![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
172 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Functions of the nervous system
|
Sensory input
Interpretation of sensory input and Motor output or response to stimuli |
|
|
Central nervous system (CNS) contains
|
The brains and the spinal cord
|
|
|
Actions of the Central nervous system (CNS)
|
Integration and command center
|
|
|
Peripheral nervous system (PNS) contains
|
Paired spinal and cranial nerves
|
|
|
The function of the Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
|
Carries messages to and from the spinal cord and brain
|
|
|
Sensory (afferent) division
is comprised of |
Somatic Sensory Fibers and Visceral Fibers
|
|
|
Somatic sensory fibers
|
carry impulses from skin, skeletal muscles, & joints to the brain
|
|
|
Visceral fibers
|
transmit impulses from visceral organs to the brain
|
|
|
Motor (efferent) division is comprised of
|
Somatic nervous system and Autonomic nervous system
|
|
|
Autonomic nervous system
|
Regulates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands
|
|
|
Somatic nervous system
|
Conscious control of skeletal muscles
|
|
|
What are the two principle cell types of the nervous system?
|
Neurons and supporting cells
|
|
|
Neurons are?
|
excitable cells that transmit electrical signals
|
|
|
Supporting cells are?
|
cells that surround and wrap neurons
|
|
|
The cell body is called
|
Soma
|
|
|
Axon
|
Generates and transmits action potentials and secretes neurotransmitters from its terminals
|
|
|
Whats fibers form the nerve
|
The Axon
|
|
|
Dendrites
|
the receptive or input regions of the neuron
|
|
|
The stuctural unit of the nervous system is composed of
|
a body, axon, and dendrites
|
|
|
Myelin Sheath
|
Whitish segmented sheath around most long axons
|
|
|
What are the functions of the Myelin Sheath?
|
Protection of the axon
Increasing the speed of nerve impulse transmission |
|
|
Depolarization
|
the inside of the membrane becomes less negative (more positive)
|
|
|
Action potentials are only generated by
|
muscle cells and neurons
|
|
|
An action potential down axons of neurons is called
|
a nerve impulse
|
|
|
Repolarization
|
the membrane returns to its resting membrane potential
|
|
|
Hyperpolarization
|
the inside of the membrane becomes more negative than the resting potential
|
|
|
Presynaptic neuron
|
conducts impulses toward the synapse
|
|
|
Postsynaptic neuron
|
transmits impulses away from the synapse
|
|
|
Nerve impulse reaches ___ ___ of the presynaptic neuron
|
axonal terminal
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter is released and binds to receptors on the
|
postsynaptic neuron
|
|
|
Postsynaptic membrane permeability changes, causing
|
change in membrane potential
|
|
|
Neurotransmitter classifications:
|
Excitatory, Inhibitory, and both
|
|
|
What is an excitatory neurotransmitter?
|
causes depolarization
|
|
|
What is an Inhibitory neurotransmitter?
|
causes hyperpolarizations
|
|
|
The type of neurotransmitter effect is determined by
|
the receptor type of the postsynaptic neuron
|
|
|
Central Nervous System White Matter contains
|
dense collections of myelinated fibers
|
|
|
Central Nervous System Grey Matter contains
|
mostly soma and unmyelinated fibers
|
|
|
What are the ventricals of the brain
|
The paired C-shaped lateral ventricles
The third ventricle The fourth ventricle |
|
|
What are the five cerebral hemispheres?
|
Frontal, Parietal,Temporal, Occipital, Insula
|
|
|
What divides the brain into hemispheres?
|
Deep grooves (fissure/sulcus)
|
|
|
What are the three functions of the cerebral cortex?
|
Motor, Sensory, and Association
|
|
|
The Cortex is made of
|
Superficial Grey Matter
|
|
|
Where is the Primary Motor Cortex located?
|
Precentral Gyrus
|
|
|
What does the Primary Motor Cortex control?
