![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
142 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atom |
The smallest chemical unit of a type of pure substance (element) |
Example: carbon atom |
|
|
Molecule |
A group of joined atoms |
Example: DNA |
|
|
Organelle |
A membrane bounded structure that has a specific function within a cell |
Example: chloroplast |
|
|
Cell |
The fundamental unit of life. Multicellular organisms consist of many cells; unicellular organisms consist of one cell |
Example: leaf cell |
|
|
Tissue
|
A collection of specialized cells that function in a coordinated fashion (multicellular life only)
|
Example: Epidermis of leaf
|
|
|
Organ
|
A structure consisting of tissues organized to interact and carry out specific functions (multicellular life only)
|
Example: Leaf |
|
|
Organ System
|
Organs connected physically or chemically that function together (multicellular life only)
|
Example: aboveground part of a plant
|
|
|
Organism
|
A single living individual
|
Example: One acacia tree
|
|
|
Population
|
A group of the same species of organism living in the same place and time
|
Example: Multiple acacia trees
|
|
|
Community
|
All populations that occupy the same region
|
Example: all populations in a savanna
|
|
|
Ecosystem
|
The living and nonliving components of an area
|
Example: the savanna
|
|
|
Biosphere
|
The global ecosystem; the parts of the planet and its atmosphere where life is possible
|
|
|
|
Emergent Properties |
When components in an organism interact they create _______. |
|
|
|
Producers
|
(also called autotrophs) - make their own food by extracting energy and nutrients from nonliving sources
|
Example: plants
|
|
|
Consumers
|
(also called heterotrophs) obtain energy and nutrients by eating other organisms, living or dead
|
Example: humans
|
|
|
Decomposers
|
(also called heterotrophs) - obtain energy and nutrients from waste or dead organisms
|
|
|
|
Homeostatis
|
which a cell or organism maintains this state of internal constancy, or equilibrium
|
|
|
|
asexual reproduction
|
genetic information comes from only one parent; all offspring are virtually identical
|
Example: bacteria, strawberries, fungi, sponges
|
|
|
sexual reproduction
|
genetic material from two parent individuals unites to form an offspring; which has a new combination of inherited traits
|
|
|
|
Adaptation
|
an inherited characteristic or behavior that enables an organism to survive and reproduce successfully in its environment
|
|
|
|
Natural selection
|
is a process in which individuals with certain inherited characteristics contribute more offspring to the next generation than do individuals lacking those characteristics
|
|
|
|
Taxonomy
|
biological science of naming and classifying organisms
|
|
|
|
Species
|
designates a distinctive "type" of organism
|
|
|
|
Genus
|
Second word in taxonomy
|
|
|
|
Domains
|
the broadest (most inclusive) three taxonomics category
|
|
|
|
Three Domains
|
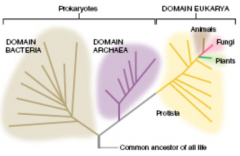
Domain Bacteria Domain Archaea Domain Eukarya |
|
|
|
Domain Bacteria
|
Cells lack nucleui (prokaryotic) Most are unicellular |
|
|
|
Domain Archaea
|
Cells lack (prokaryotic) Most are unicellular |
|
|
|
Domain Eukarya
|

Cells contain nuclei (eukarotic) Unicellular or multicellular |
|
|
|
Kingdoms
|
Protista (multiple Kingdoms) Kingdom Animalia Kingdom Fungi Kingdom Plantae |
|
|
|
Scientific method
|
general way of using evidence to answer questions and test ideas
|
|
|
|
Four steps of scientific method
|
1. Observations and questions 2. Hypothesis and Prediction 2. Data collection 4. Analysis and peer review |
|
|
|
Hypothesis
|
tentative explanation for one or more observations
|
|
|
|
Predictions
|
written as an if-then statement
|
|
|
|
Experiment
|
tests a hypothesis under controlled conditions
|
|
|
|
Peer review
|
scientists independently evaluate the validity of the methods, data, and conclusions
|
|
|
|
variable
|
changeable element of an experiment
|
|
|
|
independent variable
|
the variable being manipulated or changed
|
|
|
|
