![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
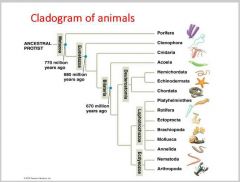
What is an Animal? |
-multicellular - Heterotrophic, Eukaryotic organsim - Cells lack cell wall, instead held together by structural proteins (collagen) - nervous and muscle tissue - most reproduce sexually with dominant diploid stage |
|
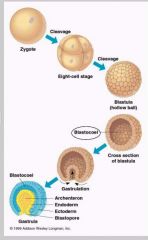
What are the four stages of development? |
1. zygote (cleavage) 2. Morula 3. Blastula 4. Gastrula - Blastopore -Archenteron -Two layers of tissue: endoderm and ectoderm3 |
|
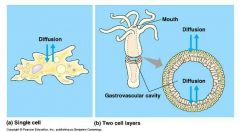
Organization level: who has cellular level and who has tissue level? Definition of Tissue level: group of cells working together to perform a function that are separated by membranous layers |
-Cellular level: Porifera (Sponges) -Tissue level: all others |
|
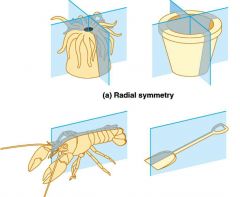
Body symmetry: who has radial symmetry and who has bilateral symmetry? |
Radial symmetry: Cnidaria and Ctenophora Bilateral symmetry: all others |
|
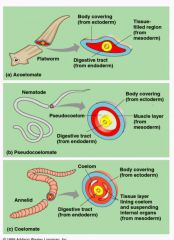
Body cavities: what are the three body cavities and who possess them? |
Acoelomate: Platyhelminthes (flatworms) Pseudocoelomates: Nematoda (roundworms) Coelomate: all others |
|
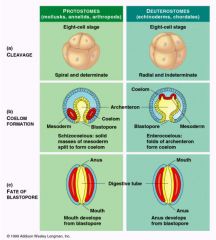
Development: Protostomes 1. Who are protostomes 2. cleavage 3. Coelom Formation 4. Fate of Blastopore |
Protostomes include: Mollusca (calms, snails), Annelida (segmented worms), Arthropoda (crustaceans, insects) -Cleavage: spiral and determinate -Coelom Formation: schizocoelous -Fate of Blastopore: mouth |
|
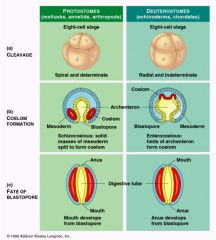
Development: Deuterostomes 1. who is included in deuterstomes 2. cleavage 3. coelom formation 4. fate of blastopore |
Deuterostomes: Echinodermata (seastars), Chordata (vertebrates) -cleavage: radial and indeterminate - coelom formation: Enterocoelous -fate of blastopore: anus |
|
|
Segmentation: who segmented and soft/hard? -Mollusca -Annelida -Arthropoda -Chordata |
-Mollusca: soft and unsegmented -Annelida: soft and segmented -Arthopoda: hard and segmented -Chordata: segmented |
|
|
Definition of tissues: |
Tissues: group of cells with a common structure and function separated by a membrane |
|
|
Tissue types: definition and name of cells -epithelial -connective -nervous -muscle |
-Epithelial (stratified squamous, simple columar): tightly packed cells used for lining. -Connective (Bone, blood, and cartilage): cells scattered through an extracellular matrix. -Nervous (neurons): transmits signals. -Muscle (smooth, skeletal, cardiac): fibers for contration. |
|
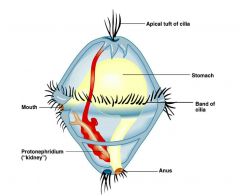
name the larva? know the structure: |
Trochophore larva |
|
name the larva? |
Lophophorate larvae |
|

