![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
electromagnetically
|
ability of an atom to form electrons
|
|
|
negative charged subatomic particles outside the nucleus
|
electron
|
|
|
___ of an atom will pull electrons towards it |
nucleus |
|
|
stronger or weaker electron have more electrons around it more often
|
stronger |
|
|
Atoms sharing electrons drift apart or stay together? |
stay together |
|
|
biology is based on the principles of __ and __ |
Chemistry and physics |
|
|
All living organisms are a collection of __ and __ |
Atoms and molecules |
|
|
Multiple forms of an element that differ in the number of neutrons |
Isotopes |
|
|
C12 contains __ protons and __ neutrons |
6 6 |
|
|
C14 contains __ protons and __ neutrons |
6 8 |
|
|
Averages of the weights of different isotopes of an element |
Average masses |
|
|
Make up 95% of the atoms in a living organism (4 elements) |
Carbon Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen
|
|
|
Hydrogen and oxygen are found primarily in this element |
Water
|
|
|
Nitrogen is mainly found in what? |
protein |
|
|
Building block of all living matter |
Carbon |
|
|
Mineral elements make up what percent of living things? |
Less than 1% |
|
|
Trace elements make up what percent of living things? |
0.01% |
|
|
Trace elements are crucial for normal __ and __ |
Growth Function |
|
|
Two or more atoms bonded together |
Molecule |
|
|
Contains chemical symbols of elements found in a molecule |
Molecular formula |
|
|
What in the molecular formula indicates how many of each atom are present |
Subscript |
|
|
Molecule composed of two or more elements |
Compounds |
|
|
Three types of bonding |
Covalent - polar and nonpolar Hydrogen Ionic |
|
|
Type of bonding where atoms share two electrons |
covalent |
|
|
bonding that occurs between two atoms whose outer electron shells are not full |
covalent |
|
|
Say the Octet rule
|
Atoms are stable when their outer shell is full |
|
|
For many atoms, their outer shell is filled with how many electrons? |
8 |
|
|
How many electrons can hydrogen hold in it's outer shell |
2 |
|
|
Water is the classic example of what kind of bonding |
Polar covalent bonding |
|
|
what type of bonding occurs between molecules having polar covalent bonds (between polar molecules)? |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Bonding represented on diagrams by dashed/ dotted lines |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
This generally weak bond when it is individual can form a strong bond overall
|
hydrogen bonds |
|
|
What type of bonds hold two DNA strands together |
Hydrogen bonds |
|
|
Substrate and enzyme bonding is what kind of bonding? |
Hydrogen |
|
|
An atom or molecule that has gained or lost one or more electrons |
Ion |
|
|
What kind of net charge does an ion have?
|
electric
|
|
|
Cations have a net _ charge |
+ |
|
|
Anions have a net _ charge |
- |
|
|
Bonding that occurs when a cation binds to an anion |
Ionic |
|
|
Occurs when one or more substances are changed into other substances |
Chemical reactions |
|
|
Chemical reactions Reactants ---> ____ |
products |
|
|
All chemical reactions require a source of _ |
Energy |
|
|
All chemical reactions with living organisms often require a.. |
Catalyst |
|
|
Catalyst |
Enzymes |
|
|
Tend to proceed in a particular direction and will eventually reach equilibrium |
Chemical reactions |
|
|
Chemical reactions occur in what kind of environment? |
Liquid environment |
|
|
Solvent |
Liquid |
|
|
Which two subatomic particles are nearly equal in size?
Protons Electons Neutrons |
Protons Neutrons |
|
|
Term stating an atom's mass relative to the mass of other atoms |
Atomic Mass |
|
|
Atomic mass of hydrogen |
1 |
|
|
Atomic mass of magnesium |
24 |
|
|
When 2 atoms with difference electronegatives form a covalent bond, will more shared electrons be in the outer shell of the more electronegative one or the less? |
More |
|
|
This bond occurs because the distribution of electrons around the atoms creates a polarity in electric charge across the molecules |
Polar covalent bonds |
|
|
Polarity |
Difference in electric charges |
|
|
In water, which atom do more electrons share with? Hydrogen or oxygen |
Oxygen It is more electronegative |
|
|
2 regions of molecules in a polar covalent bond |
(partially) negative (partially) positive |
|
|
Solutes |
Substances that dissolve in water |
|
|
In an aqueous solution, is water or the other solution's element the solvent |
water |
|
|
Ions and polar molecules will do what in water? Why? |
dissolve Ions and polar molecules are the solutes of the solution |
|
|
Hydrophilic |
water loving |
|
|
Are ion and polar molecules hydrophobic or hydrphilic? |
hydrophilic |
|
|
hydrophobic |
water fearing |
|
|
Which one doesn't readily dissolve in water? Hydrophobic Hydrophilic |
hydrophobic |
|
|
Are nonpolar molecules like hydrocarbon hydrophobic or hydrophilic? |
Hydrophobic |
|
|
Molecules having both polar or ionized regions at one or more sites and nonpolar regions at the other sites |
amphipathic molecules |
|
|
amount of a solute dissolved in a unit volume of solution |
concentration |
|
|
The concentration of 1gram of NaCl dissolved in a 1L of water = |
1g/L |
|
|
Number of moles of a solute dissolved in 1L of water |
Molarity |
|
|
1mol of a substance = |
atomic mass and also molecular mass
|
|
|
Molarity equation |
Mols of solute
Liters of solution |
|
|
changes in state involve an input or output of |
energy |
|
|
is water stable? |
very |
|
|
Four important functions of water |
Participates in chemical reaction removes toxic waste components evaporative cooling provides support of force also cohesion and adhesion hydrolysis and dehydration |
