![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
89 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Kingdom Plantae Division: Hepaticophyta -What supergroup do they belong to? -Characteristics Specific to Plants -Adaptations enabling them to move onto land? -When did they show on fossil record? |
-Supergroup: Archaeoplastidia (members engulfed in cyanobacteria) -500 MYA during Precambrian -Characteristics: Multicellular eukaryotes, plastids, Chlorophyll A&B, Carotenoids, Cell walls of cellulose -Autotrophs (nutrients by photosynthesis) -Terrestrialization: Durable layer of sporopollenin that prevents them from drying out -Lack conductive tissue -Waxy cuticle -Gametes develop in gametangia for protection of embryo |
|

Hepatophyta (Liverworts) -How is the thallus flattened? -Gametophyte or Sporophyte? |
-Nonvascular and seedless, moist areas -Gametophyte: Leafy (80%), Thalloid (20%(=) |
|
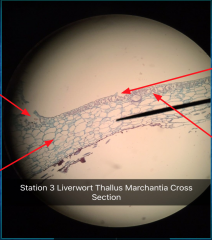
Function of upper section? Function of lower section? |
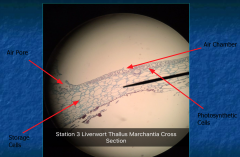
Upper section: Pores open to air chambers that surround chlorophyll and bearing cells for gas exchange Lower Section: Storage cells and rhizoids for water absorption |
|

Male (antheridia) vs Female (archegonia) receptacles |
Antheridia produces sperm Archegonia produces eggs |
|
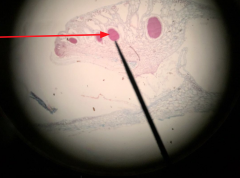
|
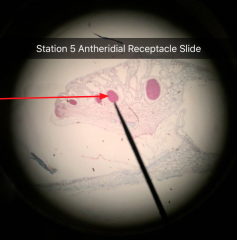
Antheridium Mother cell produces sperm |
|
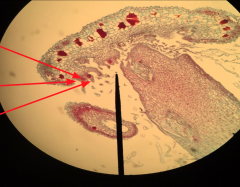
|
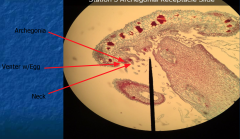
-Venter holds egg -Neck allows sperm to get to egg |
|
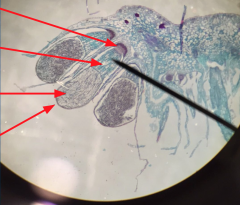
Haploid of diploid? What sex is the gametophyte? |
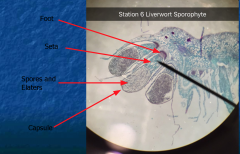
Elaters- dispersal, changes with a change in humidity Diplod (2n) -Female gametophyte attatched by seta |
|
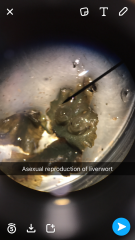
What are these? |
How are gemmae dispersed? -when it rains, water splashes out of cup -ensures conditions are right for gamma to germinate |
|

Is there a vein system present in the leaves? Gametophyte or sporophyte? |
No vein system Gametophyte |
|
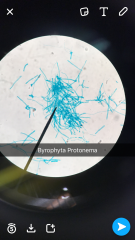
What are the two parts? |
Protonema and bud |
|
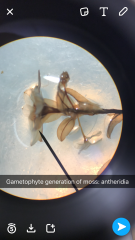
Male or female? |
-Protonema have buds that develop into leafy moss -Male: Flower like cluster of leaves at tip of gametophyte |
|
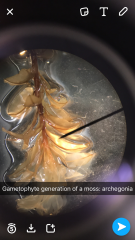
Male of female? |
Female: Leaves surround the tip |
|
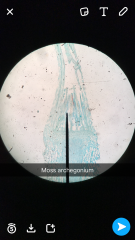
Female Where is the neck, paraphyses and venter? |
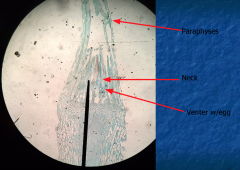
Neck is the thick tube Venter holds egg Paraphyses surrounds it |
|
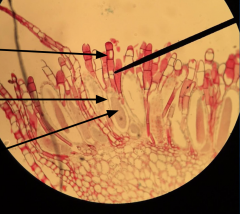
|
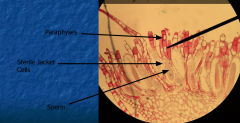
Sterile jacket is between the paraphyses which protects antheridia which is between the antheridium |
|