dependent variable
|
the observed result of the independent variable being manipulated
|
|
|
|
standardized variable
|
a variable which is maintained as a constant in all aspects
|
|
|
|
placebo
|
an inert substance that resembles the treatment given to the experimental group
|
|
|
|
statistical significance
|
the probability that results arose purely by chance
|
|
|
|
theory
|
an explanation for a natural phenomenon
|
|
|
|
technology
|
practical application of scientific knowledge
|
|
|
|
matter
|
any material that takes up space
|
|
|
|
element
|
a pure substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into other substances
|
|
|
|
bulk elements
|
required in the largest amounts because they make up the vast majority of every living cell Four more abundant bulk elements: Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogenadditional: phosphorus (P), sodium (Na), magnesium (Mg), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) |
|
|
|
Trace elements
|
required in small amounts Iron (FE) and zinc (Zn) |
|
|
|
What is an atom composed of? (3 types of subatomic particles)
|
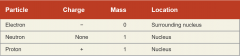
Protons, Neutrons, Nucleus |
|
|
|
Protons
|
carry a positive charge
|
|
|
|
Neutrons
|
uncharged
|
|
|
|
Nucleus
|
formed by protons and neutrons together protecting, controlling access to DNA |
|
|
|
atomic number
|
the number of protons in the nucleus
|
|
|
|
ion
|
is an atom (or group of atoms) that has gained or lost electrons and therefore has a net negative or positive charge
|
|
|
|
atomic weight
|
average mass of all isotopes
|
|
|
|
radioactive
|
means they emit energy as rays or particles when they break down into more stable forms
|
|
|
|
Isotope
|
any different forms of the same element, distinguished from one another by the number of neutrons in the nucleus
|
|
|
|
Compound
|
a molecule composed of two or more different elements
|
|
|
|
orbitals
|
chemist use to describe the most likely location for an electron relative to its nucleus |
|
|
|
valance shell
|
outermost occupied energy shell
|
|
|
|
electronegativity
|
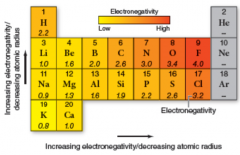
measure the atom's ability to attract electrons on a scale of 0 to 4
|
|
|
|
chemical bond
|
an attractive force that holds atoms together
|
|
|
|
ionic bond
|
bond between oppositely charged ions
|
|
|
|
covalent bond
|
bond between atoms sharing pairs of electrons |
|
|
|
polar covalent bond
|
a lopsided union in which one nucleus exerts a much stronger pull on the shared electrons than does the other nucleus Electronegativity difference between atoms is moderate or large (0.4-1.7) |
Example: O---H bond within water molecule
|
|
|
nonpolar covalent bond
|
a "bipartisan" union in which both atoms exert approximately equal pull on their shared electrons. Electronegativity difference between atoms is small (<0.4) |
Example: H---H bond in H2 molecule
|
|
|
hydrogen bond
|
bond between atom with a partial negative charge and a hydrogen atom with a partial positive charge
|
|
|
|
adhesion
|
the tendency to form hydrogen bonds with other substances
|
Example: when water soaks into a paper towel, it is adhering to the molecules that make up the paper
|
|
|
solutes
|
dissolve
|
|
|
|
solvent
|
a chemical in which other substances dissvole
|
|
|
|
solution
|
consists of one or more solutes dissolved in a liquid solvent
|
|
|
|
hydrophilic
|
substances are either polar or charge, so they readily dissolve in water (term means "water-loving")
|
Examples: sugar, salt, and ions
|
|
|
Evaporation
|
conversion of a liquid into a vapor
|
|
|
|
reactants
|
starting paterials
|
|
|
|
products
|
results of the reaction
|
|
|
|
alkaline
|
basic solution; solution has a pH greater than 7
|
|
|
|
buffers
|
pairs of weak acids and bases that resist pH changes
|
|
|
|
More acidic pH level
|
The higher the H+ concentration, (pH<7) |
|
|
|
More basic pH level
|
The lower the H+ concentration, (pH>7)
|
|
|
|
Neutral pH level |
pH of 7 |
|
|
|
dehydration synthesis reaction
|
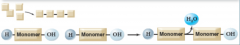
joins monomers into polymers.