|
|
acids are molecules that release _ ions into a solution |
hydrogen |
|
|
Will a stronger of weaker acid release more H+? |
Stronger |
|
|
What lowers the H+ concentration of an acid |
bases |
|
|
bases lower the hydrogen concentration by sometimes releasing _ and other times binding _ |
OH- H+ |
|
|
OH- |
hydroxide |
|
|
pH= |
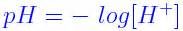
|
|
|
acidic solutions on the pH scale |
pH 6 or below |
|
|
neutral pH |
7 |
|
|
When a solution is above 7 pH, it is called a _ solution
|
alkaline |
|
|
Pure water ionizes slightly into what |
H and OH- [H+] = 10 to the -7 |
|
|
There is a lake and a cup. Tell me about their heat capacity |
Lake has higher heat capactiy |
|
|
There is a lake and a cup Tell me about their specific heat |
Specific heat doesn't change |
|
|
Hydrophilic What kind of bond(s)? Dissolves in what? Loves or no? |
Polar and ionic Water loves |
|
|
Hydrophobic What kind of bond(s)? Dissolves in what? Loves or no? |
Nonpolar NOT water; nonpolar solvents Hates |
|
|
heat of fusion |
heat needed to change the temperature by 1 unit |
|
|
effects shapes and functions of molecules, rates of many chemical reactions, ability of two molecules to bind together, and the ability of ions or molecules to dissolve in water |
pH |
|
|
Organisms tolerate (large, small) changes in pH |
small |
|
|
helps pH to keep constant |
buffer |
|
|
an acid-based __ system can shift to generate or remove H+ to adjust for changes in pH |
buffer |
|
|
In a(n) __ reaction, water is used to break apart another molecule |
Hydrolysis |
|
|
If pH rises too high in the blood, carbonic acid will release _ and form bicarbonate. This bicarbonate does what to the pH |
H+ Lowers it |
|
|
pH buffers do what to the pH of a solution? |
minimize flucuations |
|
|
pH buffers are usually what? |
weak acids and weak bases |
|
|
Will take up H+ when acids are added to them |
pH buffers |
|
|
Will release H+ when bases are added to them |
pH buffers |
|
|
If an atom looses or gains electrons, it acquires what? What does it become? |
Net charge; ion |
|
|
Acidic solutions contain more _ ions than _ ions |
H+ ions than OH- ions |
|
|
study of the nature of atoms and molecules with the exception of those that contain rings or chains of carbon
|
inorganic chemisty |
|
|
Study of carbon containing molecules |
organic chemistry |
|
|
Physical region of space where an electron may be found |
orbital |
|
|
orbitals are found in these "energy levels" in a cell |
electron shells |
|
|
the capacity to do work or cause a change |
energy |
|
|
3 orbitals from closest to the nucleus to furthest away |
1s, 2s, 2p |
|
|
indicates an atom's mass relative to the mass of other atoms |
atomic mass |
|
|
a _ of any substance contains the same number of particles as there are atoms in exactly 12 g of carbon. |
mol |
|
|
measure for one half the mass of a carbon atoms, or about the mass of a hydrogen atom |
Dalton (or atm) |
|
|
different forms of the same element that differ only in the number of neutrons they contain |
isotopes |
|
|
unstable isotopes that emit radiation to try to convert themselves into stability |
radiosotopes |
|
|
all living organisms require these. They are present in extremely small qualities and necessary for normal growth and function |
trace elements |
|
|
pH buffers will do what when bases are added to them |
Release H |
|
|
occurs when atoms share 2 pairs of electrons rather than one pair |
double bond |
|
|
weak force that occurs because electrons are located within the orbitals in a random way. At any moment they could be distributed |
van der Waals dispersion force |
|
|
when mixed with water, long amphipathic molecules aggregate into spheres called |
micelles |
|
|
heat requires to vaporize 1 mol of any substance at its boiling point |
heat of vaporization |
|
|
amount of heat needed to be withdrawn or released from a substance to cause it to chance from the liquid to the solid state |
heat of fusion |
|
|
properties defined as those that depend strictly on the total number of dissolved solutes and not the specific type of solute |
colligitive properties |
|
|
water molecules attracting to each other |
cohesion |
|
|
ability of water to be attracted to and adhere to a surface that is not electrically neutral |
adhesion |
|
|
attraction between molecules at the surface of a liquid |
surface tension |
|
|
Molecule containing an atom with a single unpaired electron |
Free radical |
|
|
(Polar, nonpolar) region of micelle is located at the surface of the micelle |
Polar |
|
|
The tail region on amphapathic molecule will always be polar or nonpolar |
Nonpolar |
|
|
Concentration is defined as what |
Amount of solute (dissolved in) Liter of solution |
|
|
Isotopes are multiple forms of an element that differ in the number of what |
Neutrons |
|
|
If pH in blood gets too low, bicarbonate will bind _ to form carbonic acid |
H+ |
|
|
atomic mass =
atomic number = |
Atoms mass relative to the mass of another atom
number of protons in an atom |
|
|
what atom can only hold 2 electron in outer shell? what atom can only hold 4 electron in outer shell? |
hydrogen has two carbon has four |
|
|
atom with higher electronegativity has electrons orbiting _ to the nucleus |
closer |
|
|
sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule |
molecular mass |
|
|
regarding the pH types of solutions, which has the lowest proton concentration |
alkaline - neutral - acidid |
|
|
water is so important to all living things because of it's |
stucture and polarity |
|
|
2 examples of pH buffers |

Carbonic acid and bicarbonate
|

