![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
21 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What type of egg is a unfertilized Starfish egg?
|

Isolecithal
|
|
|
Fertilized Egg Starfish
|
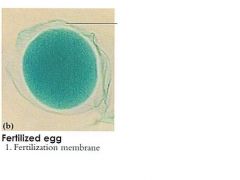
fert starfish, you can see the hazyness meaning it devolping fast block to polyspermy. AKA Fertilzation envolope
|
|
|
2 cell stage of Starfish
|

starfish holoblastic cleavage
isoelthical |
|

Blastula can be indentified how?
|
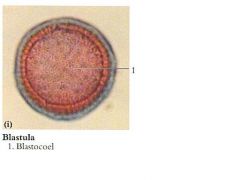
by to complete formation of the blastocoel
|
|
|
Early gastrula can be identified by?
|

Beginning formation of blastopore and archenteron
|
|
|
What is the difference between early and late gastrula
|

Deeper archenteron (5)
|
|
|
What does frog early cleavage look like? Which is the animal pole?
|
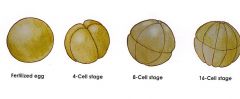
Blastomeres 2 4 8 16 cell stage
very Moderately telolectihal and holoblastic(almost complete even cleavage) Animal pole has more cleavage more blastomeres!!!! |
|
|
Late cleavage is determined by?
|

blastocoel forming in the middle
|
|
|
What does the blastula have?
|

Blastocoel
|
|
|
What does the frog have in the gastrula stage?
|
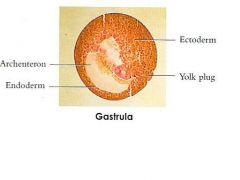
Yolk plug, archenteron
|
|
|
What is the difference between early neural tube stage and late in the frog?
|
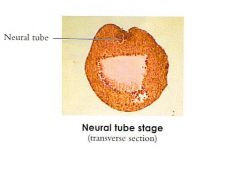
The neural tube not fully devolped, the neural grove and neural folds presnt and the gut is not devolped (archenteron still visible)
|
|
|
Late neural stage in Frog
|

Gut is present fully devolped neural tube and notocord
|
|
|
What is begining to form in 18 hour chick?
|
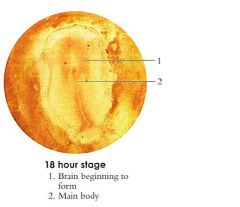
Beginning brain
Also chick is a telolecithal egg with meroblastic cleavage Ectoderm = nervous system |
|

What is beginning to form in 21 hour chick?
|

Spinal Cord also the neurla folds are devolped around the beggining spinal cord.
|
|

What is beginning (visible) form in 48 hour chick?
|

Otic and optic vsicle
Somites are the block like structures along the thin spinal cord. Vitelline blood vessels (not seen here) are tree branch like sturcuters exending out from the bottom somite |
|
|
What is the anterior and posterior limb buds look like in 96 hour chick and where are they located?
|

Anterior(wing)behind heart posterior(legs)near the tail
|
|
|
Are the animals we looked at deuterostome or protosome?
|
They are all deuterostome meaning the blastopore becomes the anus.
|
|
|
What types of eggs are the Starfish, Frog, and chick. What type of cleavage pattern do they follow?
|
The starfish is isolecithal,and the Frog mesolecithal and the chick is teloecithal.
Holoblastic cleavage, or division of the entire egg, occurs in species whose eggs have little or moderate amounts of yolk, such as sea urchins, frogs, and mammals. the Chick is the meroblastic cleavage pattern uneven. |
|
|
What does the ectoderm become?
|
The outermost of the three primary germ layers in animal embryos; gives rise to the outer covering and, in some phyla, the nervous system, inner ear, and lens of the eye.
|
|
|
What does the endoderm become?
|
The innermost of the three primary germ layers in animal embryos; lines the archenteron and gives rise to the liver, pancreas, lungs, and the lining of the digestive tract.
|
|
|
What does the mesoderm become?
|
The middle primary germ layer of an early embryo that develops into the notochord, the lining of the coelom, muscles, skeleton, gonads, kidneys, and most of the circulatory system.
|

