![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Lipid Layer |
a thin polar membrane made of two layers of lipid molecules |
|
|
Phospholipids |
-Main constituent of the membrane -Made of two non-polar fatty acid tails and a polar head |
|
|
Polar Head |
A part of the plasma membrane that is alligned so that they are surrounding the membrane |
|
|
Polar |
-hydrophilic -harder to cross membrane |
|
|
Non-Polar |
-hydrophobic -can more easily pass through membrane |
|
|
Fatty Acid Tail |
-non-polar tail |
|
|
Role of cholesterol in membrane? |
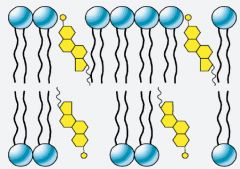
- prevents the phospholipids from moving and sliding past one another -prevents membranes from becoming too cold in rigid temperatures |
|
|
Selective permeability |
only allows certain things to pass through -small particles easily -tends not to be permeable to play unless small -IONS will not pass easily -non polar passes more easily |
|
|
Integral vs Pheripheral |
Intergral - proteins embedded in membrane Pheripheral - Proteins embedded on outside of membrane temporarily |
|
|
Channel Proteins |
- |
|
|
What are proteins made of? |
Amino Acids |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
-Energy is not required because the particles move along the concentration gradient -channel proteins |
|
|
Active Transport |
The second type of transport needs energy because it runs against the concentration gradient. This process is called active transport. -channel proteins |
|
|
Solute vs Solvent |
-A solute is the solid that is dissolved in a liquid. The solvent is the liquid in which something is dissolved in. -For example, with salt water, the Na and Cl are the two solutes, and the H2O is the solvent |
|
|
Hypertonic |
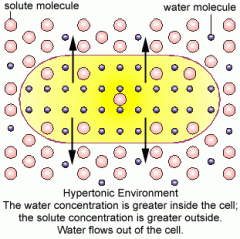
-lower concentration |
|
|
Hypotonic |
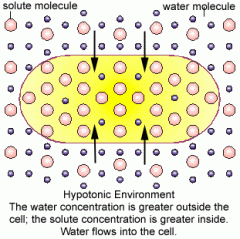
-higher concentration |
|
|
Isotonic |
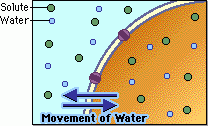
-same concentration |
|
|
What are the three types of transport proteins? |
-Channel -Carrier -Gate |
|
|
Channel Proteins |
-also called pores -small dissolved particles pass through -Ions pass through different proteins depending on size and charge |
|
|
Carrier Proteins |
--change shape to allow different molecules to cross the membrane |
|
|
Gate Proteins |
-Certain chemicals combine with the transport proteins to signal it to "open" -Glucose enters this way |
|
|
Turgor Pressure |
-pressure of water pushing the plasma membrane against the cell wall of a plant cell. |
|
|
Plasmolysis |
-contraction of the protoplast of a plant cell as a result of loss of water from the cell. |
|
|
What are the 3 types of Passive Transport? Do they require energy? |
-DIffusion -Facilitated Diffusion -Osmosis -NO |
|
|
Facilitated Diffusion |
-The cell membrane contains transport proteins that aid to transport particles from HIGH to LOW concentration |
|
|
Osmosis |
-Diffusion of water through membrane (high to low concentration) |
|
|
Diffusion |
-Movement freely through plasma membrane (high to low) |
|
|
What are 2 types of Active Transport? Do they require energy? |
-Endocytosis -Exocytosis -YES |
|
|
What are the 3 types of Endocytosis? What are they responsible for? |
-Phagocytosis =large particles, whole cells ,or solids -Pinocytosis =solutes or fluids -Receptor-aided endocytosis =proteins hook up with another molecule, and indents the cell then pinches off inside cell |
|
|
Explain Exocytosis and what role vesicles play. |
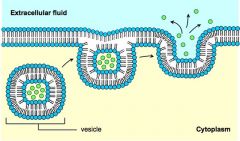
-a reverse process of endocytosis to get rid of wastes -the waste substance is in a vesicle and and fuses with cell membrane until it opens and waste is released |
|
|
Brownian Motion |
-is the random motion of particles suspended in a fluid (a liquid or a gas) resulting from their collision with the quick atoms or molecules in the gas or liquid. |
|
|
Fluid Mosaic Model |
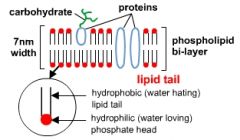
|
|
|
What is a ligand? |
-Opens "gate proteins" |
|
|
What are two substances that can act as ligands |
-Hormones -neurotransmitters |
|
|
Dynamic Equilibrium |
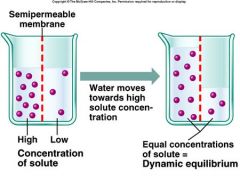
-In a dynamic equilibrium, the rate of loss is equal to the rate of gain |