Sprophyte generation of a what? What sex is the Gametophyte |

Moss Female Capsule develops on seta |
|
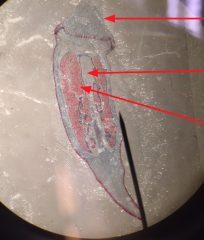
What is this? Haploid of Diploid? |
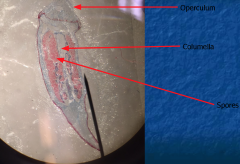
Sporophyte Capsule Haploid (M+F=Sporophyte) |
|

What category of seedless vascular plant is this? Gametophyte or sporophyte? What is a small leaf with one vein? What is a specialized leaf that produces sporangia? |
-Lycophyta -Sporophyte -Microphyll -Sporophyll |
|

What is this? Characteristics of pterophyta? Generation? |
Psilotum Do not have true roots or leaves but only stem Sporophyte |
|

Characteristics of horsetail Generation? Substance found in stem? Small cones at tip of stem? |
True stems (microphyll), true stem(silica), true roots Sporophyte Strobili |
|

Characteristics? Generation? Large leaves with more than one vein? Rolled up leaf? Specialized leaf for reproduction? |
True leaves, roots, stem Sporophyte Megaphyllis Fiddlehead=rolled up leaf -Sporophyll for reproduction |
|

Sori, frond, sporangium, indusium |
Sori: made of sporangia, small brown patches Indusium: Protective covering Ferns reproduce by spores |
|
|
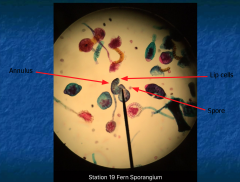
Annulus: heavy walled brownish cells that catapults spores out into environment through lip cells Monoecious |
|
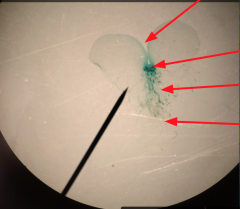
What is the antheridia? Archegonia? |
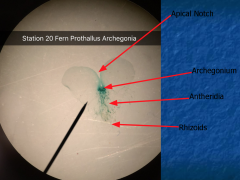
Prothallus and apical notch Rhizoids absorb and anchor Sporophyte grows out of archegonia |
|
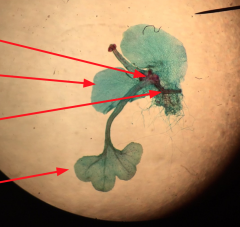
What happens to the gametophyte after the sporophyte begins to grow? |
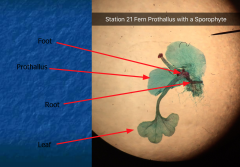
Prothallus dies off and sporophyte generation turns to a recognizable plant |
|
|
Seed plants What are characteristics specific to seed plants? Adaptations to land? Fossil record? |
-Seeds allow plants to move from mother with nourishment and protection -Sporopollenin prevents drying out -360 MYA Carboniferous |
|