know what Ecdysis is? |
Ecdysis: shedding outer cuticle |
|
|
Porifera are mostly marine, how many species are there? How many species are frreshwater? |
9000 species, 100 freshwater |
|
|
what type of symmetry do Porifera have? |
asymmetrical |
|
|
T/F: Porifera are sessile |
true |
|
|
T/F: Porifera are hermaphrodites |
true |
|
|
what is a "sleeze"? |
Porifera often live in groups called a sleeze |
|
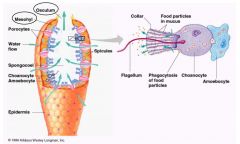
name of the flagellated cells found in porifera? |
choanocyte |
|
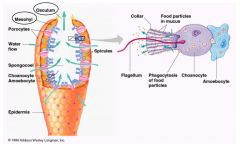
Pseudopodia found in Porifera is called? |
Amoebocyte |
|
|
Poriferas' skeleton: what makes up their skeleton? |
spicules: calcium carbone or silica spongin: protein |
|
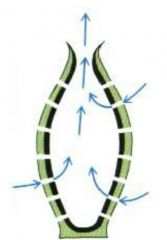
Water movement in Asconoid? where are the flagellated cells? |
Asconoid: flagllated spongocoel -Ostia, spongocoel, osculum |
|
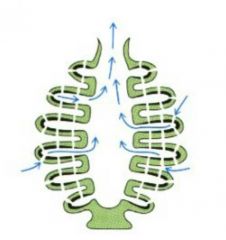
water movemenet in syconoid? where are the flagellated cells? |
syconoid: flagellated radial canals -ostia, incurrent canal, prosopyle, radial canal, apopyle, spongocoel, osculum |
|
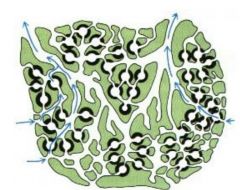
water movement in leuconoid? where are the flagellated cells? |
leuconoid: flagellated chambers -ostia, incurrent canal, flagellated chamber, excurrent canal, osculum |
|
Class: Calcarea 1. skeleton made up of? 2. which body forms? |
Class: Calcarea -calcium spicules -asconoid, syconoid, leuconoid |
|

Class: Hexactinellidae 1. whats the skeleton made up of? 2. which body forms do they have? |
Class: Hexactinellidae - silica spicules - syconoid, and leuconoid |
|

Class: Demospongiae 1. what is the skeleton made up of? 2. what body forms does it have? |
Class: Demospongiae -silica spicules and/or spongin - leuconoid |
|
|
Phylum: Cnidaria 1. who is included? 2. symmetry? 3. tissue layers? 4. body forms? 5. name of cavity they have? |
Phylum: Cnidaria - includes: hydras, jellies, sea anemones, and coral - Diploblastic: endoderm and ectoderm - Two body forms: polyp and medusa - Gastrovascular cavity |
|
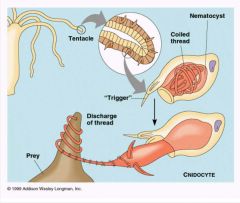
Cnidocytes: 1.whate are nematocyst? 2. what are Cnidocil? |
nemetocyst: thread with barbs cnidocil: trigger |
|

Class: Hydrozoa 1. who does it include? 2. where do most of species live? 3. which body forms do they possess? which body form is colonial? 4. how do they reproduce asexually? sexually? |
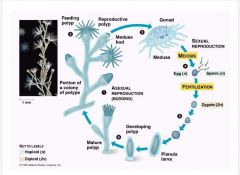
Class: Hydrozoa -portuguese man of war, hydra, obelia -most species are marine -most species have a polyp and medusa stage (polyp stage often colonial) -Reproduction: asexual (budding), sexual (zygote and larvae-planula) |
|

Class: Scyphozoa 1. common name? 2. where do they live? 3. what happened to their polyp stage? 4. What does the medusa stage live? |
Class: Sycphozoa -all are marine -polyp stage reduced or absent -medusa stage is free living |
|

Class: Anthozoa 1. where do they live? 2. which body form stage is dominant? 3. is there a medusa stage? |
Class: Anthozoa -all are marine -polyp stage dominant -no medusa stage |
|

Class: Cubozoa 1. which jellies are included? 2. complex eye belong to which body form stage? 3. which species can kill 60 people? |
Class: Cubozoa -box jellies -complex eyes embedded in medusa stage -sea wasp venom can kill 60 poeple |
|
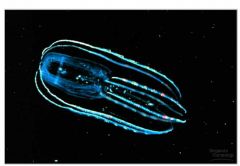
Phlyum: Ctenophora 1. who is included? 2. what do their plates contain? 3. what are they known for? 4. what do their tentacles have? 5. what are colloblasts? |
Phylum: Ctenophora -comb jellies -contain plates with cilia -largest animal to move with cilia -tentacels with colloblasts (adhesive cells) |
|
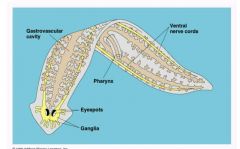
phylum: Platyhelminthes 1. who does it include? 2. what type of body cavity? 3. what body cavity does it have instead? 4. level of organization? 5. tissue layers? |
Phylum: Platyhelminthes -flatworms -acoelomates -gastrovascular cavity -organ system level of organization -triploblastic |
|
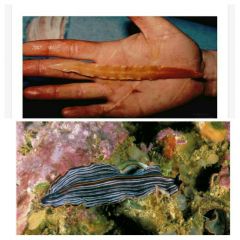
Class: Turbellaria 1. where do they live and what type of live style? 2. the concentration of sense organs at the anterior end of the body 3. type of cavity? 4. special ability? |

