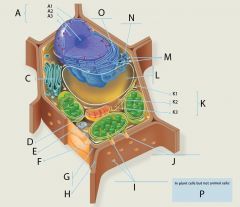
D?
|
Mitochondrion
|
Function: Site of cellular respiration
Structure: Enclosed by 2 membranes: Outer membrane smooth, inner membrane folded into cristae Inner membrane encloses the matrix that contains ribosomes and DNA |
|
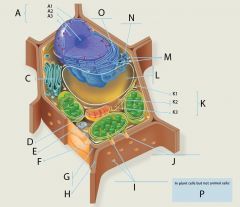
E?
|
Peroxisome
|
Function: Both produce and destroy H2O2 Peroxisome: Breaks down fatty acids into smaller molecules that are used as fuel for cellular respiration; detoxify alcohol and other drugs Glyoxysomes: Converts fatty acids to sugars
Single-membrane-bound spherical sac with no internal structure May contain a large crystal |
|

F?
|
Plasma Membrane
|
The membrane at the boundary of every cell that acts as a selective barrier, regulating the cell’s chemical composition.
|
|

G?
|
Cell Wall
|
A protective layer external to the plasma membrane in the cells of plants, prokaryotes, fungi, and some protists. Polysaccharides such as cellulose (in plants andsome protists), chitin (in fungi), and peptidoglycan (in bacteria) are important structural components of cell walls.
|
|
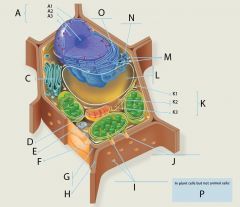
H?
|
Wall of adjacent cell
|
|
|
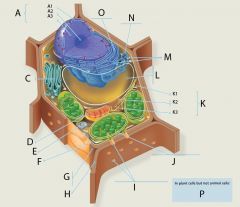
I?
|
Plasmodesmata
|
Structure: An open channel through the cell wall that connects the cytoplasm of adjacent plant cells, allowing water, small solutes, and some larger molecules to pass between the cells.
|
|
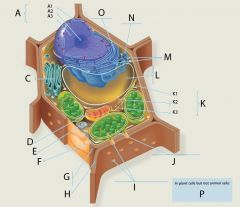
J?
|
Chloroplast
|
Function: Site of photosynthesis
Structure: Enclosed by 2 membranes Third membrane system of flattened sacs called thylakoids stacked in grana Fluid surrounding grana called stroma which contains ribosomes and DNA Grana and thylakoids contain chlorophyll |
|
|
K?
|
Cytoskeleton
|
Built up of microfilaments??? .....more info
|
|

K1?
|
Microfilaments
|
Structure: 2 intertwined strands of the protein actin
Function: Maintenance of cell shape (cytoskeleton). Changes in cell shape. Muscle contraction. Cytoplasmic streaming (cyclosis). Cell motility (amoeboid movement). Formation of cleavage furrow during cell division. |
|
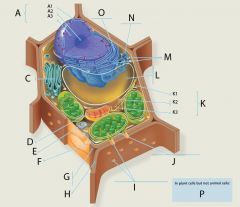
K2?
|
Intermediate Filaments
|
Structure: Fibrous proteins (such as keratin) supercoiled into cables
Function: Maintenance of cell shape (cytoskeleton). Anchorage of nucleus and other organelles. Nuclear lamin type forms meshwork that stabilizes inner membrane of nuclear envelope |
|
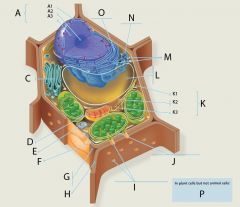
K3?
|
Microtubules
|
Structure: Hollow tubes composed of the protein tubulin
Function: Maintenance of cell shape (cytoskeleton). Cell motility (major component of cilia and flagella). Chromosome movement in cell division. Organelle movements. |
|
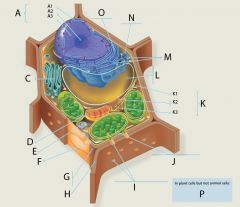
L?
|
Central Vacuole
|
Structure: In a mature plant cell, a large membranous sac with diverse roles in growth, storage, and sequestration of toxic substances.
|
|
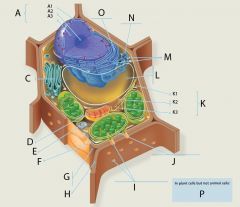
M?
|
Ribosomes
|
Function: Site of protein synthesis
Structure: Composed of 2 subunits, one large, one small Each subunit is an aggregation of proteins and rRNA |
|
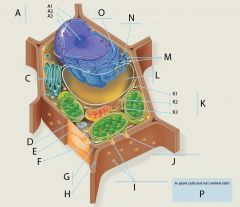
N?
|
Smooth ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
|
Function: Synthesis of lipids, such as oils, phospholipids and steroids Carbohydrate metabolism Detoxification of drugs
Structure: Network of membranous tubules Membrane lack ribosomes |
|
|
O?
|
Rough ER (Endoplasmic Reticulum)
|
Structure: Network of membranous sacs called cisternae; ribosomes attached to the cytoplasmic surface of the membranes.
Function: Synthesis of proteins that are secreted from the cell Membrane factory |
|
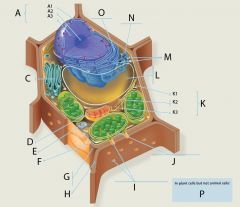
P? 4 answers
|
1. Chloroplasts
2. Central Vacuole 3. Cell Wall 4. Plasmodesmata |
|