|
Allows conscious control of precise, skilled, voluntary movements
|
|
|
Where is the Primary Somatosensory Cortex located?
|
Located in the postcentral gyrus
|
|
|
What bug?: Urease-positive gram-negative bacteria
|
Proteus, H. Pylori, Klebsiella
|
|
|
Where is the Primary visual cortex
located? |
Located on the extreme posterior tip of the occipital lobe
|
|
|
What does the Primary visual cortex
control? |
Receives visual information from the retinas
|
|
|
Where is the Primary auditory cortex
located? |
Located at the superior margin of the temporal lobe
|
|
|
What does the Primary auditory cortex
control? |
Receives information related to pitch, rhythm, and loudness
|
|
|
The Spinal Cord is protected by?
|
The bone, meninges, and CSF
|
|
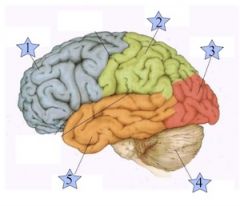
Which is the Frontal Lobe? (1, 2, 3, 4, or 5)
|
1
|
|
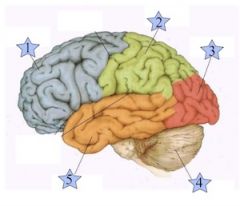
Where is the Occipital Lobe Located(1, 2, 3, 4, or 5)?
|
3
|
|
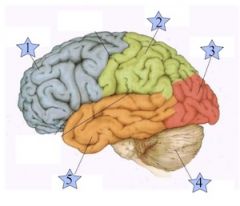
Where is the Temporal Lobe located (1, 2, 3, 4, or 5)?
|
5
|
|
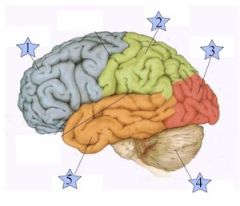
Where is the Parietal Lobe located (1, 2, 3, 4, or 5)?
|
2
|
|
|
What functions take place in the Frontal Lobe?
|
Conscious intellect (Prefrontal Cortex)
language, interpretation, and visceral association |
|
|
What functions take place in the Occipital Lobe?
|
Visual association received from the retinas (Visual Cortex)
|
|
|
What Functions take place in the Temporal Lobe?
|
Receives information related to pitch, rhythm, and loudness (Auditory Cortex)
|
|
|
What functions take place in the Parietal Lobe?
|
Sensory Information from the skin and skeletal muscles (Primary Somatosensory Cortex)
|
|
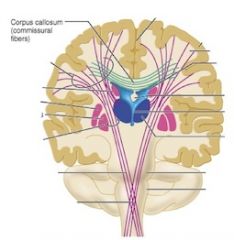
What is the function of the Corpus Collosum?
|
Communication between the cerebral cortex and the lower central nervous system
|
|
What number is the corpus callosum?
|
9
|
|
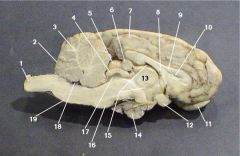
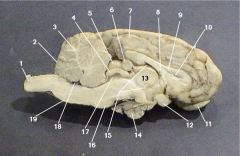
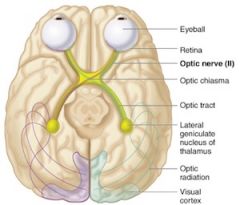
Where is the Optic Chiasm?
|
12
|
|
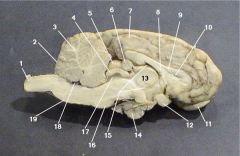
Where is the Optic Chiasm?
|
12
|
|
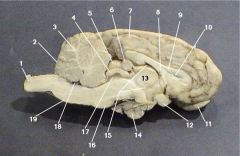
Where is the Optic Chiasm?
|
12
|
|
|
What is the function of the optic chiasm?
|
The optic nerves meet and cross there
|
|
|
What is the function of the lateral ventricles?