- free living and mostly marine -cephalization -gastrovascular cavity -regeneration |
|
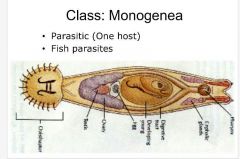
Class: Monogenea 1. what type of parasite? |
-fish parasite |
|
|
Class: Trematoda 1. what type of parasitic fluke? 2. how many hosts? 3. the female fits into what groove? 4. what type of dermatitis and how? 5. how many species? |
Class: Trematoda -endoparastic flukes -two hosts -female fits into groove on male body -swimmer's dermatitis: larvae enters skin (larvae in skin can't complete life cycle in humans) -Two species: Schistosoma and Clonorchis |
|
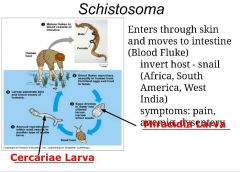
Class: Trematoda- Schistosoma (blood fluke) 1. how does it enter the body? 2. what is the invert host? 3. where is it found? 4. symptoms? |
Class: Trematoda- Schistosoma (blood fluke) -enters through skin and moves to intestine -invert host is a snail - Africa, South AMerica, West India -symptoms: pain, anemia, and dysentery |
|
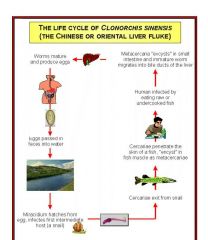
Class: Trematoda- Clonorchis (liver fluke) 1.how does it enter the body? 2. what is the invert host? 3. where is it found? 4.symptoms? |
Class: Trematoda-Clonorchis (liver fluke) -enters by eating raw fish and moves to bile ducts -invert host is a snail -China, Aisa, Japan -symptoms: Cirrhosis of the liver, death |
|
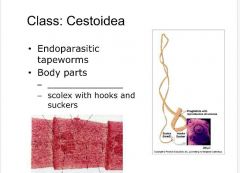
Class: Cestoidea 1. what type of parastic tapeworm? 2. what are the body parts? 3. The five species that belong is this class? |
Class: Cestoidea -endoparastic tapeworms -body parts: proglottids and scolex with hooks and suckers -Five species: Taenia saginata, Taenia solium, Diphyllobothrium latum, Dipylidium caninum, Echinococcus |
|
|
Class: Cestoidea-Taenia saginata -Beef tapeworms (adult) -undercooked beef containing cysticercus larvae -definitive host: humans -intermediate host: cattle |
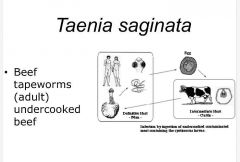
|
|
|
Class: Cestoidea- Taenia solium -pork tapeworms (adult) -undercooked pork containing cysticercus larvae -definitive/ accidental intermediate host: humans - intermediate host: pigs and humans |
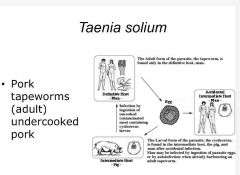
|
|
|
Class: Cestoidea- Diphyllobathrium latum -fish tapeworm (adult) -undercooked fish -definitive host: humans -1st intermediate host: copepod -2nd intermediate host-fish -3rd intermediate host: predatious fish |
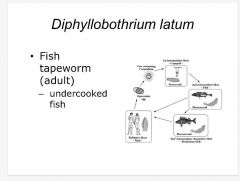
|
|
|
Class: cestoidea- Dipylidium canium -dog tapeworm -undercooked dog |

|
|
|
class: cestoidea- Echinococcus -unilocular hydatid (cyst) -association with dogs and ruminants |
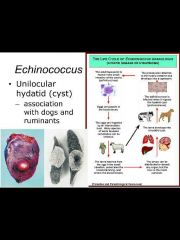
|
|
|
Pseodocoelmates -includes the phyla: Rotifera and Nematoda -false cavity: store nutrients, movement, hydrostatic skeleton, and space for organ development |

|
|
|
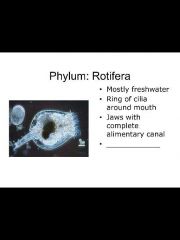
Phylum: rotifera -mostly freshwater -ring of cilia around mouth - jaws with complete alimentary canal - parthenogenesis |
|
|
|
phyla: lophophorate -ectoprocta (Bryozoans): colonial and moss-like -Phoronids: marine tube worms -Brachiopods: lamp shells |

