![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Autotroph |
posses chlorophyll and produces oxygen and carbohydrates via photosynthesis |
|
|
Heterotroph |
obtains food as saprophytes (dead or decaying organisms) or parasites |
|
|
Saprobe |
obtains nutrition by breaking down and feeding on dead or decaying organic matter |
|
|
Parasite |
obtain nutrients by other living organisms |
|
|
Mutualism |
symbiosis that is beneficial to both organisms |
|
|
Mitosis |
a type of cell division that results in 2 daughter cells each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus |
|
|
Meiosis |
a type of cell division that results in 4 daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell (gametes/spores) |
|
|
Haploid |
(n); having a single set of unpaired chromosomes |
|
|
Diploid |
(2n); containing two complete sets of chromosomes |
|
|
Dikaryotic |
(n+n); each compartment of a hypha contains two nuclei, each derived from a different parent |
|
|
Gamete |
a mature haploid germ cell that can unite with the opposite sex in reproduction to form a zygote |
|
|
Sperm |
a mature, motile male sex cell (compact head and long flagella) |
|
|
Egg |
reproductive body produced by female |
|
|
Spore |
a minute, one-celled, reproductive unit capable of giving rise to new individuals without sexual fusion |
|
|
Fertilization |
fusion of male and female gametes to form a zygote |
|
|
Plasmogamy |
cytoplasm of two parent mycelia fuse together without nucleus fusion |
|
|
Karyogamy |
final step of fusing two haploid eukaryotic cells, specifically nucleus fusion |
|
|
Zygote |
a diploid cell resulting from fusing two haploid gametes |
|
|
Embryo |
multicellular diploid eukaryote in the earliest stages of development; fertilization to birth, hatching or germination |
|
|
Sporangium (pl. sporangia) |
spore containing vesicle; a receptacle in which asexual spores are formed |
|
|
Haplodiplontic life cycle (Alternation of Generations) |
an alteration between a muticellular haploid generation and a multicellular diploid generation |
|
|
Haplontic life cycle |
a life cycle in which only the haploid phase is multicellular (e.g. basidiomycete life cycle) |
|
|
Diplontic life cycle |
a life cycle in which only the diploid phase is multicellular (e.e. human life cycle) |
|
|
Gametophyte |
gamete-producing plant; gamete producing, usually haploid phase, producing the zygote from which the sporophyte arises in dominant form of bryophytes |
|
|
Sporophyte |
spore-producing plant; asexual and usually diploid phase, producing spores from which gametophyte arise |
|
|
Isomorphic alternation of generations |
sporophyte and gametophyte have the same morphology (e.g. Ulva) |
|
|
Endosymbiosis |
symbiosis in which one of the symbiotic organisms lives inside the other |
|
|
Seven characteristics of living things |
1. Cellular organization 2. Ordered complexity 3. Sensitivity 4. Growth, development, and reproduction 5. Energy utilization 6. Homeostasis 7. Evolutionary change |
|
|
Prokaryota |
-no nuclear membrane/no defined nucleus -autotrophic (possess chlorophyll & produce O2/carbs by photosynthesis -theory of endosymbiosis - Cyanobacteria--"blue green algae" |
|
|
Eukaryota |
defined nucleus and organelles present |
|
|
Unikonta |
characterized by their single-flagellum |
|
|
Amoebozoa |
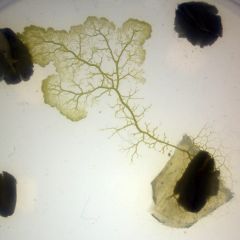
-pseudopod (extension of cytoplasm for movement and food intake) -(plasmodial & cellular) -Slime molds (e.g. Physarum sp.) -non reproductive stage moves with food supply -protoplasm develops into a sporangium |
|
|
Opisthokonta |
posterior flagellum -animals, fungi and choanoflagellates |
|
|
Fungi |
-heterotrophs (saprobe or parasite) -not photosynthetic -cell wall of chitin, terrestrial and filamentous (hypha) -many hyphae = mycelium (pl. mycelia) -basidiomycetes and zygomycete |
|
|
Basidiomycete |

-Agaricus bisporus -hyphae are dikaryotic (n+n) -hyphae grow underground and mushrooms grow on the outer edge of mycelium |
|
|
Zygomycete |
-Rhizopus sp. (bread mold) -saprobe -mycelium grows on bread and soft fruit -hyphae produce sporangia that have black spores (distributed by wind) -sexual reproduction (i.e. zygo = union) |
|
|
Asomycete |
-Candida albicans (disease) -"yeast" infection or vaginitis -Penicillium sp. |
|
|
Choanoflagellates |
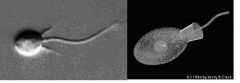
-unicellular -colonial (mostly) -funnel shaped collar and single flagellum |
|
|
Excavata |
-grooves on the side of their bodies for feeding -Euglenozoans -chloroplasts and mitochondria - mixotroph or autotroph -motile |
|
|
Rhizaria |
-unicellular -heterotrophic -marine, fresh water |
|
|
Chromalveolata |
result from one or more endosymbiotic events
|
|
|
Alveolata |
-flattened vesicles (alveoli under plasma membrane) -dinoflagellates; two flagella, marine and freshwater, mixotrophic, unicellular -apicomplexans; apical complex used to enter host, gametes have flagella/pseudopods, parasitic -ciliates; unicellular of colonial, dikaryotic, motile because of cilia, sexual or asexual |
|
|
Stramenopila |
thread-like hair on flagellum (brown algae and diatoms) |
|
|
Brown algae |

-kelps -algal body = thallus -holdfast (anchors to substrate) , stipe, blade and bladder (tip of blade & allows to float) -haplodiplontic life cycle - Fucus sp. |
|
|
Diatoms |

-double shells made of silica -unicellular -autotroph |
|
|
Oomycetes |

-zoospores have two flagella (not fungi) one forward and one backward -Saprolegnia sp. (fly fungus/"water mold") -thread-like hyphae (fuzzy growth on fly) -lost photosynthetic ability
|
|
|
Archaeplastida |
plantae -glaucophytes (unicellular algae), red algae, green algae and land plants |
|
|
Green Algae |
chlorophyll pigments mostly aquatic (marine/freshwater) some are symbiotic |
|
|
Red Algae |

haplodiplontic short holdfast so shallow water
|
|
|
Chlorophytes |
one of the two groups of green algae diverse from unicellular to colonial to multicellular |
|
|
Volvox spp. |
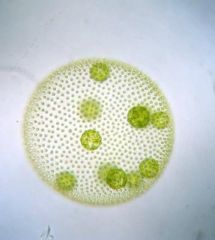
microscopic and colonial motile colony (2 flagella) daughter cells found in vegetative body
|
|
|
Ulva spp. |

sea lettuce large green marine alga haplodiplontic isomorphic life cycle
|
|
|
Zygnetales |

Spirogyra spp. -microscopic and filamentous green alga -single spiral chloroplast -pyrenoids store starch |
|
|
Charophytes |

closest living relative to land plants some have plasmodesmata do not undergo alternation of generations haplontic (sexually and asexually) Nitella sp. -oogonia inside bulbs -antheridia above the node |
|
|
Lichens |

fungi (asomycetes) and either green alga or cyanobacteria sensitive to toxic compounds (indicators of pollutants) fungi gets nutrients through algae photosynthesis green alga gets protection from environment |