|
a network of interconnected cavities in the brain through which cerebrospinal fluid flows
|
|
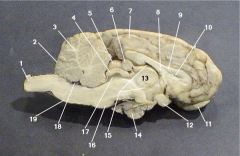
Where is the lateral ventricle?
|
10
|
|
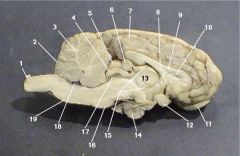
Where is the Olafactory Bulb?
|
11
|
|
|
What sense does the Olfactory Bulb provide function for?
|
Smell
|
|
Where is the optic nerve?
|
3
|
|
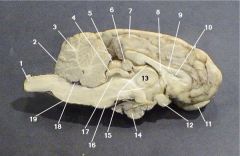
Where is the Pineal Body?
|
6
|
|
|
What is the function of the Pineal Gland?
|
Secretes Melatonin
|
|
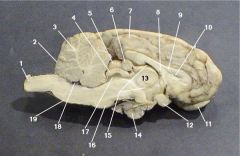
Where is the Third Ventricle
|
15
|
|
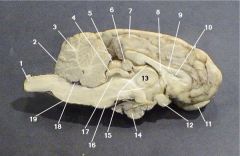
Where is the Pituitary Gland?
|
14
|
|
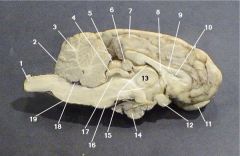
Where is the Thalamus?
|
13
|
|
|
The thalamus is responsible for what function?
|
the sorting out of impulses before it relays them to the cortex
|
|
|
The Hypothalamus is also know as the
|
Brain of the brain
|
|
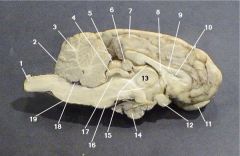
Where is the Cerebral Aquaduct
|
17
|
|
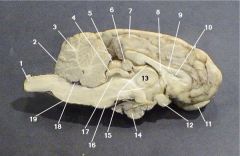
Where is the Pons?
|
7
|
|
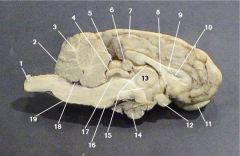
Where is the Fourth Ventricle?
|
18
|
|
Where is the medulla oblongata?
|
11
|
|
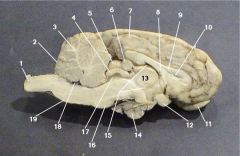
Where is the Cerebellum?
|
2
|
|
|
What is the main function of the cerebellum?
|
coordination
|
|
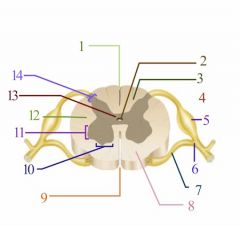
Where is the gray matter?
|
13
|
|
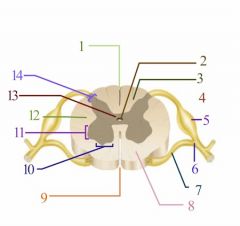
Where is the Ventral Horn?
|
10
|
|
|
The Dorsal Root contains what type of nerve impulses?
|
Sensory
|
|
|
The Ventral Root contains what type of nerve impulses?
|
Motor
|
|
|
The Neurons in the Anterior half of the spinal cord are involved in?
|
Motor
|
|
|
The Neurons in the posterior half of the spinal cord are involved in?
|
Sensory
|
|
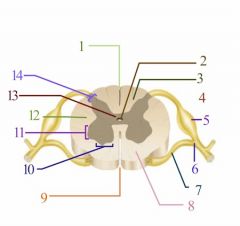
Where is the Dorsal Horn?
|
14
|
|
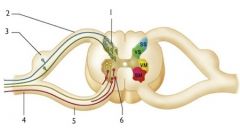
Where is the Spinal Nerve?
|
4
|
|
Where is the Dorsal root ganglion?
