![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Nucleic Acid |
Polymers specialized for th storage, transmission, and use of genetic information |
|
|
Nucleotides |
Nucleic acids are polymers composed of these monomers Consist of 3 components: a nitrogen-containing base, a pentose sugar, and 1-3 phosphate groups |
|
|
Nucleosides |
molecules consisting of pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base, but no phosphate group |
|
|
Pyrimidine |
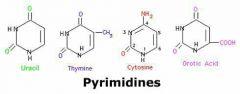
A six-membered single-ring structure that is 1 of 2 forms of the bases of the nucleic acids |
|
|
Purine |
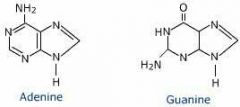
A fused double-ring structure |
|
|
Condensation |
same as dehydration reactions, having to do with loss of water results in the formation of covalent bonds |
|
|
Oligonucleotides |
Relatively short, with about 20 nucleotide monomers includes RNA molecules that function as PRIMERS to BEGIN DNA duplication, regulate the expression of genes; and synthetic DNA molecules used for amplifying and analyzing he longer sequences |
|
|
Polynucleotides |
*nucleic acids can be very long, longest polymers in the living world some DNA in humans contain hundreds of millions of nucleotides |
|
|
DNA Replication |
Reproducing DNA exactly by polymerization using existing strands as base pair templates |
|
|
Transcription |
The copying of DNA sequences into RNA |
|
|
Translation |
After transcription; the nucleotide sequence in the RNA is used to specify a sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain |
|
|
Gene expression |
Transcription + Translation |
|
|
Genome |
The complete set of DNA in a living organism |
|
|
Genes |
The small sections of DNA that are transcribed int RNA (not all of the info in DNA is needed at all times and in all tissues) |
|
|
Ribozymes |
These are catalytic RNAs Can speed up reactions involving their own nucleotides as well as other substances |
|
|
Protocell |
Prebiotic, water-filled structures, defined by a lipid bilayer membrane Large molecules like DNA and RNA can pass through bilayer, but small nucleotides can Nucleic acids inside the protocells can replicate using nucleotides from outside ex: fatty acid molecules mixed with water for a cell like structure that do not allow water in because of the hydrophibic bilayer |
|
|
Formation of Earth |
4.5 billion years ago |
|
|
Stable Hydrosphere |
4.2 billion years ago |
|
|
Prebiotic Chemistry |
4.2-4.0 billion years ago |
|
|
Pre-RNA World |
4 billion years ago |
|
|
RNA World |
3.8 billion years ago |
|
|
First Cell |
3.5 billion years ago |
|
|
RNA Polymerase |
An enzyme that catalyzes the formation of RNA from a DNA template |
|
|
tRNA |
*transfer RNA A family of folded RNA molecules. Eaach tRNA carries a specific amino acid and anticodon that will pair with the complimentary condon in mRNA during translation |
|
|
mRNA |
*messenger RNA Transcript of a region of the strands of DNA; carries info (as a sequence of condons) for the synthesis of one or more proteins |
|
|
Ribosome |
A small particle in the cell that is the site of protein synthesis |

