![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Capillaries: structure, function |

Structure: 1 cell, thick walls, very small diameter but lots of them Function: allow for the exchange of molecules between blood and E.C.F. |
|
|
Veins: structure, function, how |

Structure: thinner walls, bigger space for blood Function: to transport blood from capillaries to heart How: veins use one way valves and body muscle movement, body muscles squeeze the veins pushing blood one way through valves |
|
|
Arteries: structure, function and how it works |
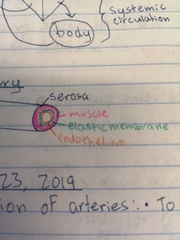
Structure: thick elastic walls, found deep in body, have a pulse Function: to transport blood from heart to capillaries How: use blood pressure created by heart pumping, arteries expand and contract to push blood |
|
|
What is an anurism |

When an artery wall fails - may result in a stroke if it occurs in brain |
|
|
Heart diagram |
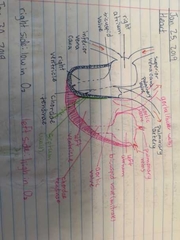
|
|
|
Heart sounds |
Lub: when ventricles contract and close the A.V. valves (bicuspid and tricuspid) Dub: when ventricles relax. Semi-lunar valves (aortic and pulmonary) close |
|
|
S.A. node |
Hearts pacemaker Group of cells in upper right atrium Sends an impulse across both atria (signal) Causes atria to contact |
|
|
A.V. node |
Group of cells at bottom of atria on the septum Relay station Responds to S.A. by: pausing, sending an impulse down to ventricles via bundle of his and possibly fibers |
|
|
Heart cycle |
Both atria fill with blood (0.5s) Both atria contract (push blood to ventricles) Short pause (0.1-0.2 sec) Ventricles contract (pushing blood out of heart) |
|
|
2 types of extrinsic controls of HR |
A) Nervous control: 2 nerves connect brain to SA node Sympathetic nerve: Increases HR Vagus nerve: slows HR B) Chemical control: Epinephrine: speeds up HR Acetylcholine (Ach): slows HR |
|
|
Fetal modifications (3 types) |
1) placenta 2) arterial duct (ductus arteriosus) 3) foramen ovale (oval hole) |
|
|
Placenta |
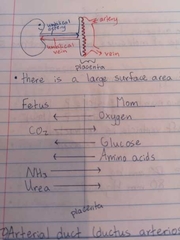
An organ that is half fetal and half maternal Allows small molecules to move (diffuse) from fetal to maternal blood and vise versa Large surface area allows for max. diffusion |
|
|
Major vessels |
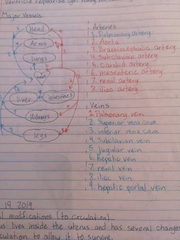
|
|
|
Heart Attack |
Occurs when part of heart muscle stops receiving oxygenated blood When one or more coronary arteries are blocked or reduced flow |
|
|
S.A. and A.V. node diagram |

|
|
|
Arrhythmia |
Occurs when heart loses coordination (SA node signal is irregular) Artificial pacemaker can fix it |
|
|
Arterial duct |
- a small connection between the pulmonary artery and the aorta - allows most of the blood to by-pass the lungs - reduces blood flow to lungs to allow them to grow and develop slowly - closes just prior to birth |
|
|
Blood pressure: what it is, functions |
- created in circulatory system by muscle contractions and valves in heart - BP is highest in systematic arteries and created by contraction of left ventricle Functions: move blood quickly in arteries, involved in exchange of molecules between blood and E.C.F. at capillaries |
|
|
How is BP measured |
Using a sphygmomanometer |
|
|
What are the two numbers in BP |
Systolic pressure - when left ventricle is contracted Diastolic pressure - when left ventricle is relaxed |
|
|
Hypertension |
- called silent killer because it often goes unnoticed - BP above 140/90 |
|
|
Hypertension may result in what? Short term and long term |
Short term: anurisms, strokes, arrythmia (heart beat is disorganized), heart failure Long term: vision loss, kidney failure, dementia |
|
|
What is the average resting BP |
120 mmHg 80 mmHg |
|
|
Foramen ovale |
- hole between the right and left atria of heart - also acts as a lung by-pass - also closes just prior to birth (if it does not close then the baby will be a "blue baby") |
|
|
Causes of hypertension |
Stress, genetics, high fat diet, smoking, high salt diet, alcohol, obesity |
|
|
What can be done if you have high blood pressure |
Change lifestyle factors and/or medications |
|
|
Pulmonary vs systemic circulation |
Pulmonary - to and from lungs Systemic - to and from rest of body |

