![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
68 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Four Key Processes of Evolution
|
1) Natural Selection & Sexual Selection
2) Genetic Drift 3) Mutations 4) Genetic Flow |
|
|
Sources of Genetic Variation
|
1) Rapid reproduction (Higher rate of mutations)
2) Chromosomal Mutations 3) Sexual Reproduction |
|
|
Hardy Weinberg Equilibrium
|
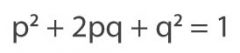
Equation that determines if a certain gene is evolving.
Genes have two alleles. One allele is p and the other is q. p^2 and q^2 are homozygous while 2pq is heterozygous. When proportions does not conform to HW equation then there is non random mating AND evolution occurring. |
|
|
5 Conditions to be in HW equillibrium
|
1) No Natural Selection
2) No genetic drift or random allele frequency changes 3) No gene flow 4) No mutations 5) Random mating |
|
|
Genetic Drift
|
Mainly affects small populations from a chance event. Ex) Someone stepping on a group of insects which causes allele frequencies to fluctuate.
|
|
|
Founders Effect
|
Animals who get isolated on another area which causes a decreases in allele frequencies.
|
|
|
Bottleneck Affect
|
Sudden decrease in an animal population due to natural causes. Causes lack of genetic diversity
|
|
|
Gene Flow
|
Animals from area move into another causing increased genetic diversity. Could possibly cause decrease in fitness.
|
|
|
Directional Selection
|
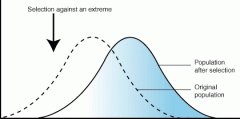
Where one extreme of a population is favored
|
|
|
Stabilizing Selectrion
|
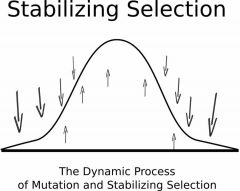
Where well-rounded animals are preferred
|
|
|
Disruptive Selection
|
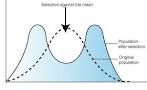
Where both extremes are preferred.
|
|
|
Balancing Selection
|
Selection in different times or places
|
|
|
Frequency Dependent Selection
|
Selection based on the number of organisms.
|
|
|
Sexual dimorphism
|
Traits that differ between male and females
|
|
|
Why we can't have the perfect organism?
|
1) Selection can only act on existing variations
2) Evolution is limited by historical constraints (Only modifications of original body plan 3) Adaptations are often compromise 4) Chance, natural selection, and the environment |
|
|
Speciation
|
When the populations of species get separated, it causes new species to form.
|
|
|
Biological Species Concept
|
Species based on if they are reproductively isolated.
|
|
|
Prezygotic Barriers
|
Barriers before zygote is even made.
temporal isolation- isolated through different mating seasons mechanical isolation- doesn't fit behavioral isolation- different mating patterns habitat isolation- mate in different environments gametic isolation- Egg doesn't or can't fertilize |
|
|
Post Zygotic Barrier
|
Barriers after the hybrid is born
Hybrid Viability- Hybrid won't survive Reduced Hybrid Fertility- Hybrid isn't fertile Hybrid Breakdown- Hybrid is too weak to survive |
|
|
Morphological Species Concept
|
Definition of species based on appearances such as bone structures
|
|
|
Phylogenetic Species Concept
|
Species based on the family tree or history
|
|
|
Ecological Species Concept
|
Species based on what ecological niche certain things live in
|
|
|
Allopatric Speciation
|
Speciation through geographical isolation.