|
3
|
|
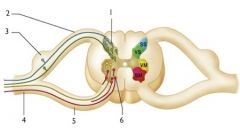
Where is the cervical plexus located?
|
c1-c5
|
|
Where is the Brachial Plexus located?
|
c5-t1
|
|
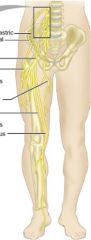
Where is the Lumbar Plexus located?
|
L1-L4
|
|
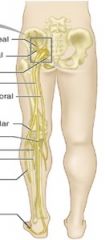
Where is the Sacral Plexus located?
|
L4-S4
|
|
|
The Spinal cord ends at?
|
L1
|
|
|
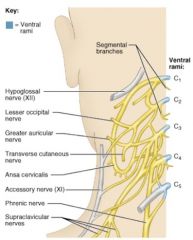
What is the most important nerve of the cervical plexus?
|
The Phrenic Nerve
|
|
|
The Cervical Plexus innervate what parts of the body?
|
The neck, ear, back of the head, and shoulders
|
|
|
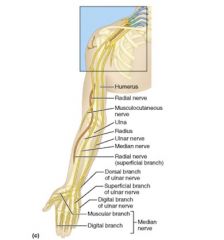
The Brachial Plexus innervates the?
|
upper limb
|
|
|
The lumbar plexus innervates what parts of the body?
|
The thigh and lower abdominal wall
|
|
|
The major nerves of the Lumbar Plexus are?
|
The femoral and obturator
|
|
|
The Sacral Plexus innervates the?
|
legs
|
|
|
The major nerve of the sacral plexus is?
|
The sciatic
|
|
|
The torso is innervated by nerves t1-t12 which are located where?
|
They run along the bottom of each rib
|
|
|
The branches of a spinal nerve are called?
|
Rami
|
|
|
The dorsal ramus innervate?
|
back muscles and joints
|
|
|
The ventral ramus innervate?
|
front and side skin and muscles
|
|
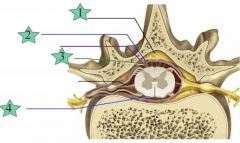
Dura
|
2
|
|
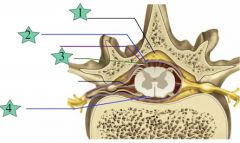
Subarachnoid
|
3
|
|
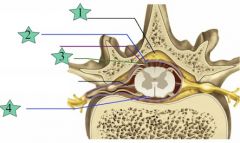
Pia mater
|
4
|
|
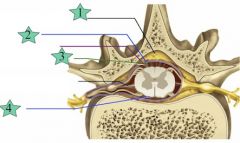
Epidural
|
1
|
|
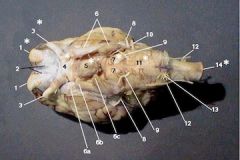
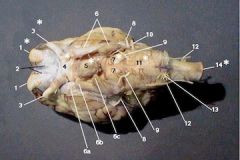
1 - Olfactory
|
sense, smell
|
|
2 - Optic
|
sense, vision
|
|
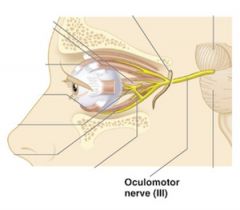
3 - Oculomotor
|
motor, impulses to move the eyeball, raise eyelid, iris, and lens shape
|
|
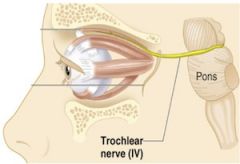
4 - Trochlear
|
Motor, Nerve that directs the eyeball superior oblique
|
|
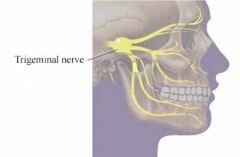
5 - Trigeminal
|
Motor and Sensory, muscles involved in chewing
|
|
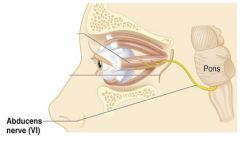
6 - Abducens
|
Motor, lateral rectus of the eye
|
|
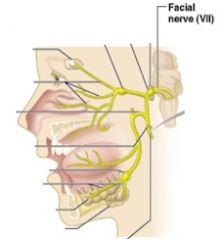
7 - Facial
|
Sensory and Motor, innervates most facial muscles and taste