|
Example: protein called an enzyme removes an ----OH (hydroxyl group) from one molecule and hydrogen atom from another forming H2O and a new covalent bond between the two smaller components
|
|
|
hydrolysis |
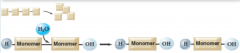
breaks polymers into monomers
|
Example: enzymes use atoms from water to add a hydroxyl group to one molecule and a hydrogen atom to another (means "breaking with water") |
|
|
carbohydrates
|
monomer for monosaccharide
|
|
|
|
monosaccharides
|
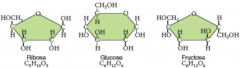
Smallest of carbohydrates, contain five or six carbon atoms
|
|
|
|
disaccharide
|
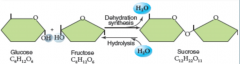
("two sugars") two monosaccharides joined by dehydration synthesis
|
|
|
|
oligosaccharides
|
Complex carbohydrates. consists of three to 100 monomers. |
|
|
|
polysaccharides
|
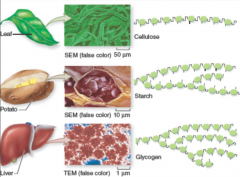
("many sugars") are huge molecules consisting of hundreds or thousands of monosaccharide monomers
|
|
|
|
protein
|
monomer for amino acid
|
|
|
|
amino acids |
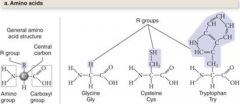
has a central carbon atom bonded to four other atoms or groups of atoms |
|
|
|
R group
|
the fourth is a side chain
|
|
|
|
peptide bond
|
forms by dehydration synthesis, is the covalent bond that links each amino acid to its neighbor
|
|
|
|
polypeptides
|
chains with 100 or more amino acids
|
|
|
|
Primary Structure
|
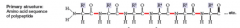
amino acid sequence of polypeptide (not touched slinky)
|
|
|
|
Secondary Structure
|
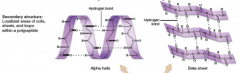
localized areas of coils, sheets, and loops within polypeptide (stretched slinky)
|
|
|
|
Tertiary Structure
|

overall shape of one polypeptide (mixed of slinky)
|
|
|
|
Quaternary Structure
|
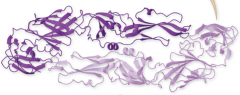
take two or more tertiary structures (multiple slinkys mixed together) |
|
|
|
nucleic acid
|
monomer for nucleotide
|
|
|
|
Two types of nucleic acids
|
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) Ribonucleic acid (RNA) |
|
|
|
Nucleotide
|
monomer consists of three components
|
|
|
|
nitrogenous base
|
adenine (A) guanine (G) thymine (T) cytosine (C) uracil (U) |
|
|
|
The nitrogenous bases DNA contain
|
adenine (A) cytosine (C) guanine (G) thymine (T) |
|
|
|
The nitrogenous bases RNA contain
|
adenine (A) cytosine (C) guanine (G) uracil (U) |
|
|
|
triglyceride
|
consists of three long hydrocarbon chains
|
|
|
|
trace
|
Iron and zinc are examples of ____ elements because they are required in small amounts by living things
|
|
|
|
radioactive isotope
|
Another name for an unstable isotope is a(n)
|
|
|
|
monosaccharides
|
The smallest carbohydrates are called ____ and consist of a single monomer.
|
|
|
|
Protein
|
Once a polypeptide or multiple polypeptides are folded into a functional shape, it is referred to as a(n)
|
|
|
|
1. Organization 2. Energy Use 3. Maintenance internal constancy (homeostasis) 4.Growth, maintenance, and reproduction (GMR) 5. Evolution |
What are the 5 living characteristics?