|
|
|
Phylum: Nemertea-Proboscis worms (ribbon) -closed circulatory system -complete digestive tract |

|
|

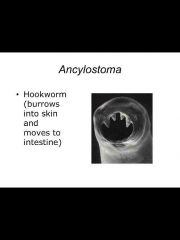
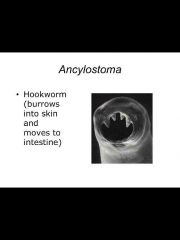
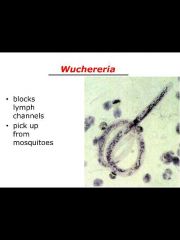
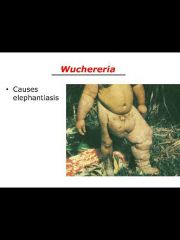
Six species that belong to this phylum: Ancylostoma, enterobius, ascaris, trichinella, wuchereria, dracunuclus |

|
|
Phylum: Nematoda |
Phylum: Nematoda |
|

Phylum: Nematoda |

Phylum: Nematoda |
|

Phylum: Nematoda |

Phylum: Nematoda |
|

Phylum: Nematoda |

Phylum: Nematoda |
|
Phylum: Nematoda |
Phylum: Nematoda |
|

Phylum: Nematoda |

Phylum: Nematoda |
|
|

|
|

|
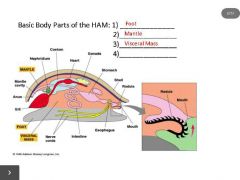
4) radula |
|

class: Polyplacophora (chitons) |
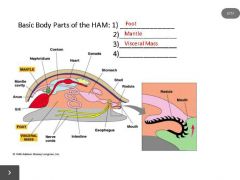
4. radula |
|

|

|
|

|

torision |
|

radula |
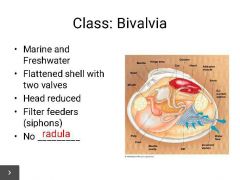
|
|

closed |

closed |
|

Class: Oligochaeta-earthworms |

no parapodia |
|

|

|
|

1. Open circulatory systems 2. Closed circulatory systems |
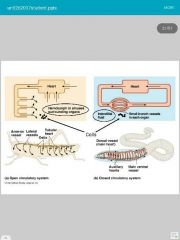
|
|
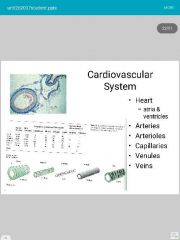
|
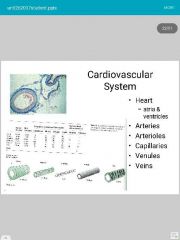
|
|

Phlyum: Onychophora |

|
|

|

|
|

|

Subphlyum: Trilobita |
|

|

|
|
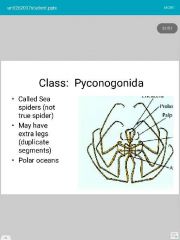
|
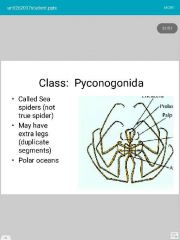
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|

|

class: chilopoda (left)class: diplopoda (right) |
|

|
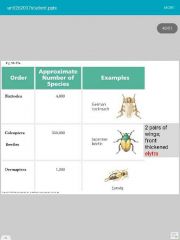
|
|
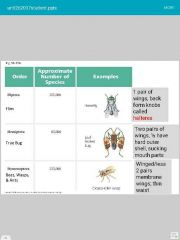
|

|
|

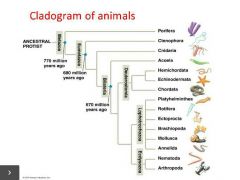
Deuterostomes |

|
|
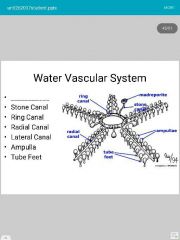
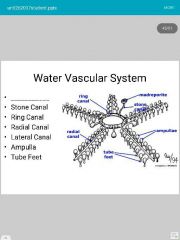
madreporite |
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
|

|
|

|

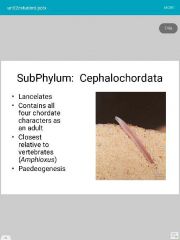
Notochord |
|

|
|
|

|
|
|

|

|
|

|

|
|
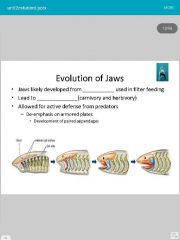
1. Gill arches 2. Moving jaws |

1. Cartilage 2. Placoid 3. Liver |
|

1. Viviparity 2. Oviparity 3. Ovoviviparity |

|
|

Operculum |

|