|
|
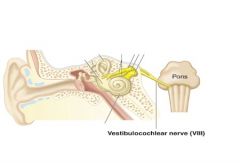
8 - Vestibulocochlear
|
sensory, hearing and balance
|
|
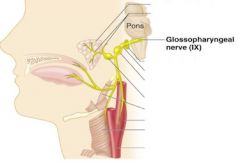
9 - Glassopharyngeal
|
motor and sensory, taste and tongue movements
|
|
|
10 - Vagus
|
motor and sensory, smooth and cardiac muscle and taste
|
|
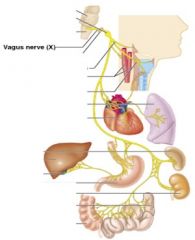
10 - Vagus
|
motor and sensory, smooth and cardiac muscle and taste
|
|
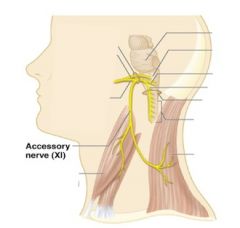
11 - Accessory
|
Motor, Throat and soft pallete
|
|
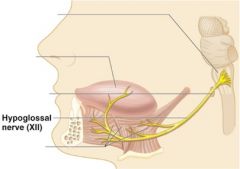
12 - Hypoglossal
|
Motor, muscles that move the tongue for swallowing and speach
|
|
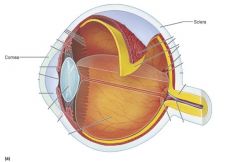
The Cornea and the Sclera make up the?
|
Fibrous Tunic
|
|
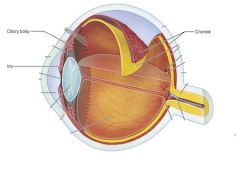
The Choroid, Ciliary Body, Iris, and Pupil make up the?
|
Vascular Tunic
|
|
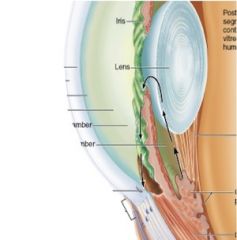
What allows precise focusing of light onto the retina?
|
The Lens
|
|
|
What does the cornea do within the eye?
|
lets light enter
|
|
|
What does the sclera do within the eye?
|
protects and anchors extrinsic muscles
|
|
|
What does the choroid do within the eye?
|
supplies blood
|
|
|
What does the ciliary body do within the eye?
|
holds the lens in place
|
|
|
What does the iris do within the eye?
|
regulates the amount of light entering the eye
|
|
|
What is a sympathetic function of the iris?
|
to dialate
|
|
|
What is a parasympathetic function of the iris?
|
to constrict
|
|
|
In bright light or when looking close, the pupils
|
contract
|
|
|
In dim light or when looking far, the pupils
|
dialate
|
|
|
Macula Lutea is the area in the eye with
|
the greatest cone concentration
|
|
|
Where is the fovea centralis located?
|
In the macula lutea
|
|
|
Rods respond to
|
Dim light and peripheral vision
|
|
|
cones respond to
|
bright light and high-acuity color vision
|
|
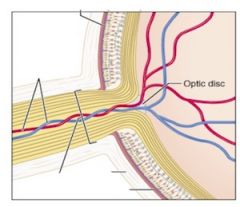
The optic disc is where what leaves the eye?
|
The optic nerve
|
|
|
Ganglion cells leave the eye as
|
the optic nerve
|
|
|
the anterior of the eye is filled with a clear liquid that is called?
|
Aqueous humor
|
|
|
The posterior of the eye is filled with a clear gel called?