|
|
|
|
1. Domains (bacteria, archaea, eukaraya 2. Kingdoms (6) 3. Phylum 4. Class 5. Order 6. Family 7.Genus 8. Species |
What is the 8 tier system?
|
|
|
|
3 components the cytoskeletal system is made up of |
1. microfilaments 2. intermediate filaments 3. microtubules |
|
|
|
functions of the cytoskeleton |
1. structural support 2. aids in cell division 3. organelle transport 4. cell movement |
|
|
|
Four main organic molecules |
1. carbohydrates 2. proteins 3. nucleic acids 4. lipids |
|
|
|
1. polar 2. hydrogen bond 3. cohesion 4. adhesion 5. ability to stick 6. hydrophilic (dissolve) 7. water expands 8. controls temperature |
What are the 8 properties of water? |
|
|
|
Full electrons on the most outer shell (8 electrons)
|
What does it mean to be stable?
|
|
|
|
same amount of electrons and protons
|
What does it mean to be neutral?
|
|
|
|
Components of all cells
|
1. Ribosome 2. Plasma membrane 3. DNA containing region 4. Cytoplasm |
|
|
|
surface-to-volume ratio
|
inside creases much more rapidly than surface area restricts cell size by limiting transport of nutrients and waste |
|
|
|
Prokaryotes
|
1. do not have a nucleus 2. all unicellular |
|
|
|
Eukaryotes
|
1. have a nucleus 2. can be unicellular or multicellular 3. more complex 5. internal membrane system |
|
|
|
Biofilm
|
single-celled organisms sharing a secreted layer of polysaccharides and glycoproteins
|
|
|
|
Phospholipids
|
1. Hydrophilic head Polar bonds, which attract water "water loving" 2. Hydrophobic tails Nonpolar bonds. repel water |
|
|
|
fluid mosaic model
|
structure of a membrane
|
|
|
|
endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
|
routing, modifying new polypeptide chains; synthesizing lipids
|
|
|
|
Golgi body
|
Modifying now polypeptide chains; sorting, shipping proteins and lipids
|
|
|
|
vesicles
|
transporting, storing, or digesting substances in a cell
|
|
|
|
mitochondrion
|
masking ATP by glucose breakdown energy extraction from food |
|
|
|
Chloroplast
|
Photosynthesis in plants, some protists
|
|
|
|
Lysosome
|
Intracellular digestion
|
|
|
|
Peroxisome
|
Inactivating toxins
|
|
|
|
Vacuole
|
Storage
|
|
|
|
Ribosomes
|
assembling polypeptide chains
|
|
|
|
Centriole
|
Anchor for cytoskeleton
|
|
|
|
Cytoskeleton
|
Contributes to cell shape, internal organization, movement
|
|
|
|
Central vacoule
|
found in plants - much of the interior is made of the central vacuole
|
|
|
|
flagella
|
- Longer - usually found in singular or in pairs - either snake-like movements propels cell through environment - rotary arrangement to push the cell through water |
|
|
|
cilia
|
- more short hair like in large concentrations on cells surface - work in unicin - move a cell in an environment - move water around surfaces |
|
|
|
tight junctions
|
fuse the membranes of adjacent animal cells together, preventing substances from flowing between cells
|
|
|
|
anchoring junctions
|
use intermediate filaments to hold cells together
|
|
|
|
plasmodesmata
|
cells communicate through - nutrients and biochemical travel through these channels to adjacent cells |
|
|
|
gap junctions
|
found in animal cells, protein channel links the cytoplasm of neighboring cells
|
|
|
|
Early Cell Theory
|
- All organisms are made of one or more cells - The cell is the fundamental unit of life - All cells come from preexisting cells. |
|
|
|
Modern Cell Theory
|
- All cells have the same basic chemical composition - All cells use energy - All cells contain DNA that is duplicated and on as each cell divides |
|