What is first seen in the trunk of this plant in evolutionary time? |
Leaves found in cluster at the top of the trunk |
|
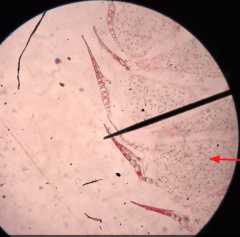
Male Cone What type of cell division produces pollen? |
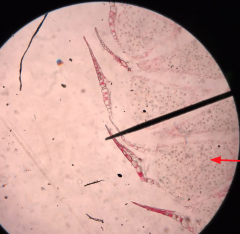
Meiosis |
|
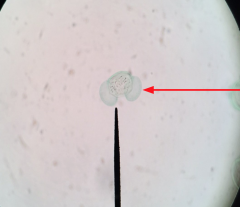
Pollen Grain What do the "wings" do? |
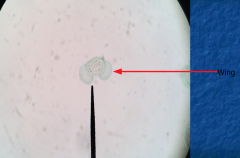
Dispersal |
|
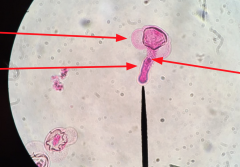
Pine Pollen Tube What actual cell produces the two perm cells? |
Spermatogenous cells |
|
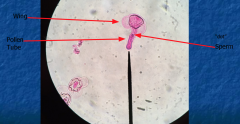
What does the megaspore produce? What is the function of the nucleus? What do the megaspores develop into? |
Megapores>4 megaspores Nucleus surrounds megaspore Megaspores develop to female gametophyte |
|
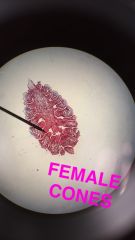
Female Cone with Mature Embryo What is the function of the nucleus? Cotyledons? What does the hypocotyl develop into? What does the ridicule develop into? |
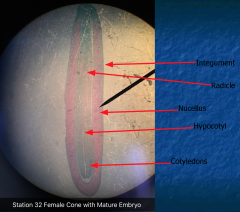
Nucleus: Protection Cotyledon: Food source Hypocotyl: Shoot system Radicle: Root system |
|
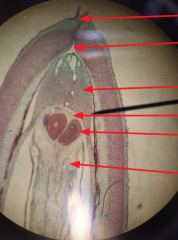
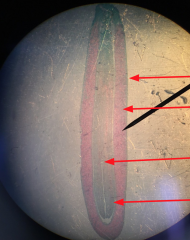
Pine Ovule with Mature Archegoneum Which structures are haploid?Diplod? |
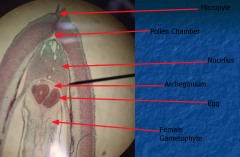
Haploid: Eggs Diploid: Nucleus and integument |
|

Parts of the flower: |
Petal, Sepal, Receptacle Stamen: Anther and filament Carpal: Stigma, Style, Ovary, Ovule |
|

Know about the cone life cycle |
Pollination n stuff lol |
|
|
Placentation Parietal Axile Free-Central |
Parietal: Top of the ovary; cucumber, zucchini (Seed on the outside) Axile: Middle- bell pepper- attached to inside Free-Central: Bottom: oranges attached to the middle but do not have big walls |
|

|
Axile placentation |
|

|
Parietal placentation |
|

|
Free-Central placentation |
|
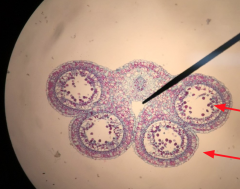
Male Gametophyte |
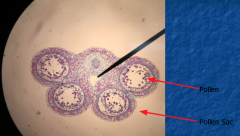
|
|
|
Fertilization What is cross pollination? What is he most common method to prevent flowers from pollinating themselves? |
Cross pollination: the transfer of pollen from one individual plant to another Self- incompatibility: biochemical block prevents the pollen from completing development |
|

Where is the pollen and the pollen tube? What three nuclei may be seen in a pollen tube? |
Sperm? |
|
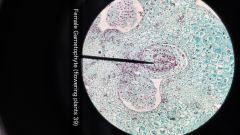
Where is the ovule, embryo sac, and 4 megaspores? |
Embryo sac holds the megaspores Ovule holds embryo sac |
|
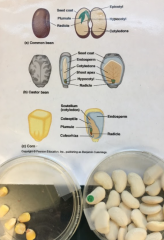
Different types of seed dispersal? Most efficient transporters of fruits and seeds? |
Types of dispersal: seed and anima Efficient transporter: Humans |
|

