![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is multifactorial inheritance? Give examples. |
Occurs when many genes and environmental factors contribute to a trait. Ex: skin color, height, eye color, congenial and age onset diseases, fingerprint ridge count |
|
|
What is polygenic inheritance? |
Involves many genes coding for a trait |
|
|
What are the two types of inheritance? |
Pollygenetic inheritance and multifactorial inheritance |
|
|
What does dermatoglyphics study? |
Ridge counts on fingers and toes |
|
|
What are the three main types of ridge patterns? What are the two subtypes? |
Main types - Loop - Arch - Whorl Subtypes - Tented Ark - Double Loop Whorl |
|
|
What causes Ridge patterns? What causes the three specific Ridge patterns? |
Volar pads developed at 10 weeks gestation for mesenchymal tissues. The regression of the roller pads determines Ridge patterns. Whorl- volar pads are still present/ have not been absorbed into the tips of fingers/toes Loops- developing the volar pads are partially absorbed Arches- develop when the pads are almost completely absorbed |
|
|
Do identical twins have identical Ridge patterns? |
They are similar but not the same |
|
|
What two things affect Ridge patterns in utero? |
- The timing of volar regression is genetically linked - The fetus touching the amniotic sac |
|
|
Identify the triradius (Delta), the core Ridge and a bifurcation |

Delta: three Ridges at 120 degree angles meet at one point Core: single Ridge surrounded by many ridges Bifurcation: fork in a single ridge count it as two ridges |
|
|
Which Ridge pattern has 2 triradii? |
Whorl |
|
|
Which Ridge pattern has an automatic ridge count of 0? |
Arch |
|
|
How do you count the different Ridge patterns? |
Loop: count from the tri radius to the Core Whorl: has two triradii, therefore you must count from the core to the triradii and the ridge count that has the higher number is recorded Arch: automatically zero |
|
|
What type of trait is ridge count? |
Polygenetic, multiple genes are involved |
|
|
Define: -Homozygous Dominant -Homozygous Recessive -Heterozygous |
Homozygous dominant: both alleles are dominant (AA) Homozygous recessive: both alleles are recessive (aa) Heterozygous: one allele is dominant and the other is recessive (Aa) |
|
|
How to count ridge count for males and females? |
Males: minimum of 80 + 12 ridges for each dominant allele Female's: minimum of 70 + 9 ridges for each dominant allele |
|
|
What are mitosis and cytokinesis? |
Mitosis: nuclear division Cytokinesis: cytoplasmic division |
|
|
What's the purpose of mitosis? (3 things) |
-Growth -Reproduction -Repair |
|
|
What are the four phases of the cell cycle in order? |
1- G1 2- S (for DNA synthesis) 3- G2 4- Mitosis (only small potion of cycle) |
|
|
Define chromatin, chromatid and chromosome |
Chromatin: loose DNA bound to proteins (during interphase) Chromatid: each half of a duplicated chromosome Chromosome: supercoiled DNA (during mitosis) |
|
|
Define centromere, centrioles and centrosome. |
Centromere: the middle of the chromosome where the two sister chromatids meet Centrioles: a pair of microtubules arranged in a ring Centrosome: non-membranous organelle which contains the centrioles. Microtubules radiate from this organelle and bind to chromosomes |
|
|
What are the four phases of mitosis? |
Prophase, metaphase, anaphase telophase / cytokinesis |
|
|
What is a mutation? Can this be corrected? What happens if it's not? |
A mutation is a spontaneous random alteration of the genetic code (DNA) Can be corrected, but if not the mutation will be passed to the next generation via Vertical Gene Transfer from parent to offspring |
|
|
What is a wild-type DNA? |
Naturally occurring unaltered DNA |
|
|
What are mutagens? |
Substances that cause mutations such as radiation or chemical agents |
|
|
What are phenotypic changes? |
Physical changes |
|
|
What does agar stand for? Where does it come from? |
Stands for agarose, , a polysaccharide, comes from red algae |