|
Vitreous humor
|
|
|
The Aqueous humor holds what function?
|
Supports, nourishes, and removes waste
|
|
|
What is it called when the Aqueous humor doesn't drain quickly and pressure builds up?
|
Glaucoma
|
|
|
What is the function of the Vitreous humor?
|
Supports the retina and posterior lens as well as transmits light.
|
|
|
What is another name for nearsighted?
|
Myopic
|
|
|
What is another name for farsighted?
|
Hyperopic
|
|
|
Emmetropic is?
|
Normal vision
|
|
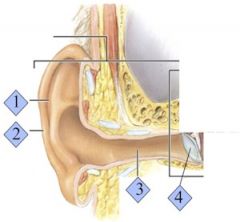
Which is the Pinna?
|
1
|
|
Which is the Helix?
|
2
|
|
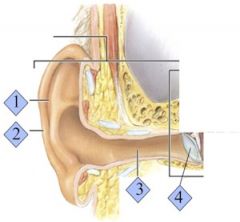
Where is the external auditory canal?
|
3
|
|
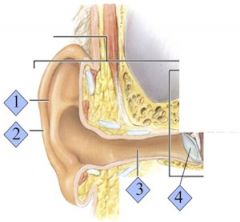
Where is the Tympanic Membrane?
|
4
|
|
|
What is the eardrum also known as?
|
The tympanic membrane
|
|
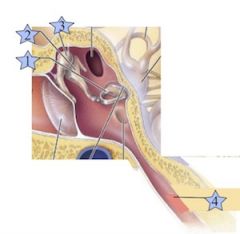
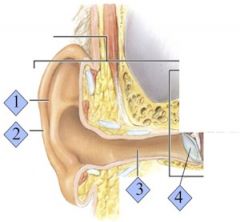
Where is the Malleus?
|
3
|
|
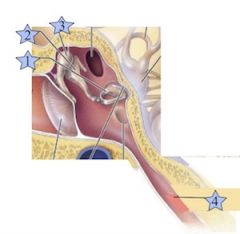
Where is the Incus?
|
2
|
|
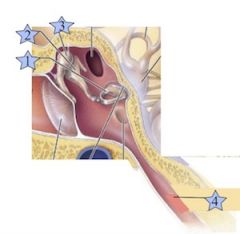
Where is the Stapes?
|
1
|
|
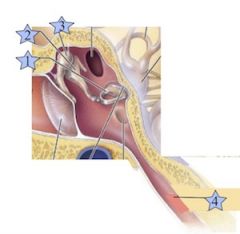
Where is the Eustacian Tube?
|
4
|
|
|
The ear ossicles are the three small bones in the middle ear which serve which purpose?
|
They transmit vibratory motion of the eardrum to the inner ear.
|
|
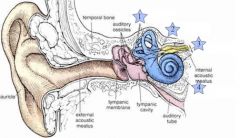
Where are the semicircular Canals?
|
1
|
|
|
What purpose do the semicicular canals serve?
|
equalibrium
|
|
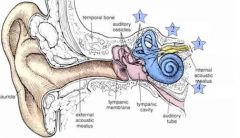
Where is the Vestibule
|
2
|
|
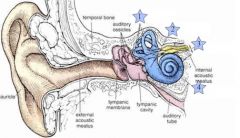
Where is the Cochlea?
|
4
|
|
|
The organ of corti is located where?
|
In the Cochlea
|
|
|
Where are the sensory receptors for dynamic equilibrium located?
|
Vestibule
|
|
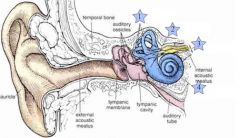
Where is the vestibocochlear nerve?
|
3
|
|
|
Conduction deafness
|
hampers sound conduction
|
|
|
Sensorineural deafness results from
|
damage to neural structures
|
|
|
Conduction deafness
|
hampers sound conduction
|
|
|
Sensorineural deafness results from
|
damage to neural structures
|