Know where the Exo, Meso, and Endocarp are |
Exo: skin Meso: white part Endo: flesh |
|
|
Drupe |
Olives, Almonds, Coconuts |
|
|
True Berry |
Tomato, Bell Pepper, Grape, Banana |
|
|
Pepos |
Cucumber, Zucchini |
|
|
Hesperidium |
Oranges, Lemon |
|
|
Aggregate |
Strawberries |
|
|
Multiple |
Pineapples |
|
|
Follicle |

Milkweeds, Magnolias |
|
|
Legume |

Peanuts, Peas, Beans |
|
|
Silique |

Mustards |
|
|
Capsule |
Irises, Snapdragons |
|
|
Achene |

Sunflower seeds, Dandelions |
|
|
Nuts |

Walnuts, Acorns, Brazil Nuts |
|
|
Grain |

Corn, Grasses |
|
|
Samara |

Maple, Ashes |
|
|
Schizocarp |

Parsley |
|
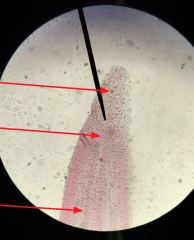
Regions of Root Tip |
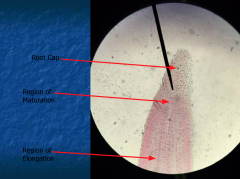
Root Cap Apical Meristem Region of Elongation Region of Maturation |
|
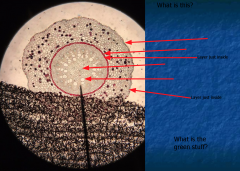
Three types of meristem origins? Three types of tissue? |
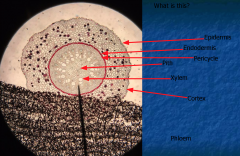
MONOCOT ROOT 1. Protoderm 2. Procambium 3. Ground meristem Epidermis- Outside layer Stele- Xylem, Phloem, Pericycle Cortex- Between stele and epidermis; Storage, Endodermis, Passage Cells |
|
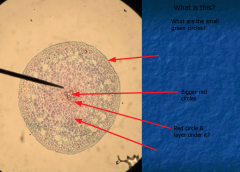
|
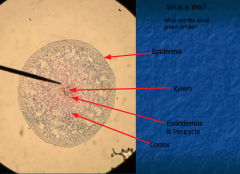
DICOT ROOT |
|
|
CARROT!! Where is the steele, cortex, and pericycle? |

|
|

What is the function? Which cells produce root hairs? How do they accomplish these functions? What conditions should the soil have for optimal growth? |
Function: Absorb water and dissolved minerals from soil Epidermal cells produce root hairs They increase absorptive surface Loosely packed soil allows for gas exchange |
|
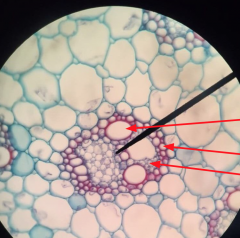
What is this? |
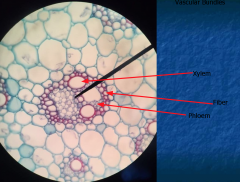
Xylem faces the pith, Phloem faces the cortex |
|
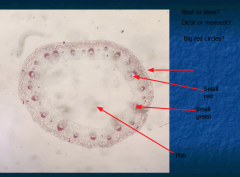
|
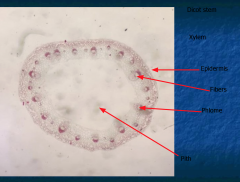
DICOT STEM Vascular bundles arranged in a ring There is a pith Fibers add support |
|