|
|
What type of DNA exists in a bacterial cell? |
Circular DNA chromosome but may also contain a small circular DNA molecule called a plasmid |
|
|
What's special about plasmid DNA? |
It's separate from bacterial chromosome and they may cocntain antibiotic resistance genes and genes that code for structures involved in conjugation (aka pilus) |
|
|
What is genetic recombination? What are the three types? |
Occurs when foreign DNA is introduced to a cell Transformation Transduction Conjugation |
|
|
What is transformation? How does it occur? |
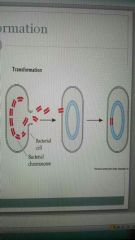
The uptake of foreign DNA from a liquid medium
When a bacterial cell lyses the DNA is released and enters another bacterial cell (recombination) |
|
|
What is transduction? How does it occur? |
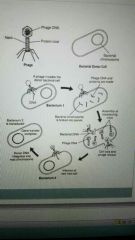
When a bacteriophage (virus that infects bacteria) injects its DNA into bacteria and new viruses are produced which will eventually acquire both viral and bacterial DNA
These viruses infect another bacterial cell (recombination) |
|
|
What is conjugation? How does it occur? |
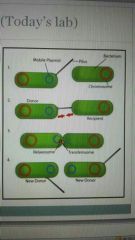
Pilus rape When two bacterial cells come in close contact, one is a donor while the other is a recipient...
The donor transfers copy of its plasmid DNA through the pilus to the recipient and they both replicated their DNA
But this is a ONE WAY TRANSFER! |
|
|
What do the two types of mutant E. coli lack, respectively? What are the two sources of completion? |
E-coli A: lacks methionine gene E-coli B: lacks threonine gene Both are amino acids Mutants obtain these from -the media/agar -each other |
|
|
What is binary fission? What does require a lot of? |
Bacterial cell growth requires a lot of proteins |
|
|
What are equalized stored in? |
Lb (Luria Bertani) broth- has necessary amino acids and mimics natural environment |
|
|
What is a restriction site? |
Each restriction enzyme cuts at a specific sequence of DNA (inverted repeats) |
|
|
Where are restriction sites found? |
Randomly throughout the day, locations are different for each individual |
|
|
How are restriction enzymes used in crime labs? |
DNA is taken from the scene, the victim and the suspects The samples are digested by restriction enzymes |
|
|
What is agarose gel electrophoresis? |
A technique used to separate DNA fragments according to size in agarose (gelatinous matrix) DNA fragments travel through the pores of The Matrix |
|
|
Is DNA positively or negatively charged? Why? |
Phosphate groups in DNA are -ve |
|
|
What is the purpose of loading dye in DNA? |
-It gives the DNA density when loading into Wells - Contrast |
|
|
What are DNA fragment lines called? |
Bands |
|
|
What is bla? What is bla? What is bla? |
Gene that codes for beta lactamase which is an enzyme that deactivates certain antibiotics (ampicillin) giving the transformed bacterial cell antibiotic resistance |
|
|
What is ori? |
Every plasmid has an origin of replication which is a sequence of DNA for DNA replication begins |
|
|
What is GFP |
Gene that codes for green fluorescent protein which is regulated by the araC gene |
|
|
What is araC? |
A regulatory gene which codes for the araC protein |
|
|
What are phenotype and genotype? |
Phenotype: physically observable traits Genotype: genetic makeup (Aa bb etc) |
|
|
What is an allele? Give an example |
Alleles are different versions of the same gene Ex: Gene is eye color, allele is blue |
|
|
Do identical twins have the same Ridge patterns? |
No |
|
|
What is auxotrophy? |
The inability of an organism to synthesize an essential organic nutrient required for survival, they must consume this from the environment |
|
|
Where do restriction enzymes cut DNA? |
In double-stranded sequences of DNA both strands of the molecule are cut between the sugar and phosphate in the sugar-phosphate backbone |
|
|
Is DNA an acid or a base? Why? |
An acid, it can donate hydrogen ions from its phosphate groups and thus is negatively charged |

