![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Latissimus dorsi |
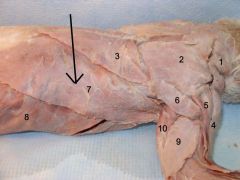
Movement: main function is to adduct and medially rotate the humerus |
|
|
External oblique |
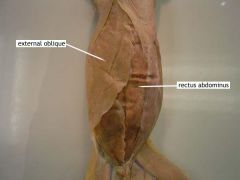
Movement: helps compress the abdomen and rotates vertebral column |
|
|
Internal oblique |
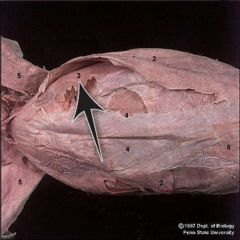
Movement: serves to compress the abdomen and rotate the vertebral column |
|
|
Transverse abdominus |
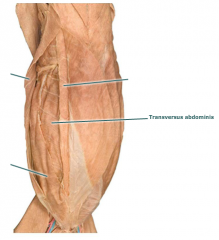
Movement: serves to compress the abdomen |
|
|
Rectus abdominus |
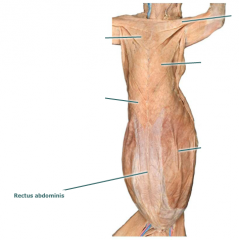
Movement: serves to compress the abdomen and flex the vertebral column in an anterior direction |
|
|
Multifidus spinae |
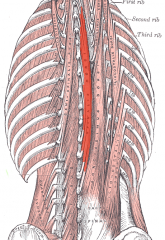
Movement: functions in arching or extending the back |
|
|
Erector spinae |

Movement: functions in arching or extending the back as well as in lateral (side-to-side) flexion of the back (2) |
|
|
Pectoantibrachialis |
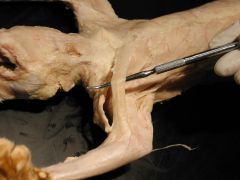
not found in humans |
|
|
Pectoralis major |
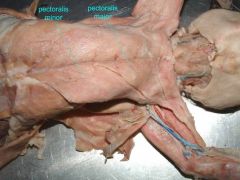
smaller than the pectoralis minor in the cat. the opposite is true in humans. |
|
|
Pectoralis minor |
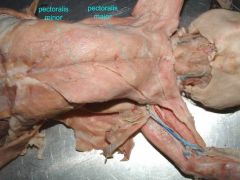
Movement: protects the scapula |
|
|
Xiphihumeralis |
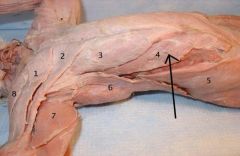
runs from the end of the sternum to the humerus |
|
|
Clavorapezius |
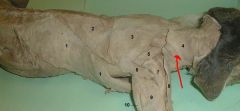
Movement: elevates and rotates the scapula medially |
|
|
Acromiotrapezius |
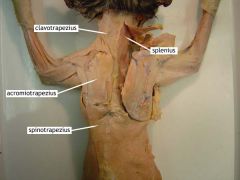
Movement: adduct the scapula |
|
|
Spinotrapezius |
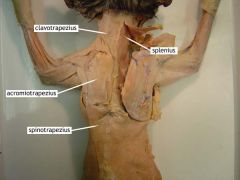
Movement: depresses and rotates the scapula medially |
|
|
Sternomastoid |
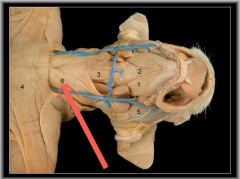
Movement: flexes the neck laterally and rotates the head |
|
|
Cleidomastoid |
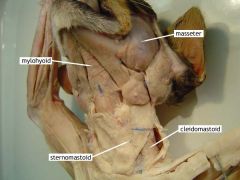
Movement: flexes the neck laterally and rotates the head |
|
|
Levator scapulae |
Movement: pulls the scapula cranially |
|
|
Clavodeltoid |
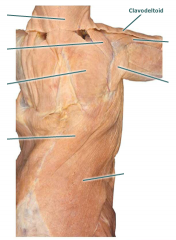
Movement: protracts the arm |
|
|
Acromialdeltoid |
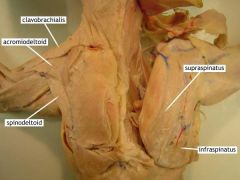
Movement: abducts the arm |
|
|
Spinodeltoid |
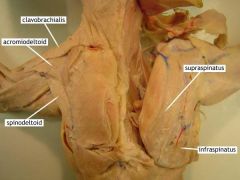
Movement: retracts the arm |
|
|
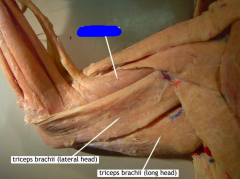
Triceps brachii |
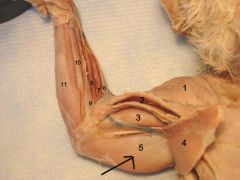
Movement: extends the antebrachium (forearm) |
|
|
Biceps brachii |
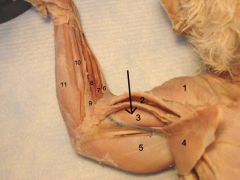
Movement: flexes the antebrachium (forearm) |
|
|
Brachialis |
Movement: flexes the antebrachium (forearm) the blue one |
|
|
origin |
the structure to which the muscle is attached that remains relatively fixed when the muscle contracts |
|
|
insertion |
the structure to which the muscle is attached that moved when the muscle contracts |
|
|
belly |
the thick part of the muscle between the insertion and origin |
|
|
tendon |
cords of fibrous connective tissue by which a muscle is connected to its insertion and origin |
|
|
aponeurosis |
a broad, flat sheet of fibrous connective tissue by which a muscle is attached to its origin and insertion; these are less common than tendons |
|
|
flexor |
a muscle which decreases an angle between two structures; or a muscle that bends one skeletal part in relation to another (the biceps of the arm flexes the forearm) |
|
|
extensor |
increases the angle between two structures; or a muscle that straitens (the triceps extend the forearm) |
|
|
abductor |
moves part away from the main axis (midline) of the body (the gluteus maximus moves the leg away from the body) |
|
|
adductor |
moves a part toward the main axis (midline) of the body (the adductor femoris muscle brings the leg toward the body) |
|
|
levator |
raises a part of the body |
|
|
depressor |
lowers a part of the body |
|
|
protractor |
moves a part of the body forward |
|
|
retractor |
moves a part of the body backward |
|
|
lumbodorsal fascia |
wide sheet of tough, white connective tissue |