Causes natural selection, Genetic Drift, Gene Flow. It is an example of Founders' Effect |
|
|
Sympatric Speciation
|
No separation. Isolated through habitat preferences. Can be caused through polyploidy in which a species is formed through an error in cell division. Can be caused by sexual selection.
|
|
|
3 Outcomes of a hybrid zone
|
Reinforcement- reproductive barriers stay the same
Fusion- reproductive barriers fuse Stability- continued reproduction of hybrids |
|
|
Why fossilization is biased
|
1) Animals with hard shells are more likely to be fossilized (Taxonomic Bias)
2) Certain habitats will develop fossils better than others (Habitat Bias) 3) Abundant animals= abundant fossils (Abundance Bias) 4) More recent fossils are easier to find than older ones (Temporal Bias) |
|
|
radiometric dating
|
Used to determine relative age of organism
|
|
|
adaptive radiation
|
Periods of evolutionary change in which groups of organisms form many new species
|
|
|
Rooted Phylogenetic Tree
|
The organisms in the tree have one common ancestor
|
|
|
Basal taxon
|
the point where the earliest divergence occurs
|
|
|
Homologies
|
Phenotypic and Genetic similarities between organisms
|
|
|
Analogous
|
Phenotypic similarities which occurred through adaptations to an environment. An example of convergent evolution. Also called homoplaisies
|
|
|
Monophyletic
|
one ancestor with all its descendants
|
|
|
Paraphyletic
|
Single ancestor but not all the descendants
|
|
|
Polyphyletic
|
Species with different common ancestors
|
|
|
Outgroup
|
Group that diverged the earliest such as the basal taxon
|
|
|
Max. Parsimony
|
The tree that requires the lowest number of evolutionary changes. (Occam's Razor)
|
|
|
Max. Likelihood
|
The tree that displays what was most likely in the evolution of certain organisms.
|
|
|
The 3 domains of life
|
Eukarya, Archaea, Bacteria
|
|
|
Distinguishing Traits of prokaryotes
|
Size, shape, and motility
|
|
|
Gram staining
|
Gram (+)- Appears purple. Has peptidoglycan wall
Gram (-)- Appears pink. Has thin layer of peptidoglycan but an outer phospholipid bilayer. It is more complex |
|
|
Why do bacteria have a large genetic diversity
|
Mutations, Rapid reproduction, and Genetic recombination
|
|
|
Transfomation of bacteria
|
This is when the bacteria is surrounded by DNA which then combines it with its own
|
|
|
Transduction of bacteria
|
Recombination of DNA through other sources such as bacteriophages
|
|
|
Conjugation
|
Recombination of DNA through a sex pili.
|
|
|
F factors
|
transferred during conjugation and gives of a plasmid or part of the chromosome
|
|
|
R plasmid
|
transferred through conjugation. Gives antibiotic resistance
|
|
|
Source of Energy for:
Autotrophs Heterotrophs |
Autotrophs make their own energy such as photosynthesis.
Heterotrophs rely on molecules produced from other organisms |
|
|
Cyanobacteria
|
First bacteria to form O2 through photosynthesis
|
|
|
Obligate aerobes
|
rely on O2
|
|
|
Obligate anaerobe
|
doesn't want O2
|
|
|
Facultative anaerobes
|
Can have/not have O2
|
|
|
Extromophiles
|
Organisms that live in extreme environments
|
|
|
Extremehalophile
|
Lives in areas with high saline amount
|
|
|
Extreme thermophiles
|
Lives in extreme temperatures
|
|
|
Methanogens
|
Releases methane as a by-product. They don't want oxygen
|
|
|
mutalism
|
where both organisms benefit
|
|
|
commensalism
|
one benefits but the other is not harmed or helped
|
|
|
parasitism
|
one benefits while other organism is harmed
|
|
|
exotoxins
|
toxins that bacteria release
|
|
|
endotoxin
|
toxins that bacteria release when they die
|
|
|
monocot
|
one cotyledon
parallel veins Petals in multiples of 3 |
|
|
dicot
|
2 cotyledons
branched veins petals in multiples of 4 or 5 |
|
|
Taproot
|
main vertical root of a plant
|
|
|
Apical meristem
|
primary space for plant growth
|
|
|
Axillary buds
|
point where lateral stems form
|
|
|
Non-vascular plants
|
They are gametophyte dominant
|
|
|
Vascular Plants
|
They are sporophyte dominant
|