How does it differ from dicot? |
Vascular bundles scattered, no pith |
|

What is secondary growth? What two tissues produce it? |
Secondary growth- increase in girth Vascular Cambium (xylem and phloem) Cork Cambium (touch covering) |
|
|
Functions of Pith Primary Xylem Secondary Xylem Vascular Cambium Secondary PHloem Primary Phloem Cortex Phelloderm Cork Cambium Cork Cells |
Pith: Storage Primary Xylem: Move water and minerals upward Secondary Xylem: Move water and minerals upward Vascular Cambium: Produces Secondary Growth Secondary Phloem: Moves nutrients around plant Primary Phloem: Moves nutrients around plants Cortex: Storage Phelloderm: Made up of parenchyma cells Cork Cambium: Produces phelloderm and cork cells Cork Cells: Physical barrier for protection |
|
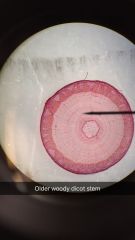
How old is this? |
6 |
|

What is heartwood? What is sapwood? |
Heartwood is darker wood, only for water and support Sapwood: Younger, water movement |
|
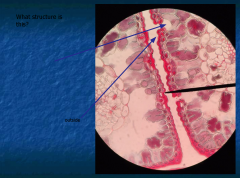
What type of xylem cells do conifers have? What is the common name of the wood from conifers? What xylem do woody dicots have? What is the common name? Function of spiral vessel elements? |
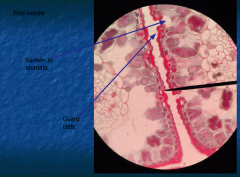
1. Conifers have Trachids, commonly called soft wood 2. Xylem has spiral cells; called vessel elements Carry water up stem |
|
Function of leaves? Three regions of leaves? |
Photosynthesis Epidermis, mesophyll, veins (vascular bundles) |
|
|
Structures of Epidermis |
Cuticle, Upper/lower epidermal cells, Guard cells, stomates |
|
|
Structures of Mesophyll |
Pasllisade Layer & Spongy Layer |
|
|
Structures of veins |
Vascular bundles |
|
What regulates guard cells? What is occurring when the stomates are closed? Open? |
Turgor pressure regulates guard cells Empty when closed Full when open |
|
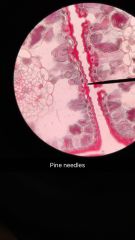
Why are they shaped this way? What adaptations minimize water loss? |
They adapted to living in air conditions Recessed (sunken) stomates minimize water loss |
|

|
Lacks nitrogen or potassium |
|

|
Lacks Phosphorous or Nitrogen |
|

|
Lacks Phosphorous or Nitrogen |
|

|
Lack Potassium |
|

Distribution, Capture Prey, Nutrition |
Pitcher Plant -Damp, boggy soil -Funnel shaped leaves covered with nectar glands and curved teeth -Insect lands and sticks>falls into fluid -Deficient in nitrate and phosphate |
|

Distribution, Capture Prey, Nutrition |
Sundew -Acidic, boggy soil (roadside ditches) -Modified leaves with stalked glands (tentacles) that contain viscid mucus -Catch only smaller or weak prey -Deficient in Nitrates |
|

Distribution, Capture Prey, Nutrition |
Venus Fly Trap -Damp, boggy soil -Modified leaves contain 2 lobes -Each lobe has outer area with trigger hairs that signal leaves to close on prey -Deficient in nitrate |
|
|
Giberellin and Seed Germination/Stem Growth Positives and negatives |
Positive: Flower shoots Negative: cause problems if stem grows too quickly |
|

Does the shoot represent negative or positive gravitropism? How do plants tell up from down? What hormone is responsible for this bending |
-Negative -Plants set the setting of statoliths (plastids with heavy starch grain) -Auxin is responsible for bending -Cells at the bottom of the plant are more affected than upper cells and elongate faster "bending" upward |
|

What part of the plants detects light? What part of the plant actually has the bending response? What hormone is thought to be responsible for the bending response? What is actually happening at the cellular level to cause this bending response? |
-Tip of the plant detects light -Stem bends in response -Auxin causes it to bend -Cells away from the light are affected by more auxin and bends the plant to light |
|

What is the name of the specialized cell that allows for this movement? Why do plants do this? |
Pulvini at the base of the plant leaf facilitates growth This is a dorm of presumptive defense from predators |

